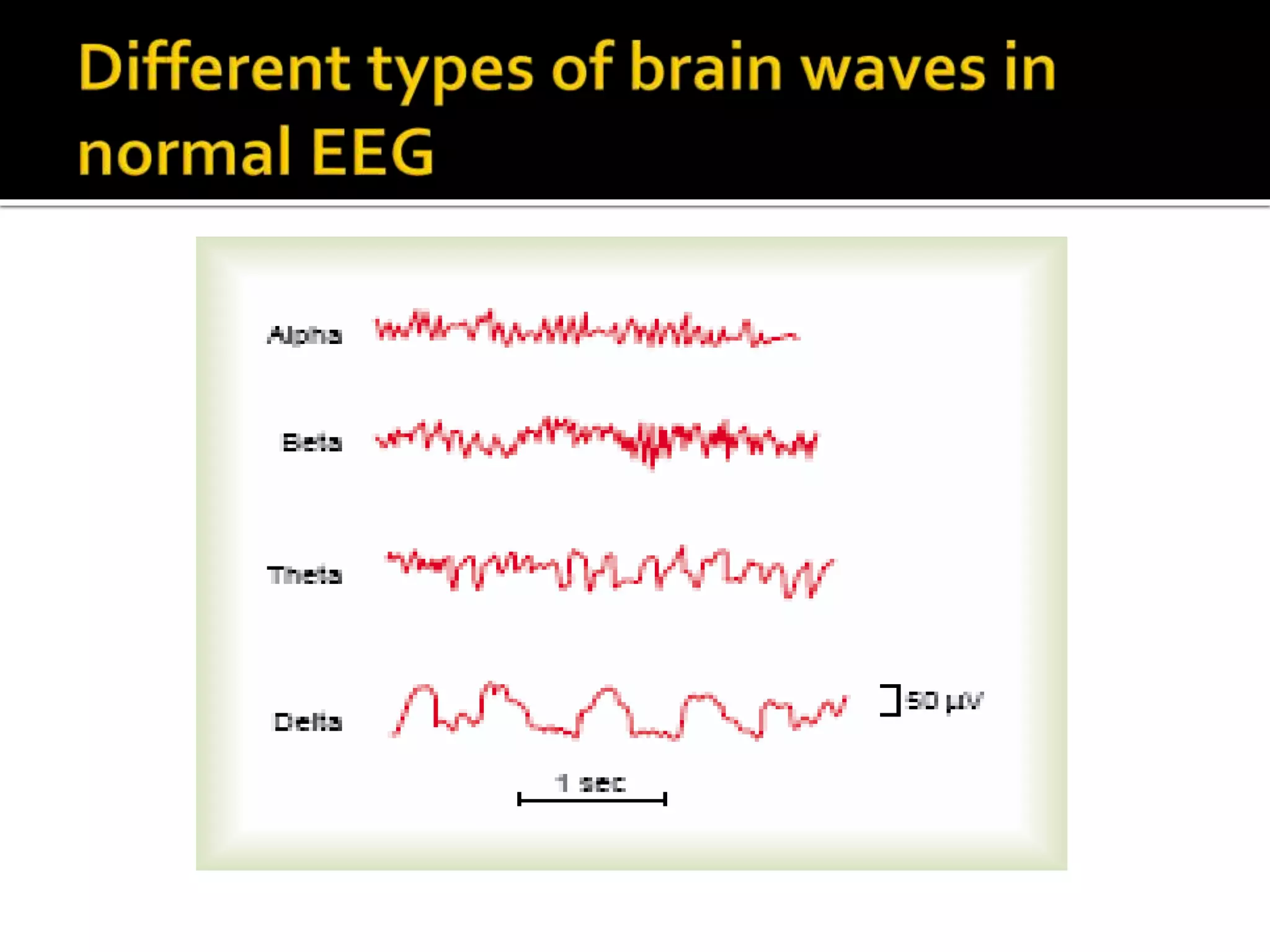
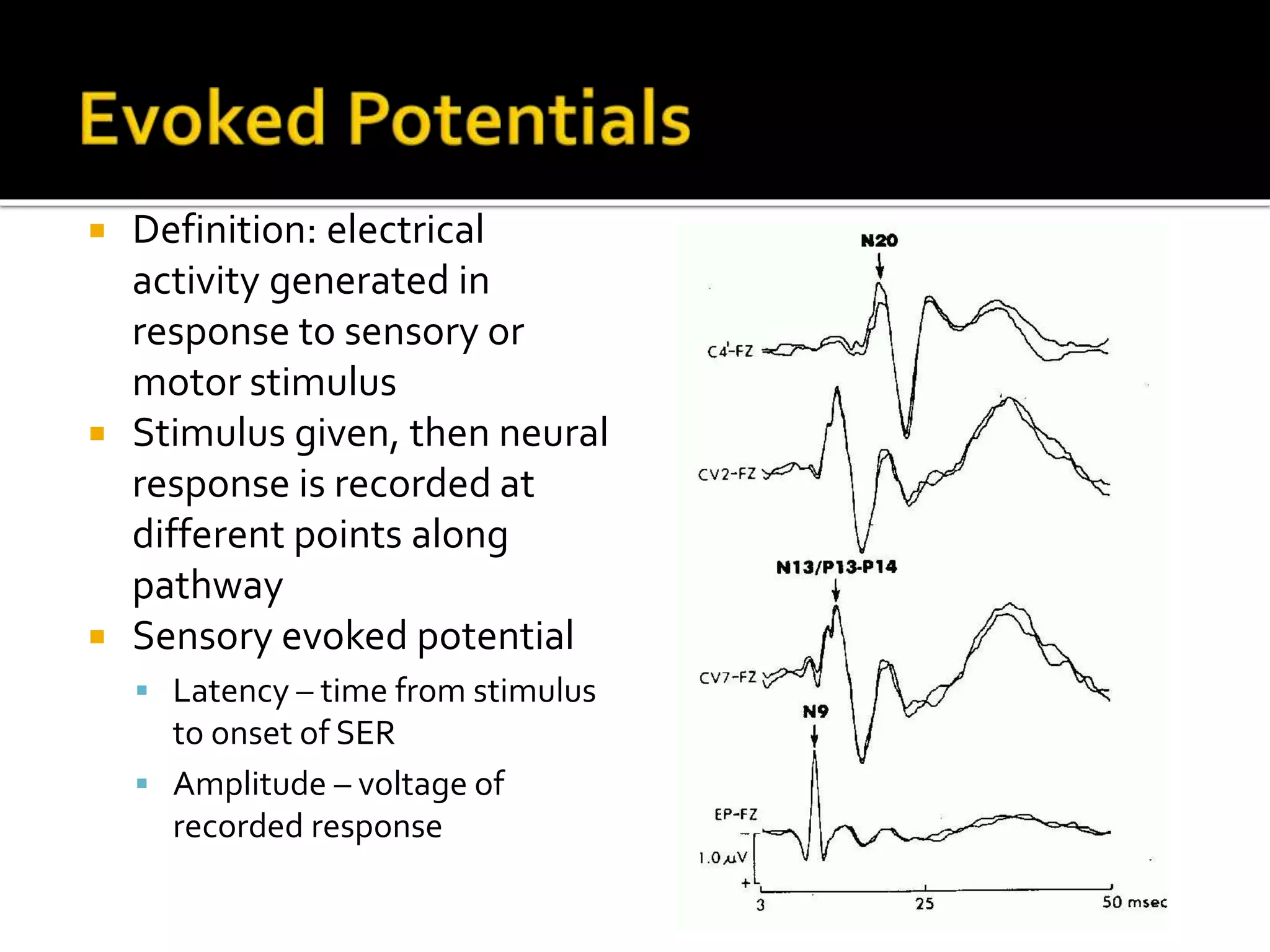
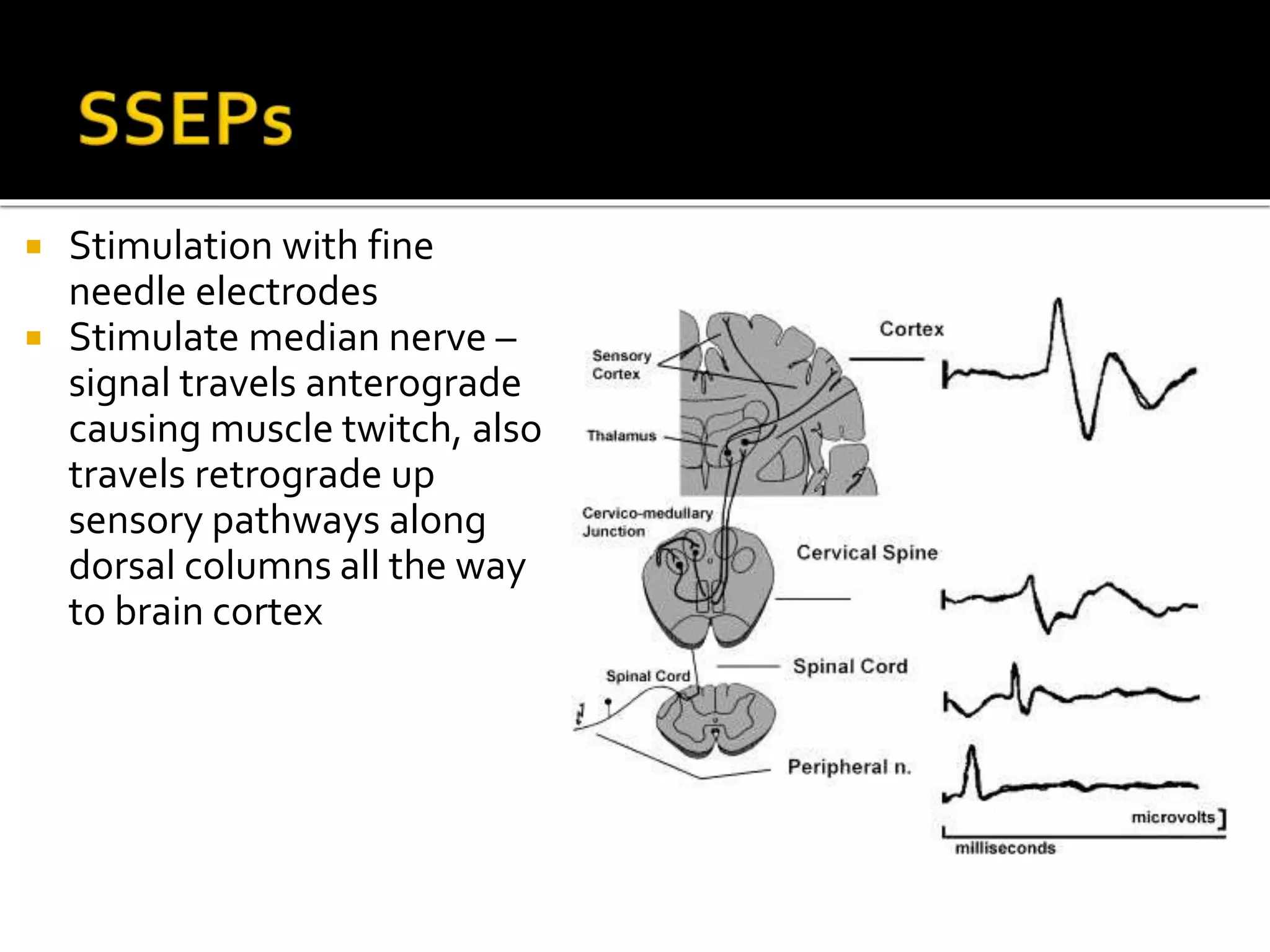
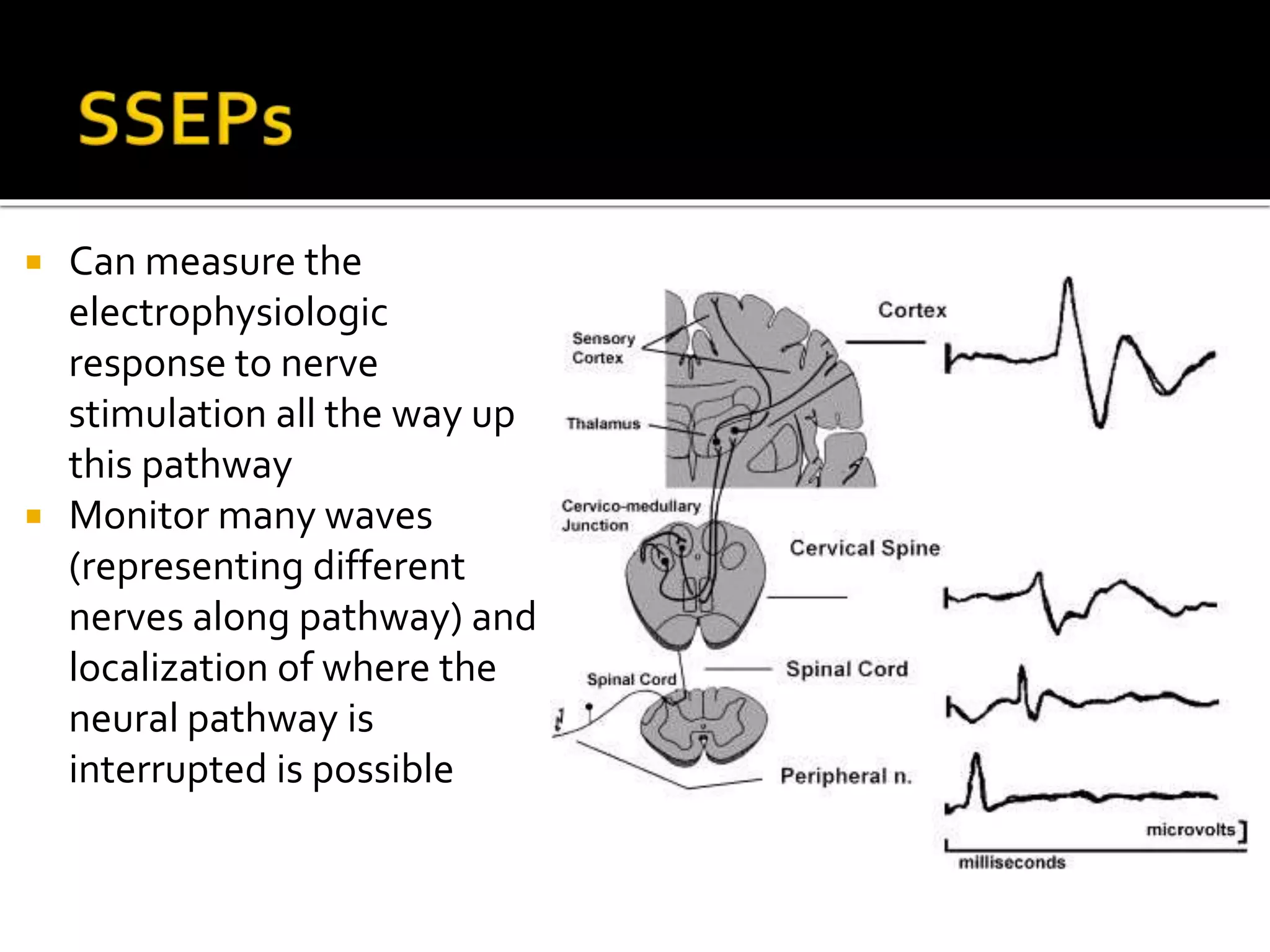
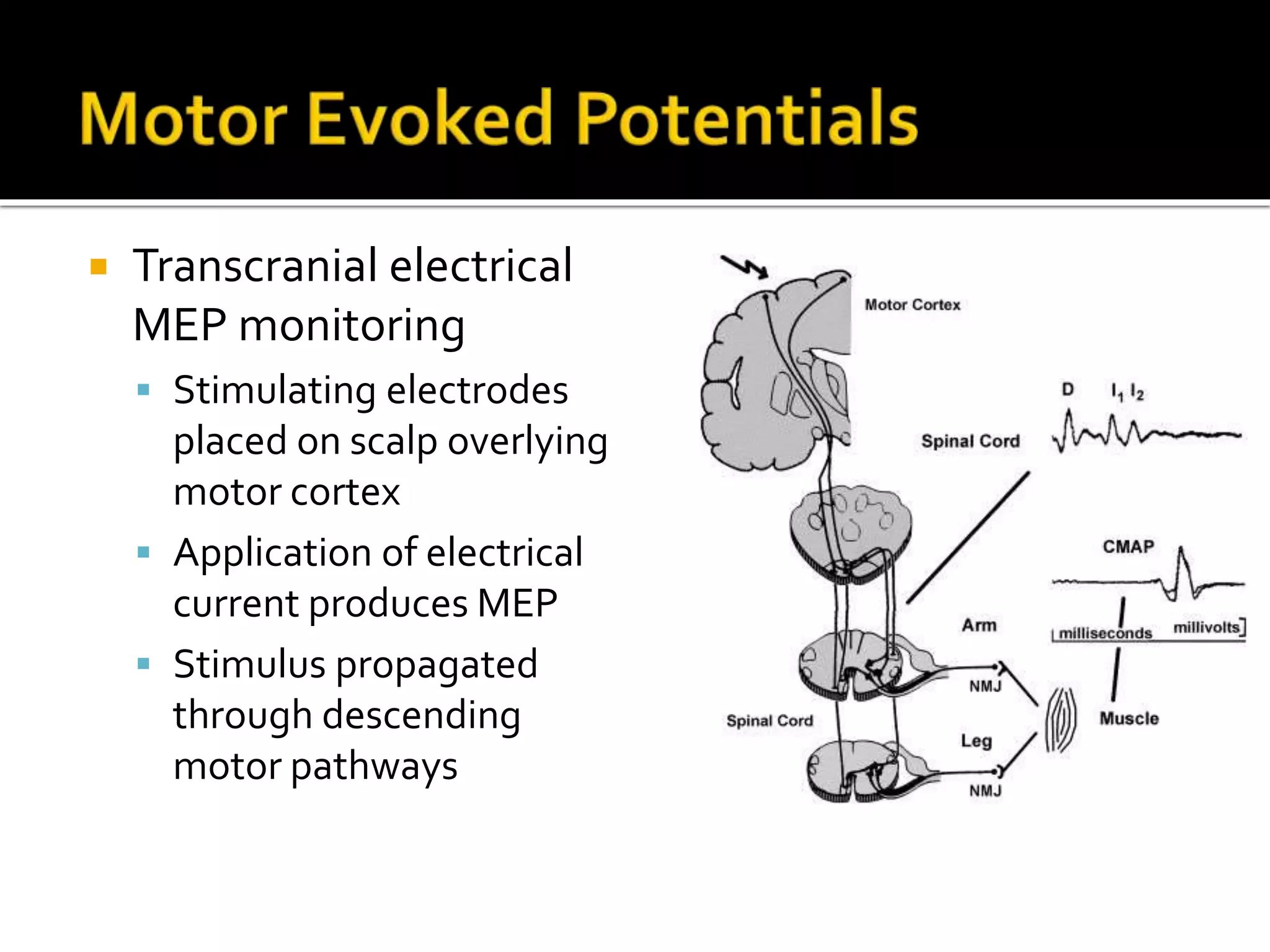
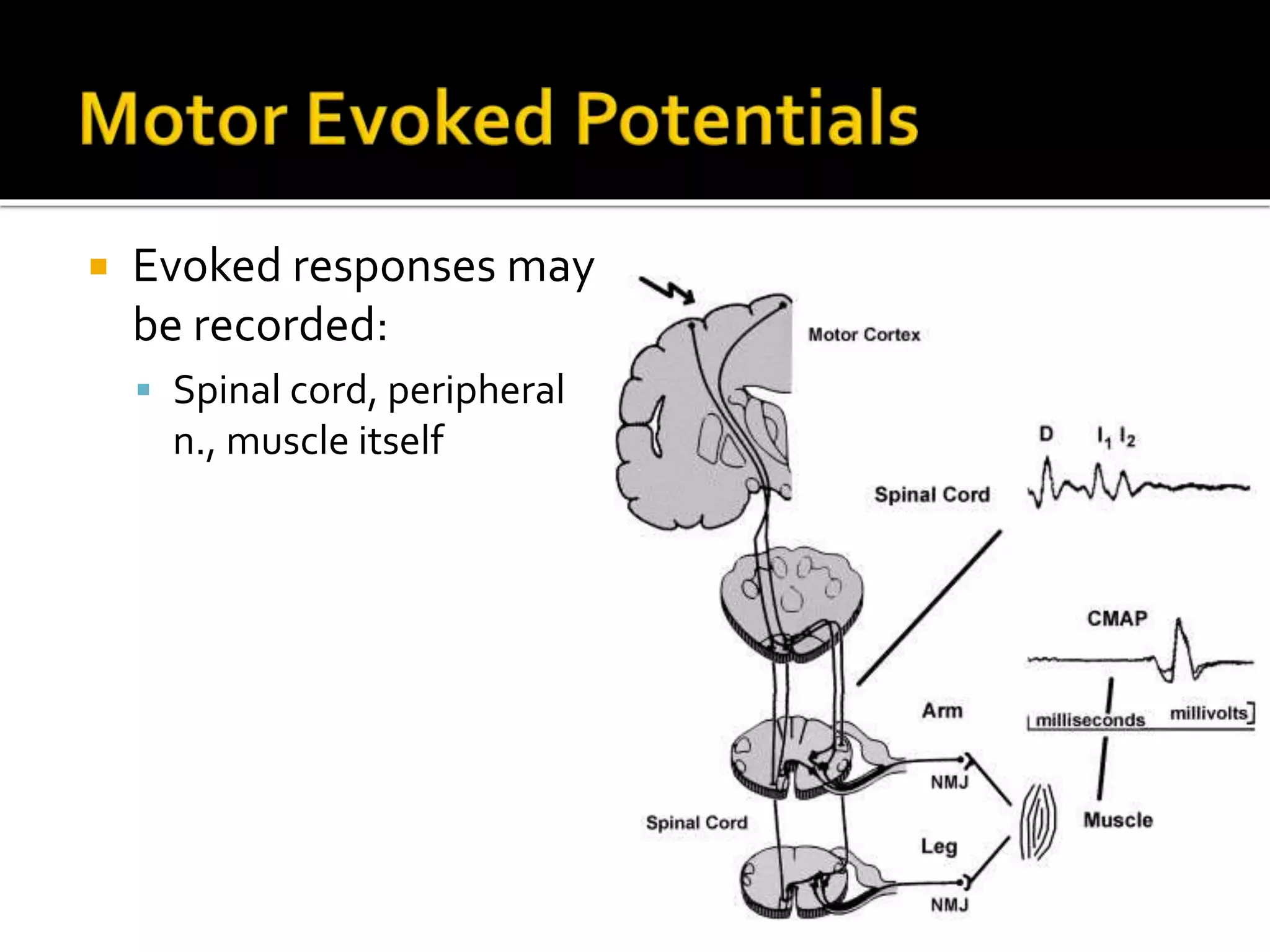
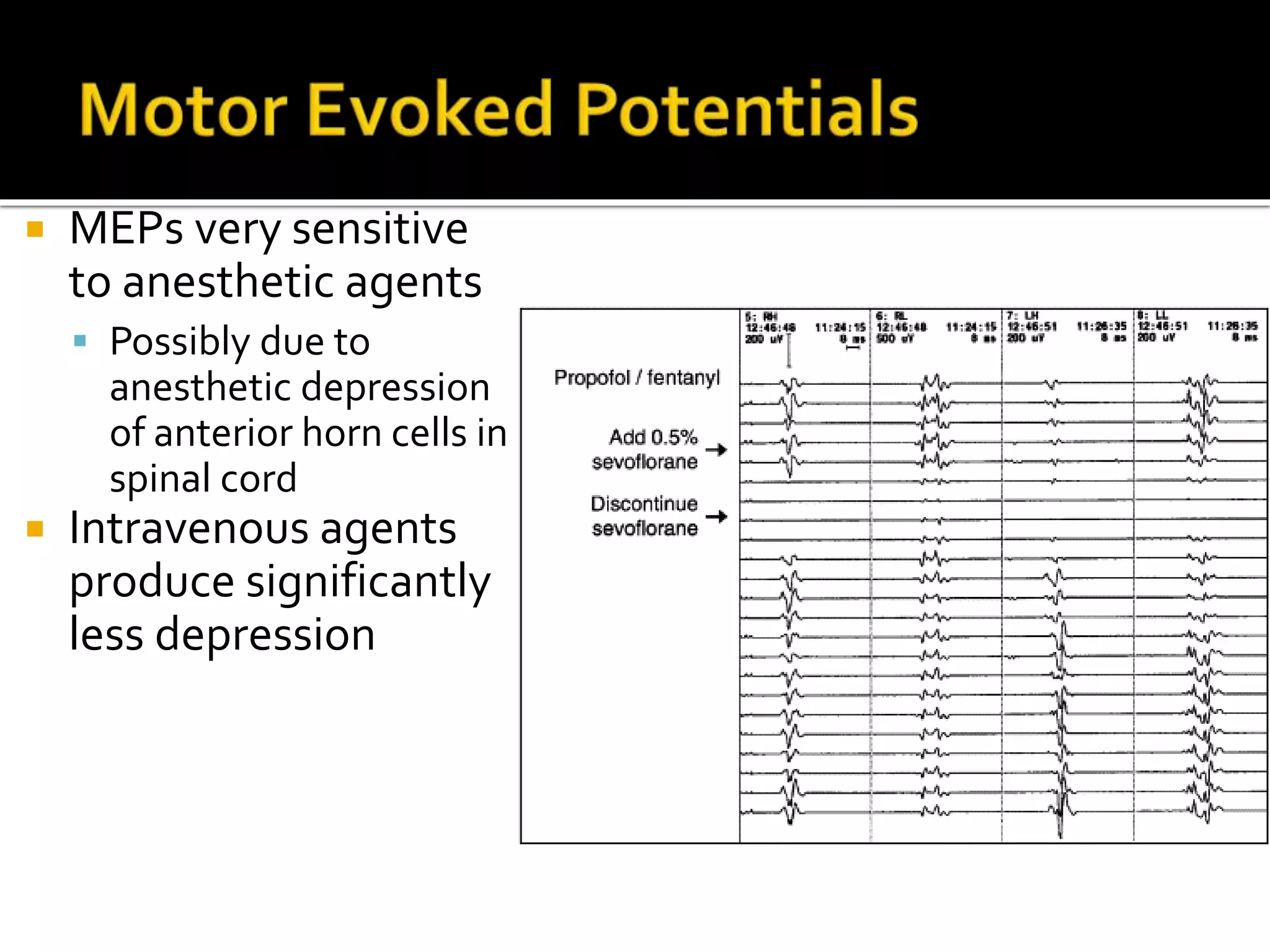
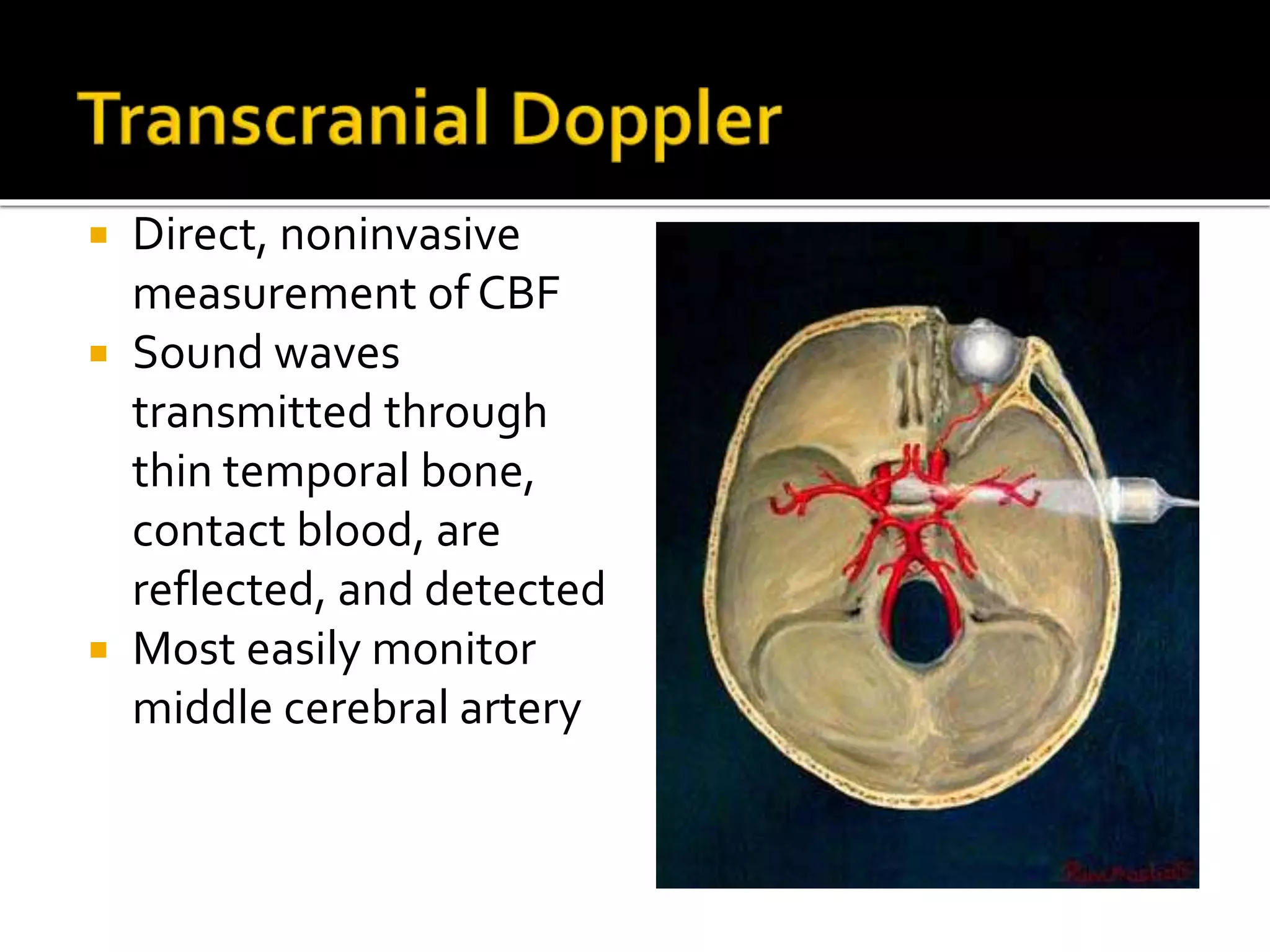
The document discusses various techniques for intraoperative neurological monitoring during surgery, including EEG, SSEP, MEP, transcranial Doppler, and cerebral oximetry. EEG measures electrical brain activity and can detect changes related to ischemia, anesthesia effects, or other insults. SSEP uses electrical nerve stimulation to measure sensory pathway function from peripheral nerves to the brain. MEP assesses motor pathways by recording responses to transcranial electrical stimulation. Transcranial Doppler noninvasively measures cerebral blood flow velocity. Cerebral oximetry monitors tissue oxygen saturation in the brain. These techniques provide different but complementary information and are useful for detecting adverse neurological events during surgery.