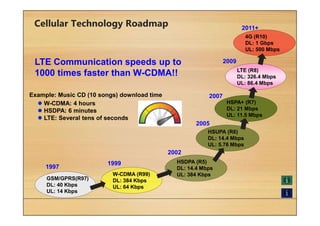
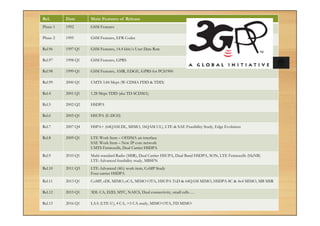
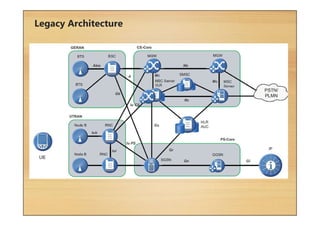
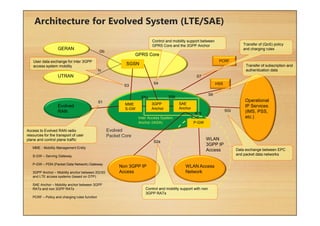
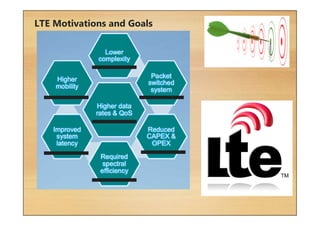
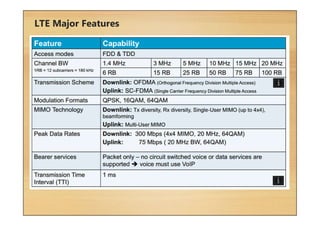
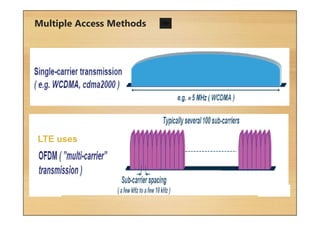
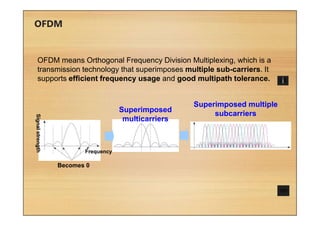
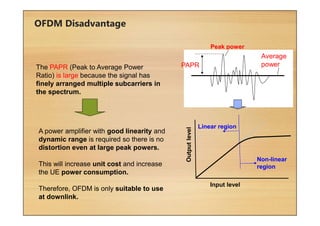
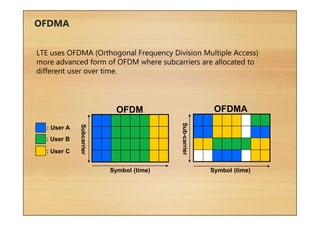
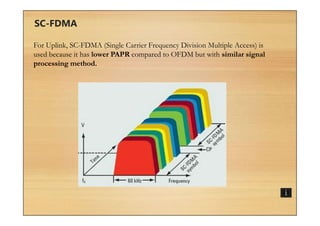
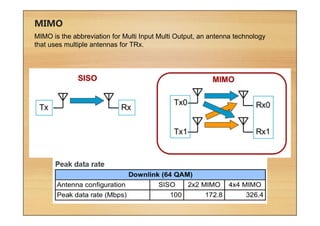
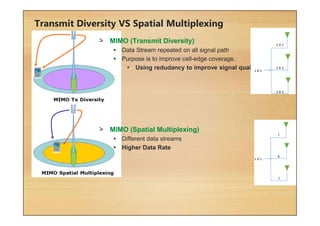
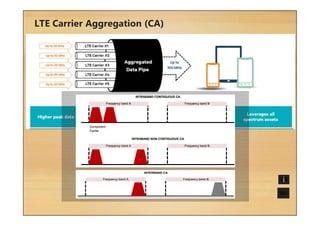
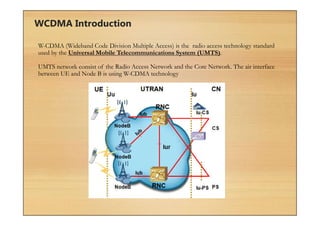
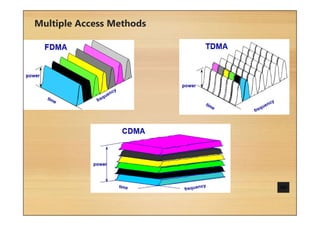
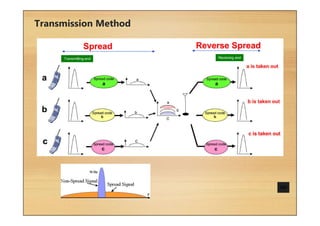
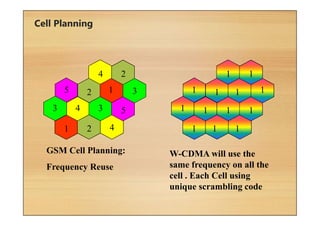
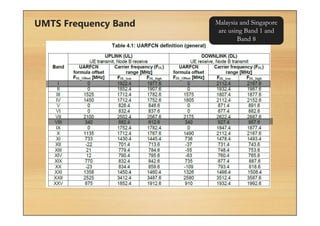
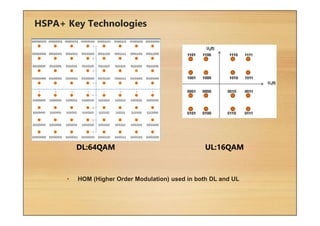
This document provides an overview of cellular technology roadmaps and standards including LTE and UMTS. It summarizes the evolution of technologies like W-CDMA, HSPA, HSPA+ and LTE over time with increasing download/upload speeds. It describes the key aspects of LTE including OFDMA, SC-FDMA, MIMO and LTE-Advanced. It also provides an overview of UMTS architecture and air interface standards like W-CDMA, HSDPA and HSUPA.