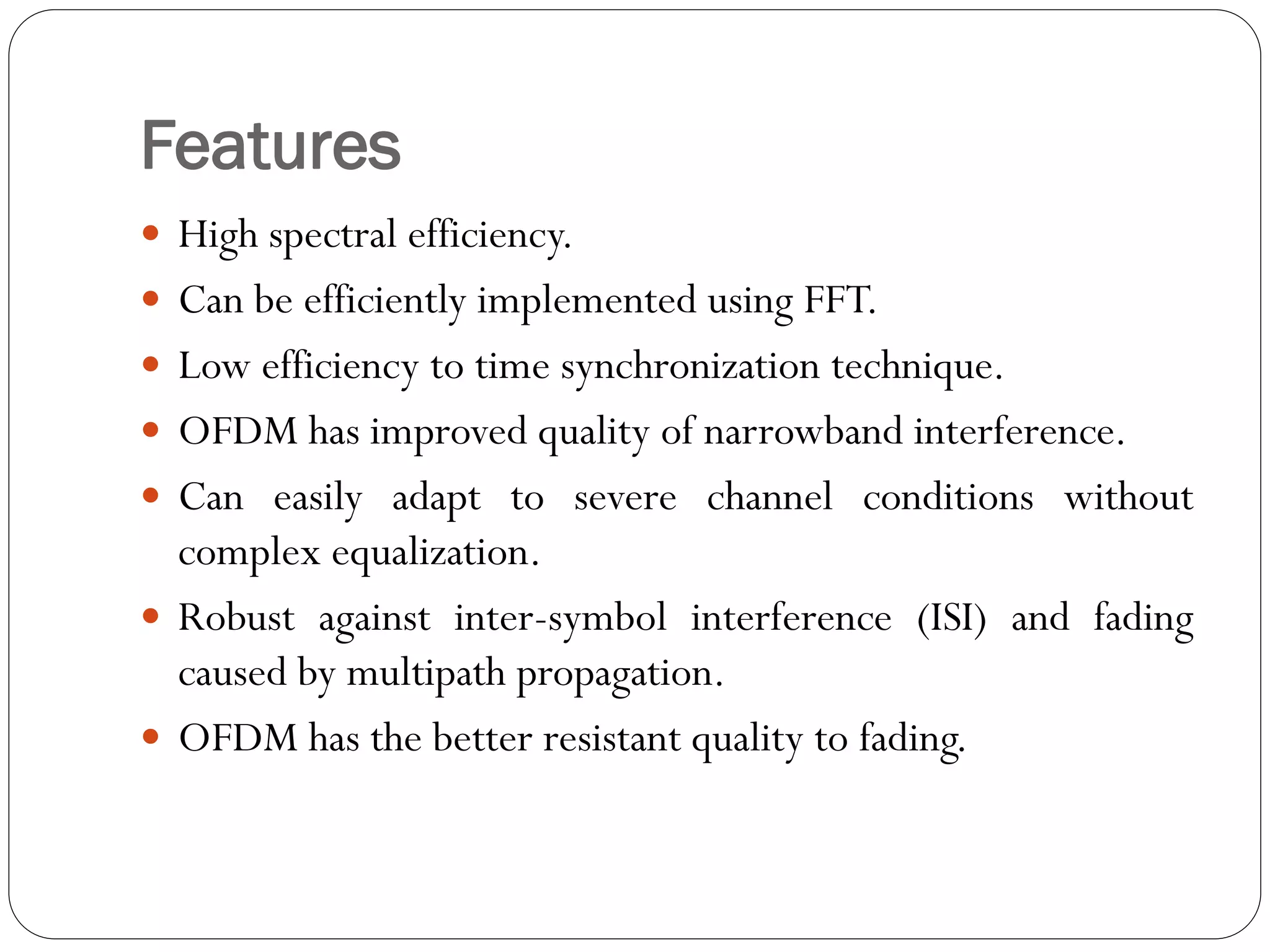
This document discusses Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM), a key technology for high data rate transmission in wireless communications, highlighting its features, applications, and challenges. OFDM offers advantages such as high spectral efficiency and robustness against multipath fading, making it widely used in standards like digital audio and video broadcasting. Despite its benefits, it faces issues such as sensitivity to frequency errors and inter-carrier interference.


![Motivation
The demand for multimedia wireless communication is
growing today at an extremely rapid pace.
Multiplexing Schemes: FDM,TDM & CDM [1].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ofdmashishsoni-161207094100/75/Orthogonal-Frequency-Division-Multiplexing-OFDM-3-2048.jpg)
![ Evolution of Mobile Communication [2].
Generation Standard Data Rate Features
2G GSM 10 kbps DigitalVoice,
SimpleText,
Simple News,
Feeds etc.
2G CDMA 10 kbps
2.5G GPRS 50 kbps
2.5G EDGE 200 kbps
3G WCDMA ~400 kbps DigitalVoice,
Mobile Broadband3.5G HSDPA/HSUPA 4-50 Mbps
4G LTE/WiMAX 100-200 Mbps Live HDTV,
Online Gaming,
High Speed.
4G LTE > 1 Gbps](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ofdmashishsoni-161207094100/75/Orthogonal-Frequency-Division-Multiplexing-OFDM-4-2048.jpg)
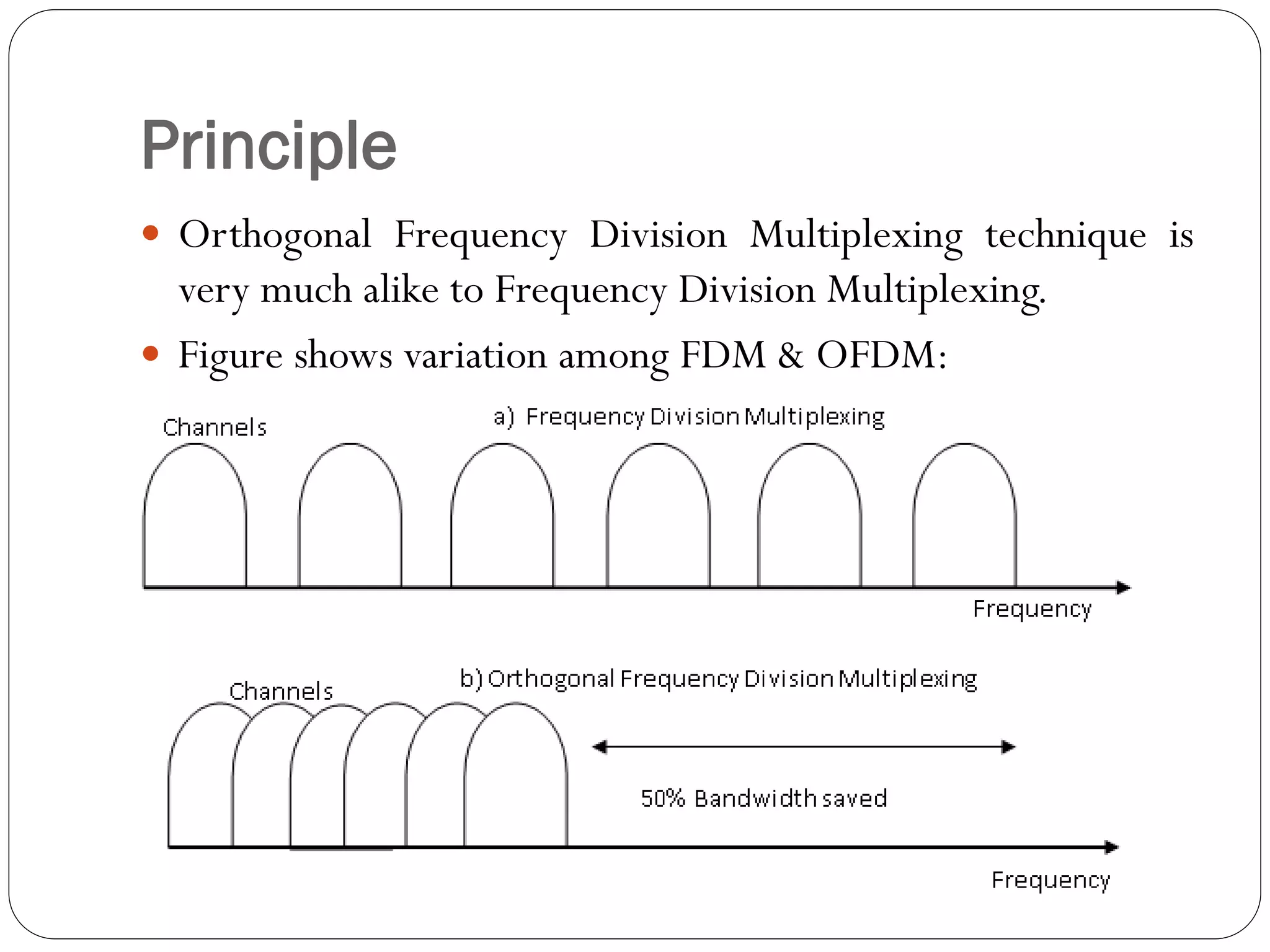
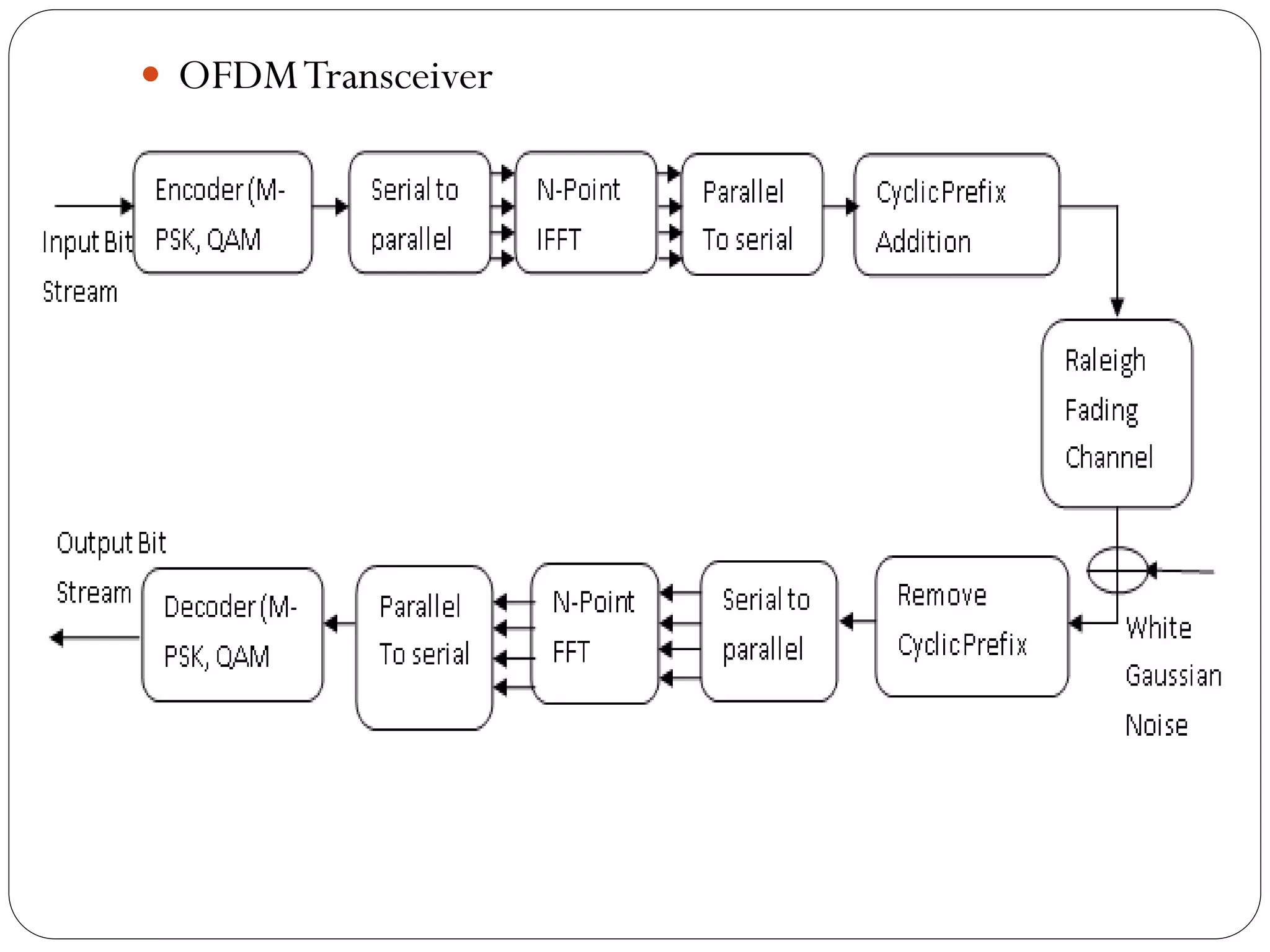
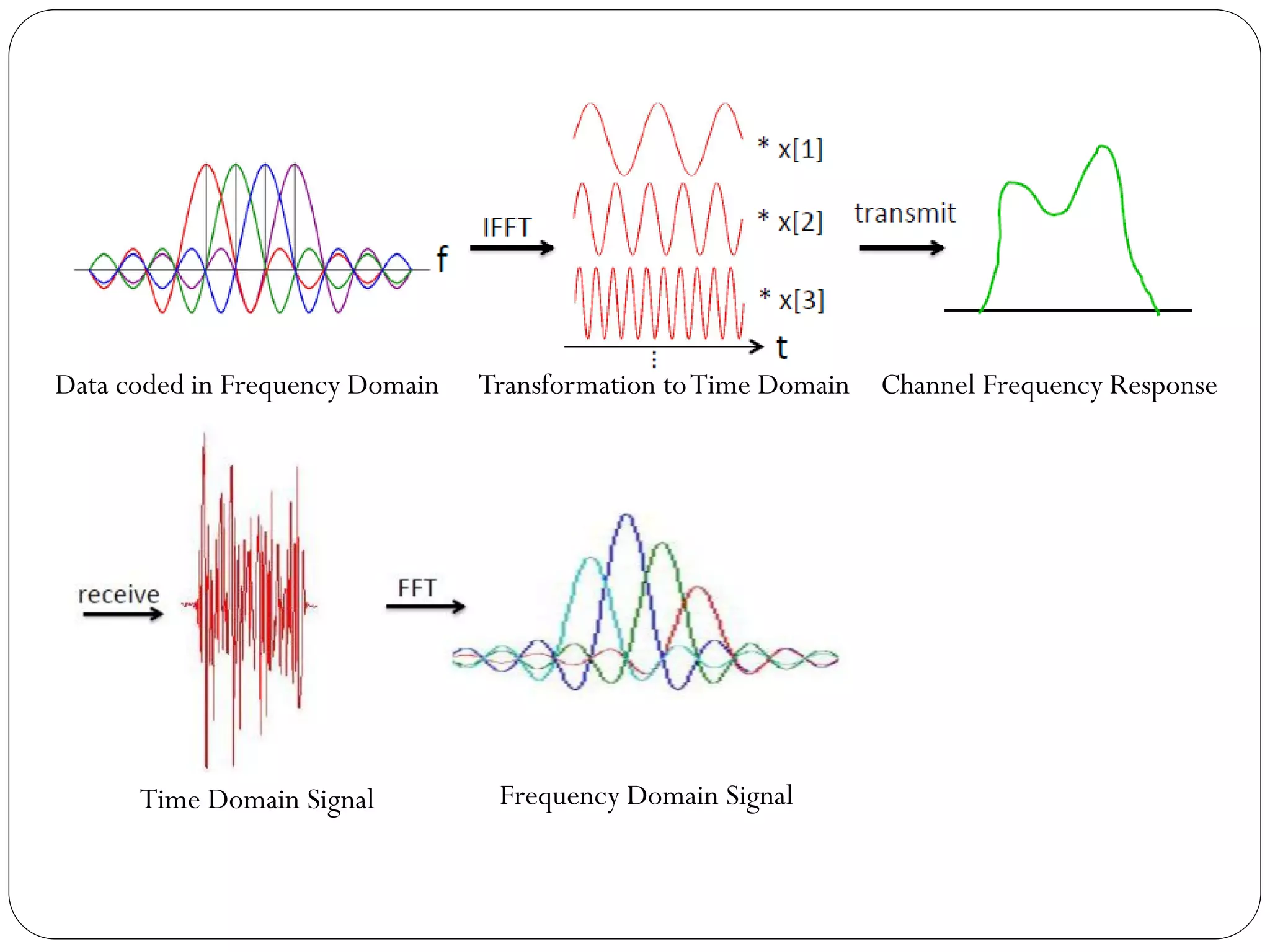
![Introduction
OFDM is promising technique for achieving high data rate
transmission in mobile environment [3].
It is a special form of multicarrier modulation (MCM),
where a single data stream is transmitted over a number of
subcarriers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ofdmashishsoni-161207094100/75/Orthogonal-Frequency-Division-Multiplexing-OFDM-5-2048.jpg)
![ It offers high spectral efficiency, multipath delay tolerance,
robustness to channel fading, immunity to impulse
interference [4].
Therefore it has been widely deployed in many wireless
communication standards such as Digital Video Broadcasting
(DAB), Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL),
DigitalTerrestrialTelevision Broadcasting etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ofdmashishsoni-161207094100/75/Orthogonal-Frequency-Division-Multiplexing-OFDM-6-2048.jpg)
![Origin
Concept of OFDM has existed since 1966.
But in 1985, Cimini [5] proposed a cellular mobile radio
system based on OFDM.
In 1995, Wu [4] suggested some high frequency military
systems using OFDM.
In 1998, Fernando proposed application of OFDM to the
satellite mobile channel.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ofdmashishsoni-161207094100/75/Orthogonal-Frequency-Division-Multiplexing-OFDM-7-2048.jpg)

![Applications
Digital Audio Broadcasting
DigitalVideo Broadcasting
IEEE 802.11 a/g
IEEE 802.16
IEEE 802.20 [6].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ofdmashishsoni-161207094100/75/Orthogonal-Frequency-Division-Multiplexing-OFDM-13-2048.jpg)