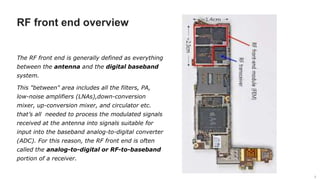
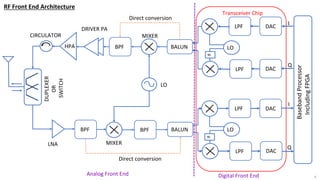
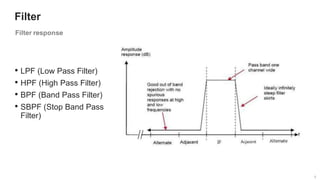
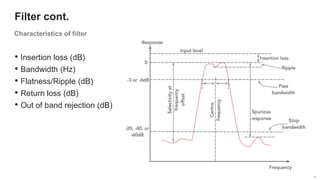
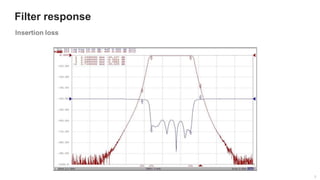
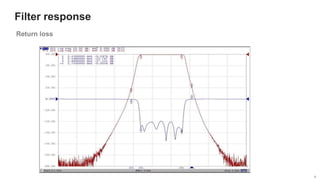
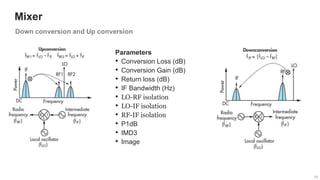
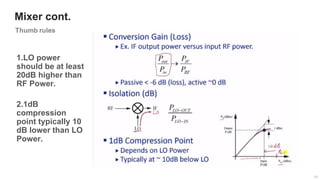
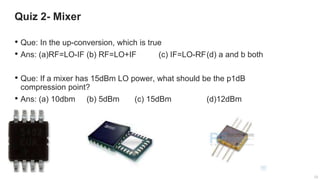
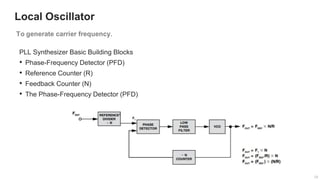
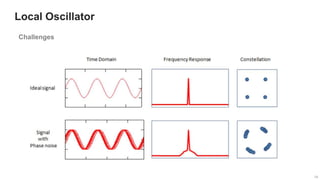
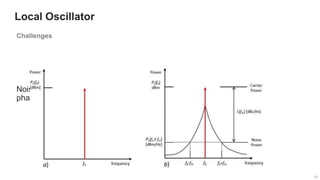
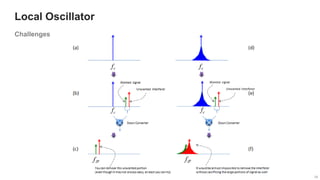
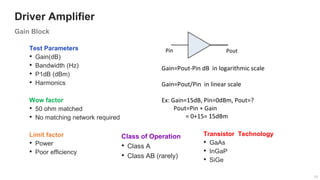
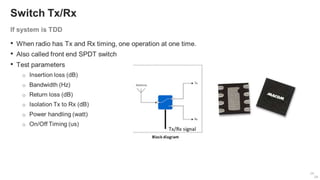
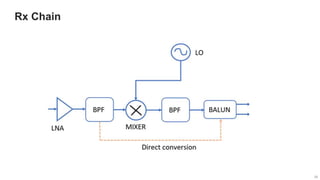
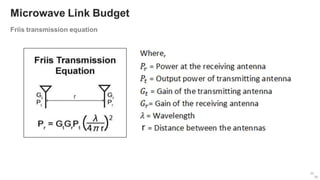
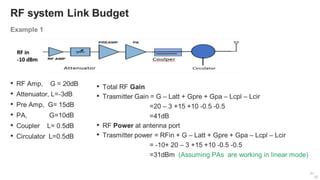
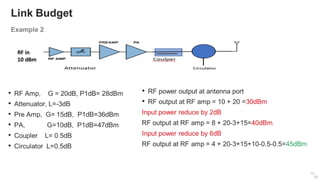
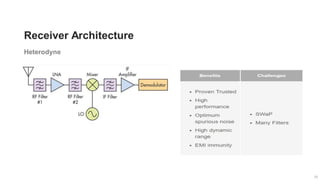
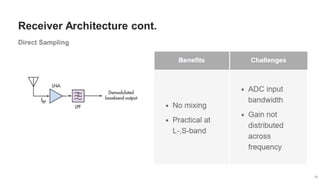
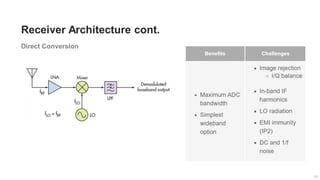
The document provides an overview of the architecture of analog RF front ends, detailing components such as low-noise amplifiers, mixers, and power amplifiers that are essential for processing signals between the antenna and the baseband system. It covers various parameters and performance metrics for filters and amplifiers, as well as quizzes to assess knowledge on the topics. Additionally, it touches on challenges in oscillator systems and tests specific to RF components.