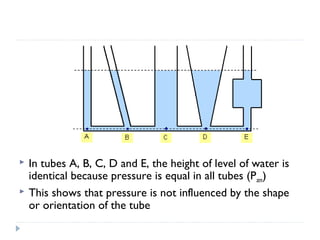
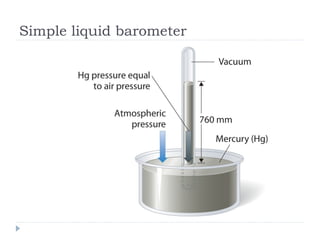
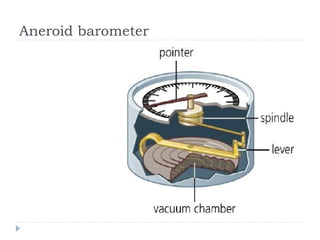
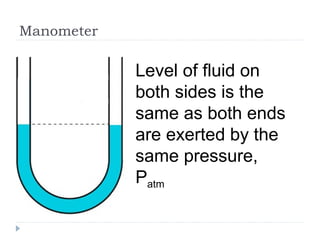
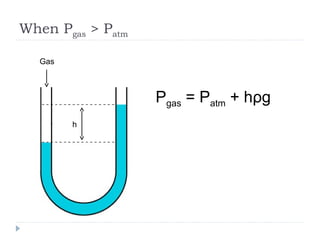
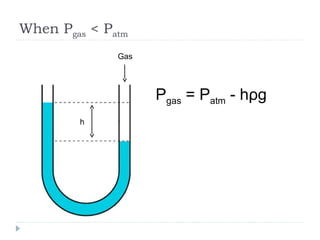
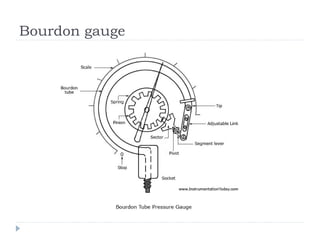
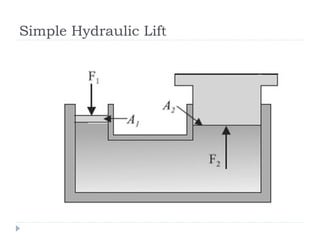
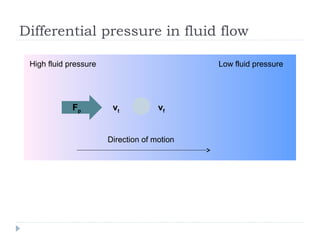
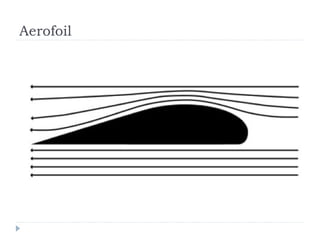
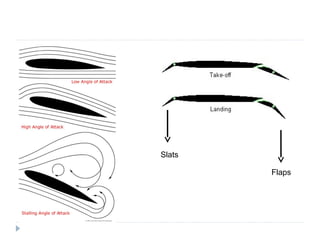
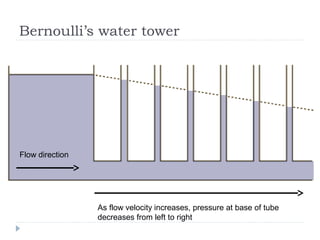
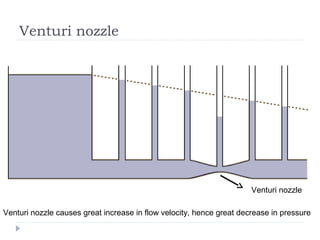
Solid pressure is defined as the force acting on a given area, measured in Pascals. Fluid pressure results from particle collisions within the fluid and increases with depth and density. It is described by the equation P=hρg. Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude and is measured using barometers. Fluids transfer pressure equally in all directions according to Pascal's principle, which has applications in hydraulic systems. Archimedes' principle describes buoyancy as the upward force equal to the weight of fluid displaced. Bernoulli's principle states that fluid pressure decreases where velocity increases, as seen in aerofoils, venturi nozzles, and other streamlined objects.