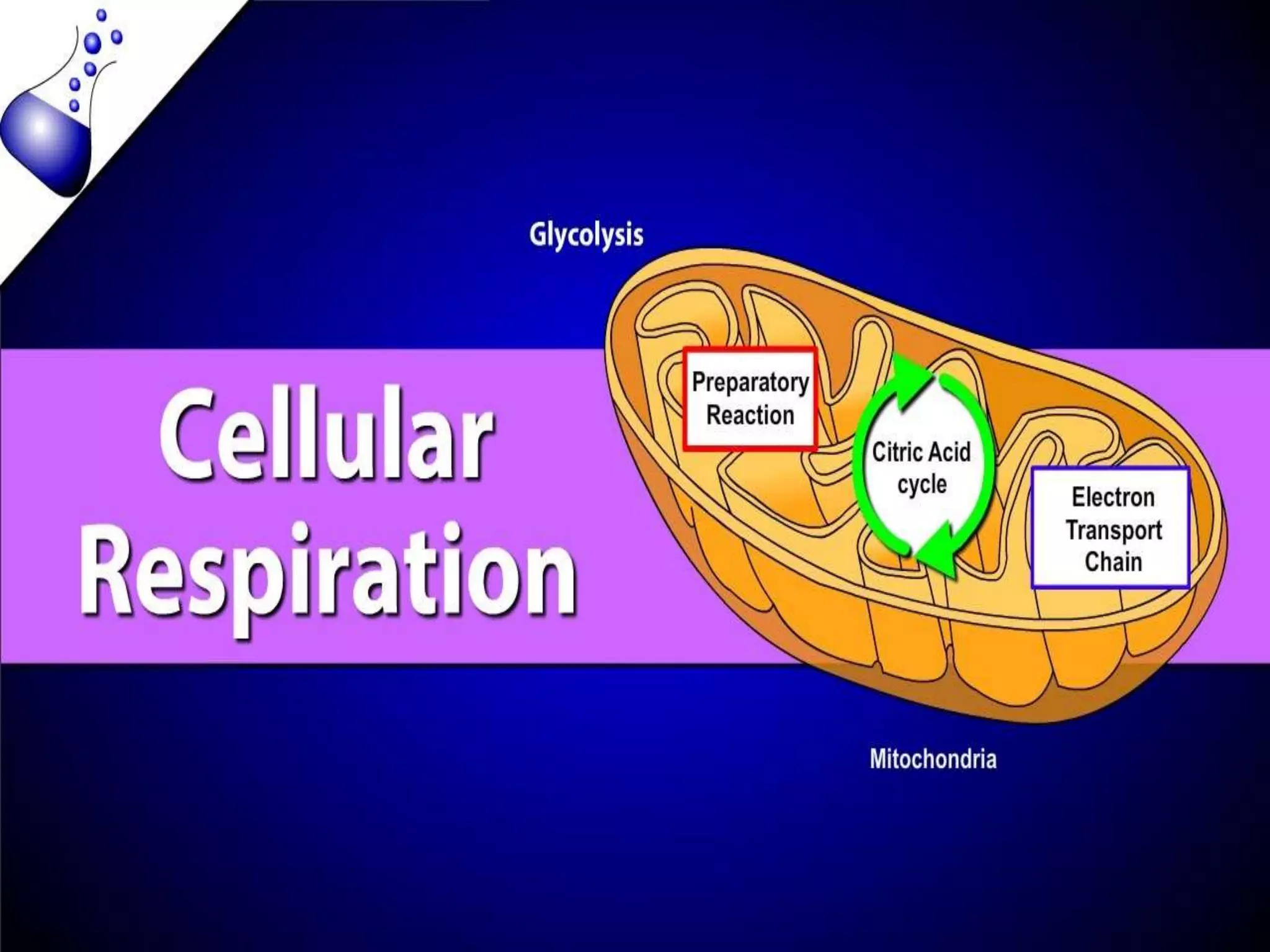
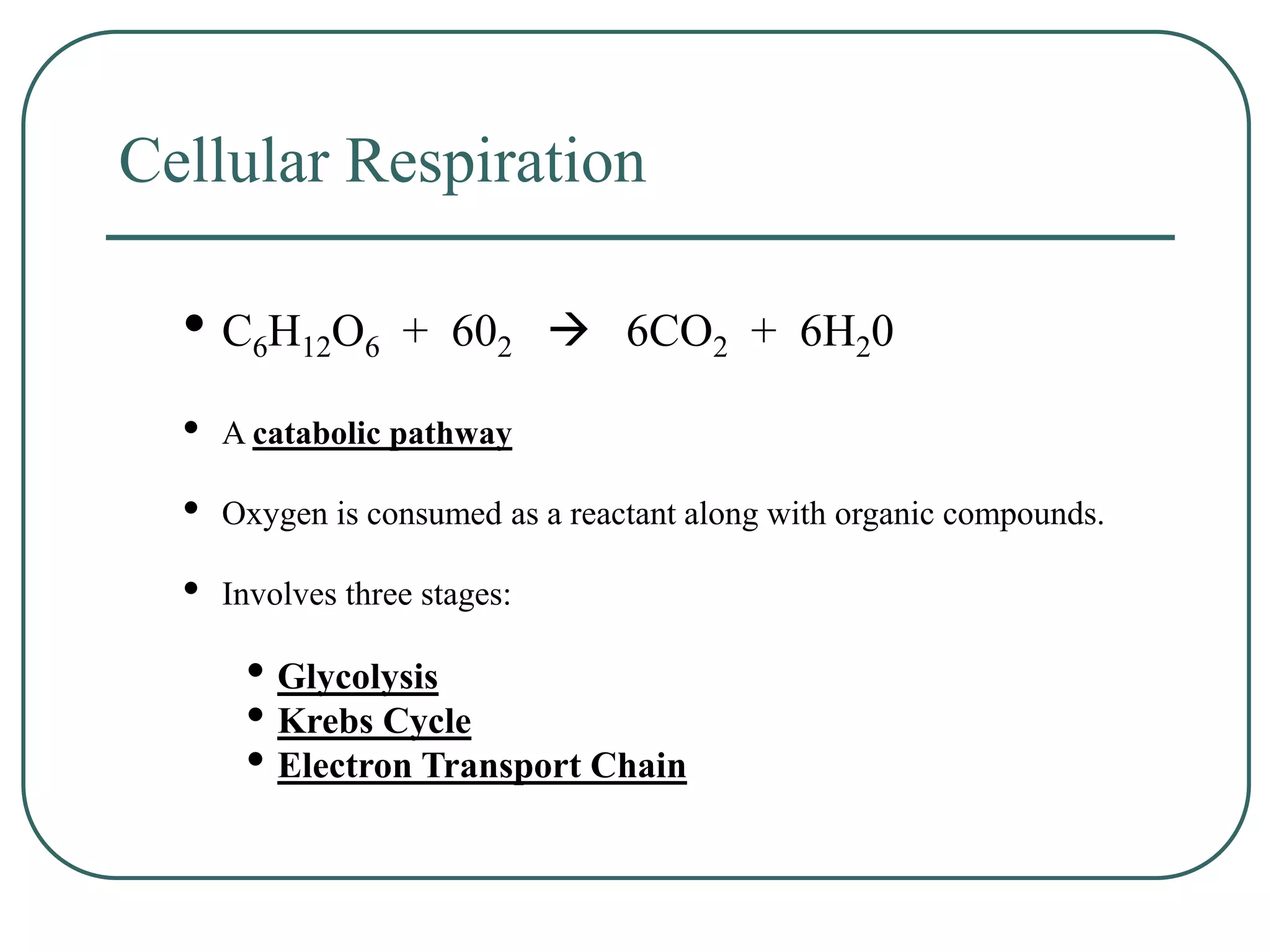
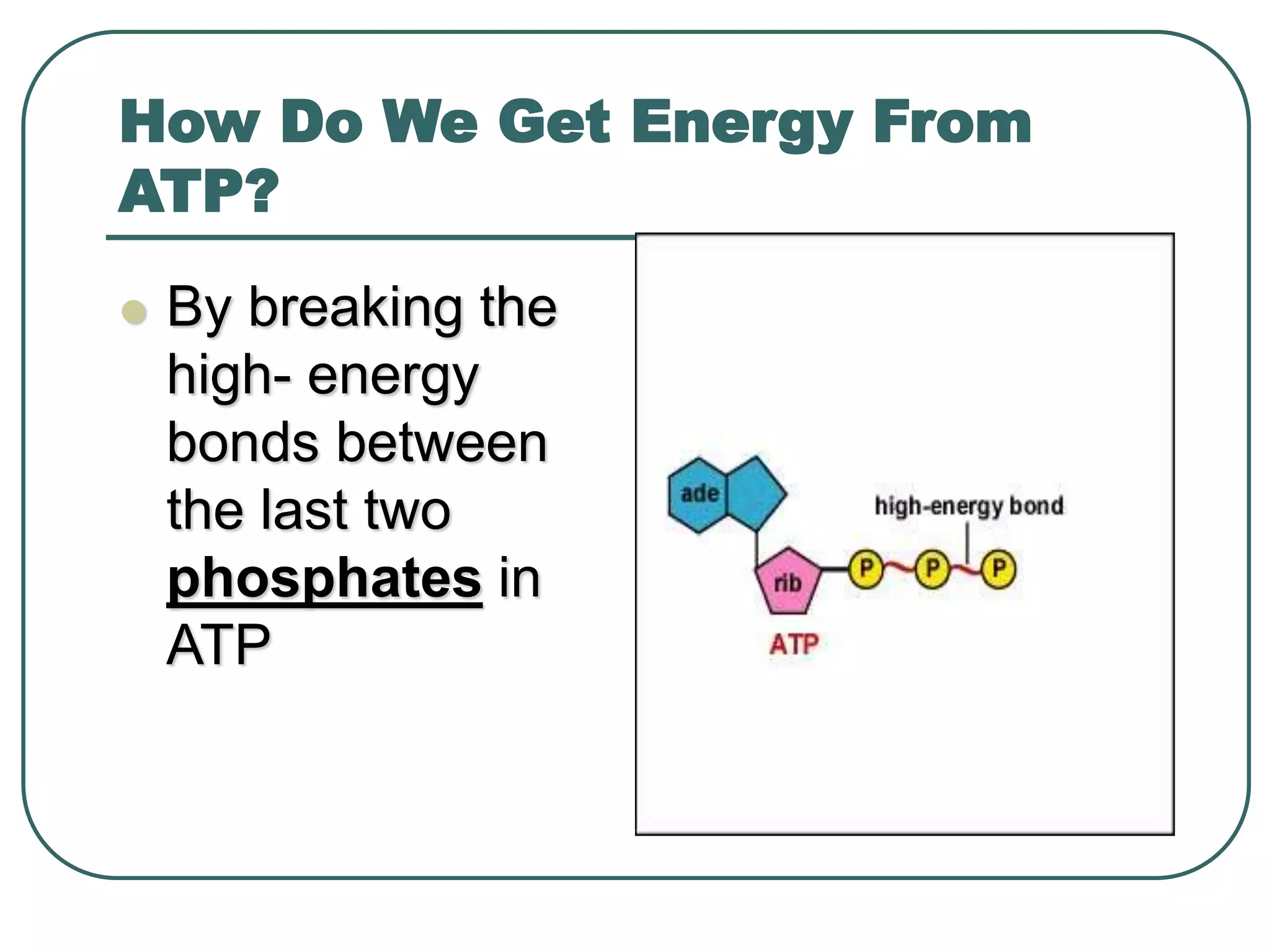
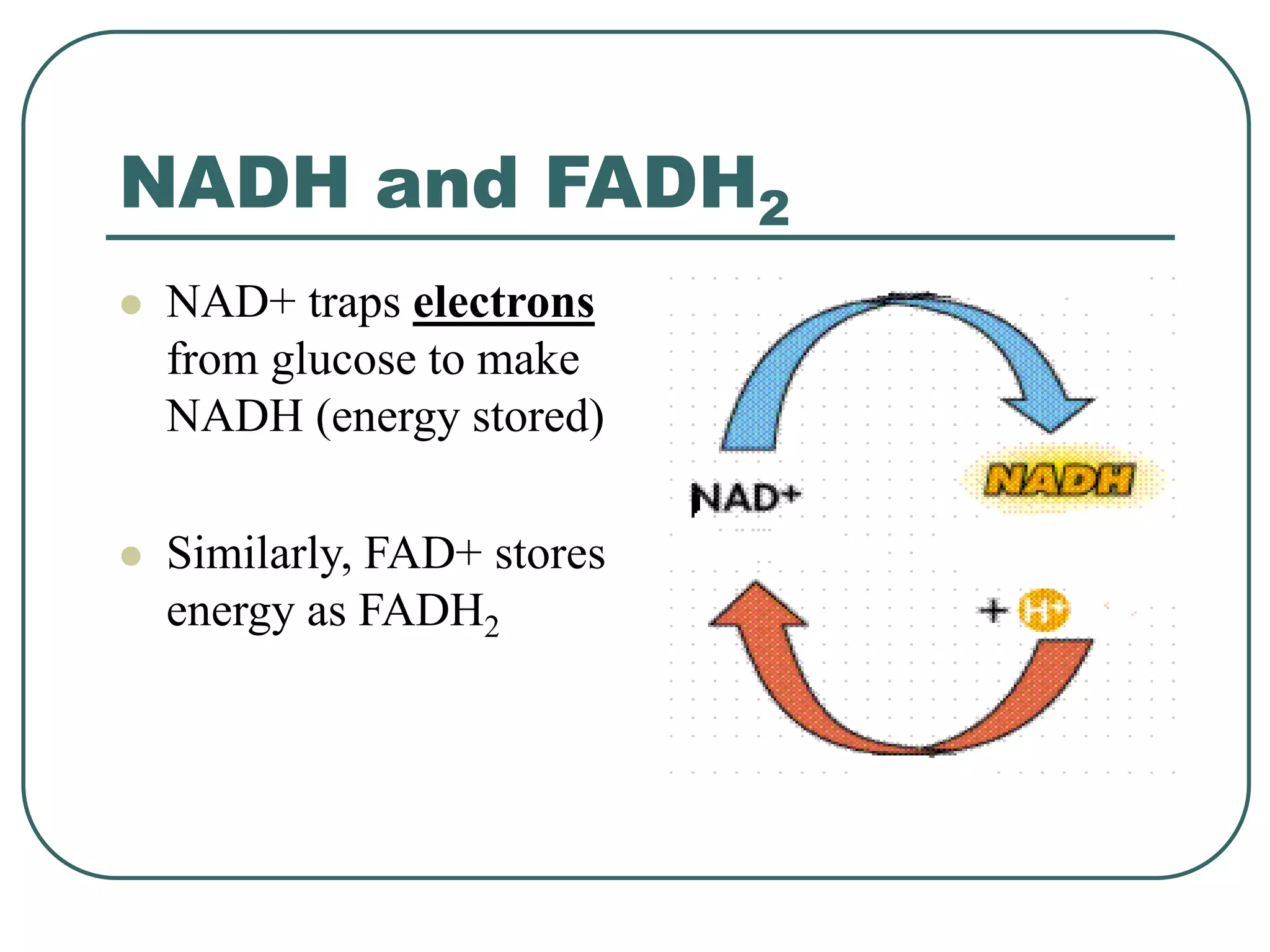
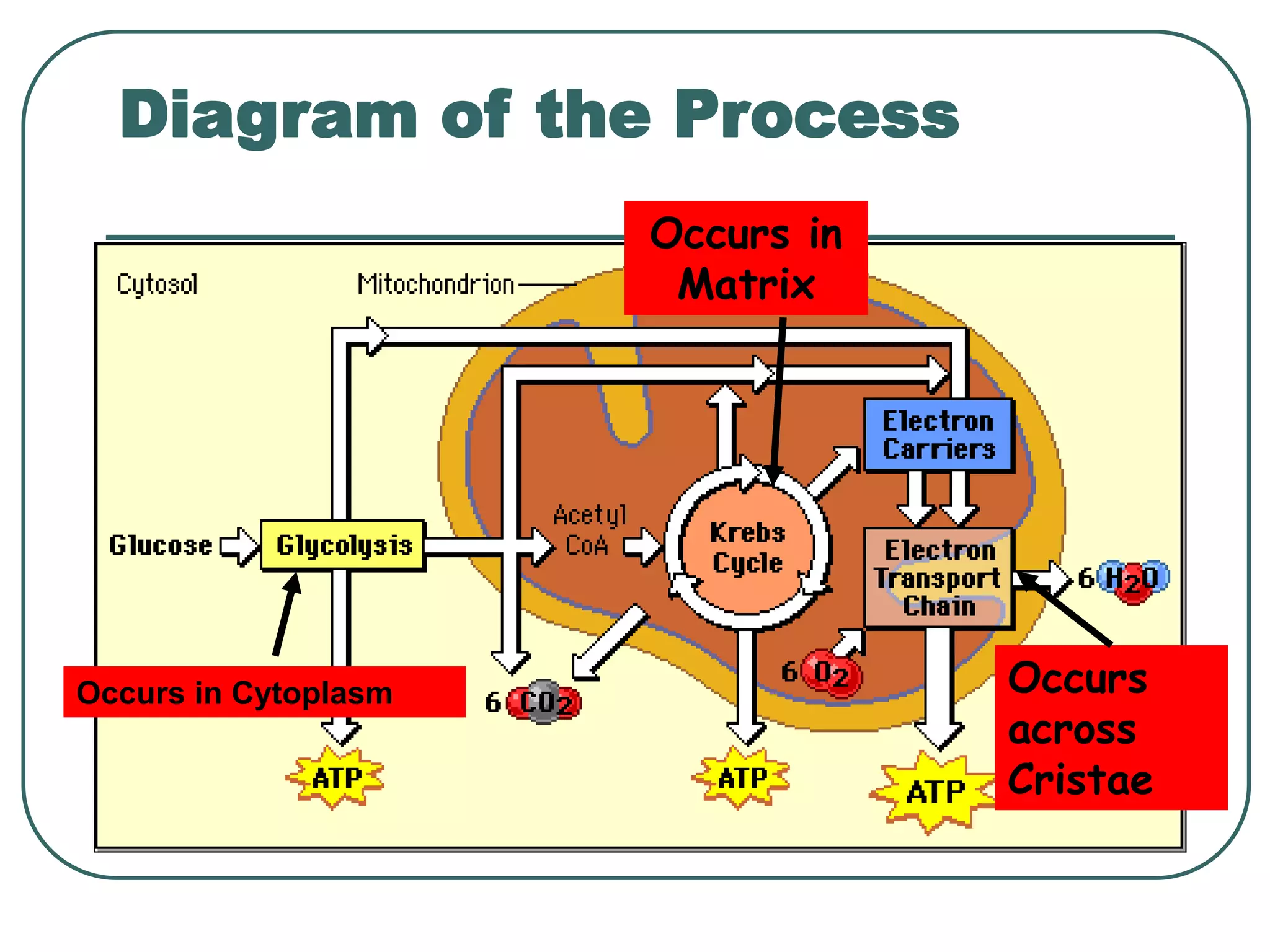
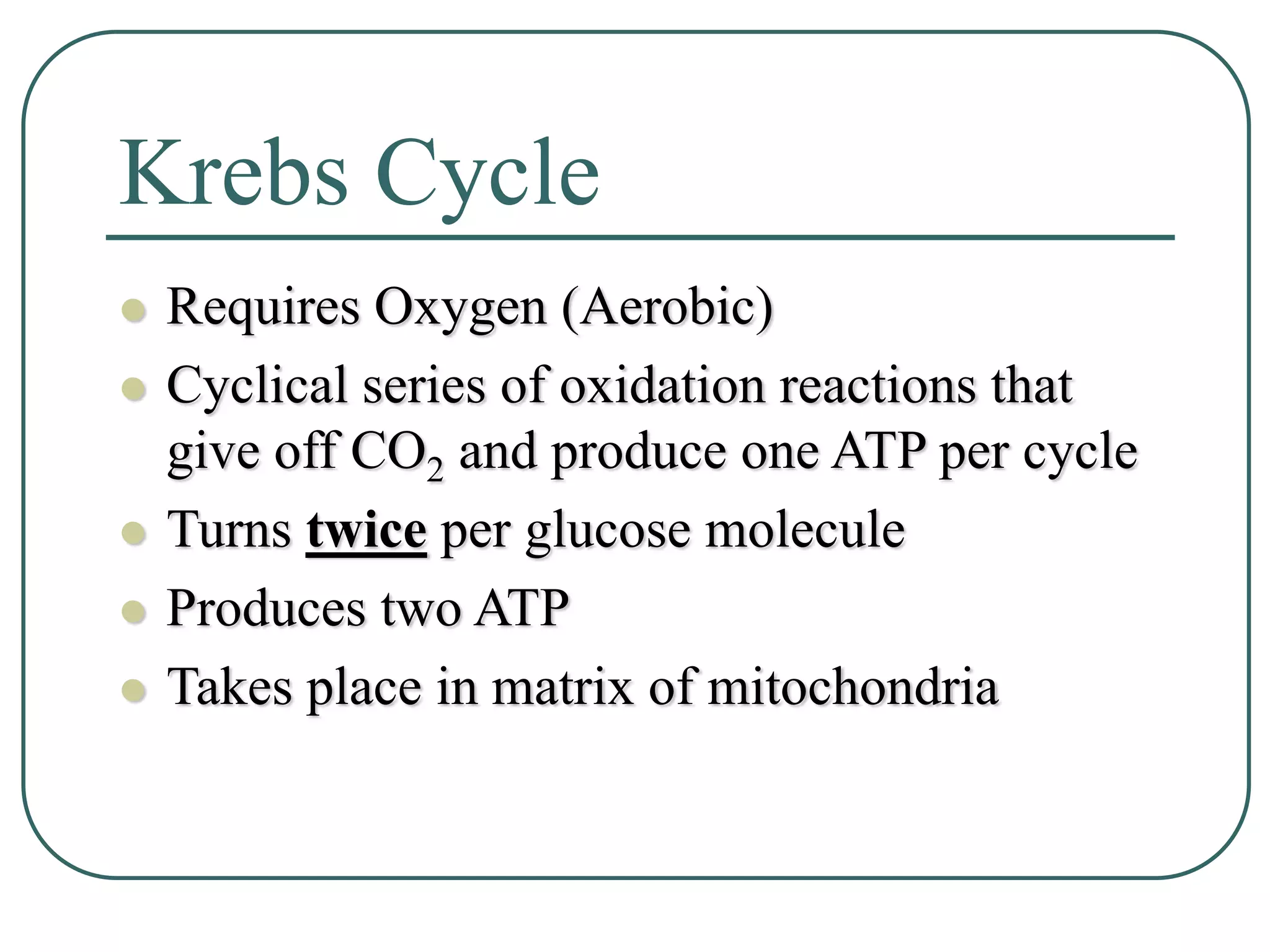
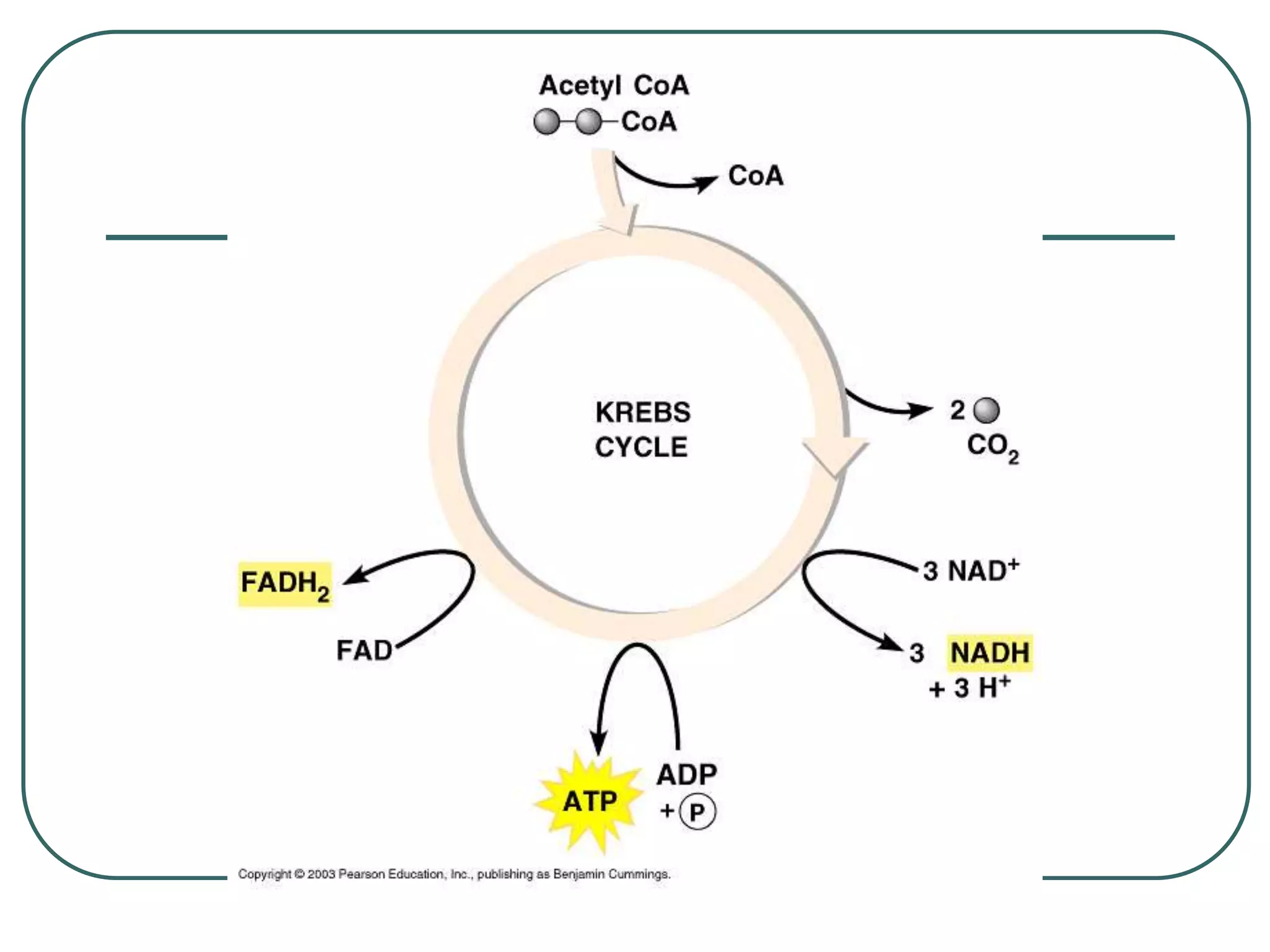
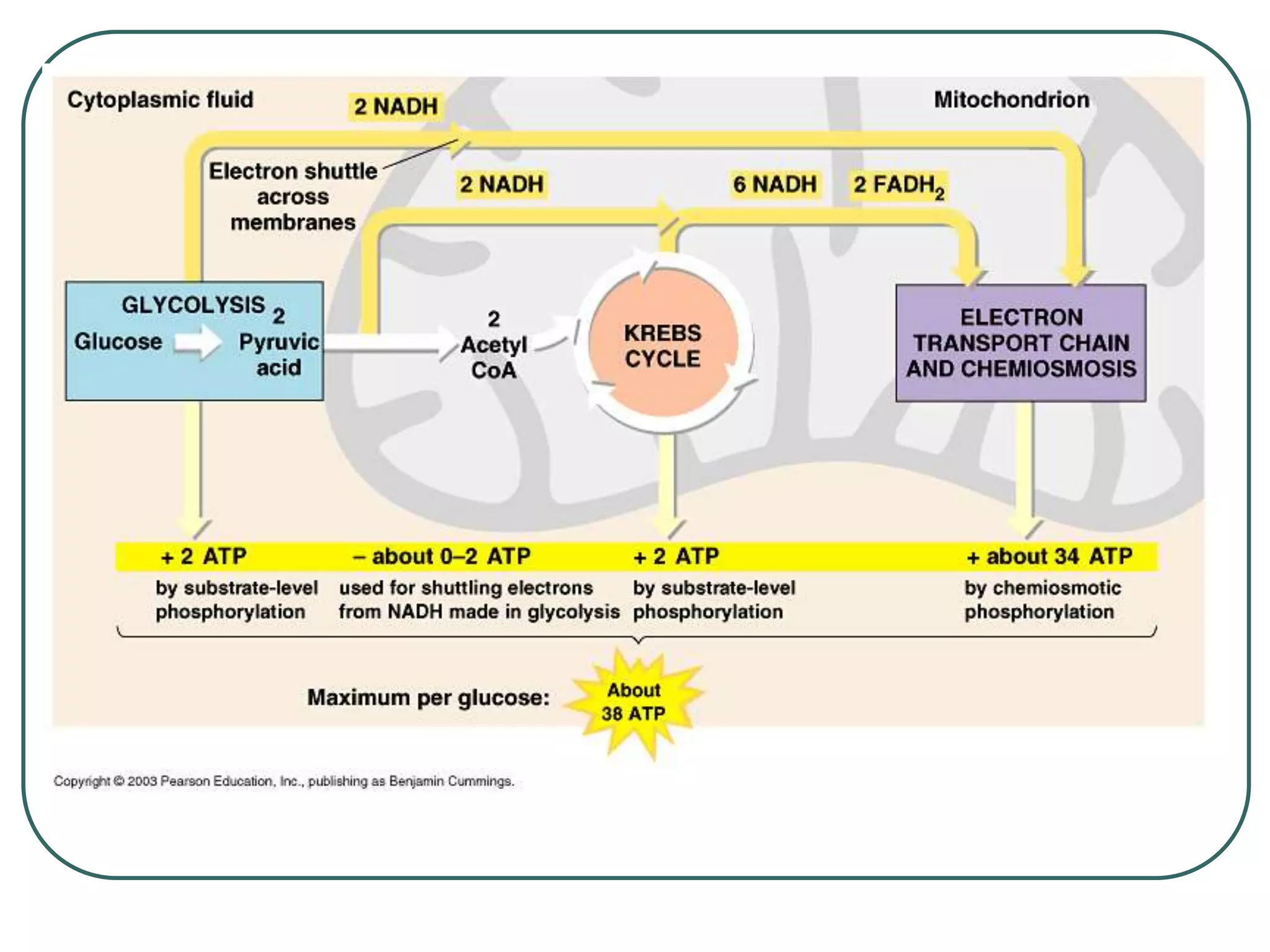
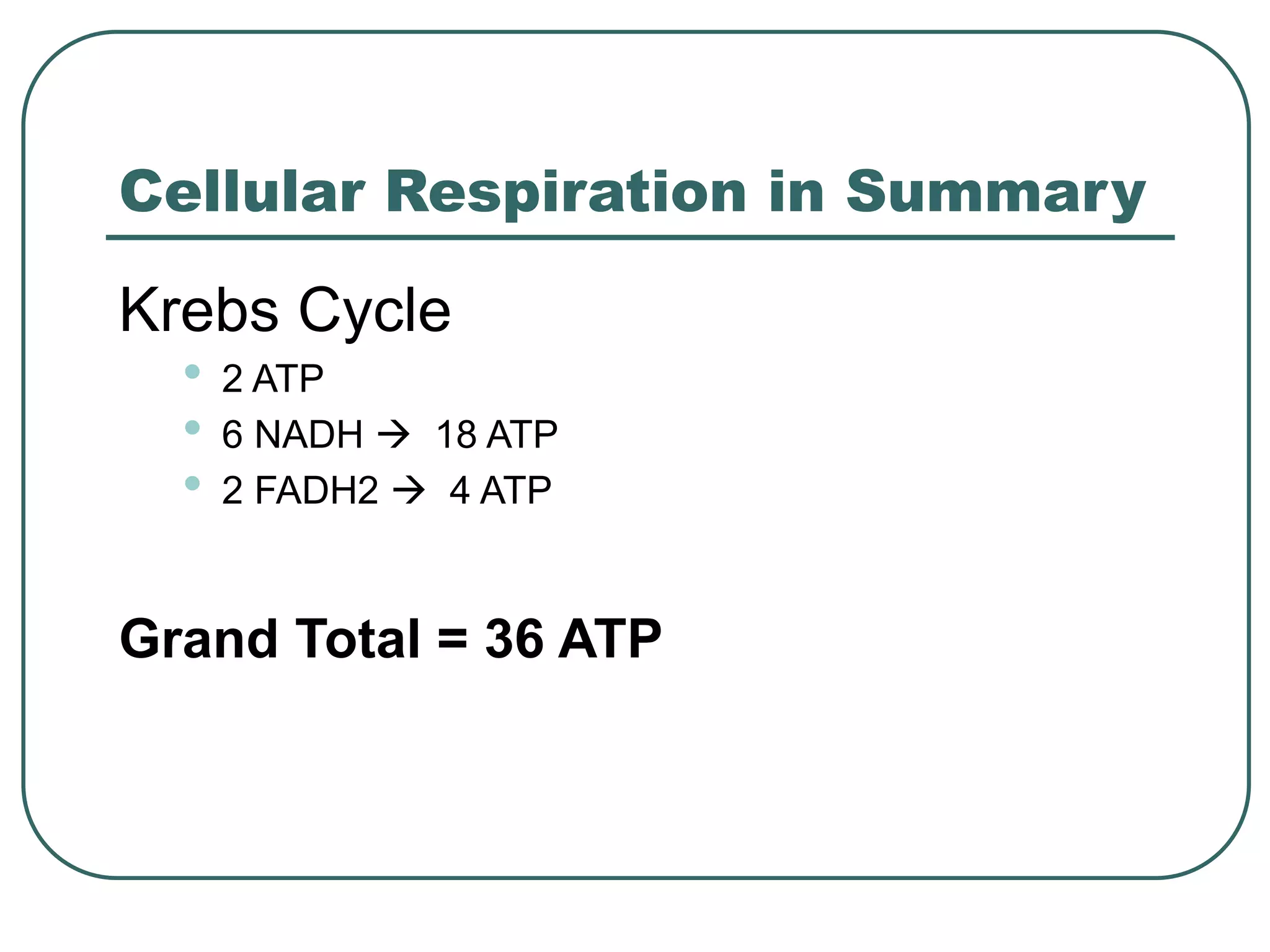
This document outlines cellular respiration and its key stages and processes. It begins by stating the objectives of describing the major features of respiration, differentiating aerobic from anaerobic respiration, distinguishing the major stages, and explaining the pros and cons of fermentation and aerobic respiration. It then defines cellular respiration and describes the three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. It provides details on each stage, including where they take place in the cell, their inputs and outputs, and how ATP is generated through chemiosmosis. In summary, cellular respiration completely breaks down glucose to produce 36-38 molecules of ATP.