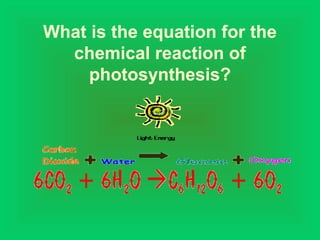
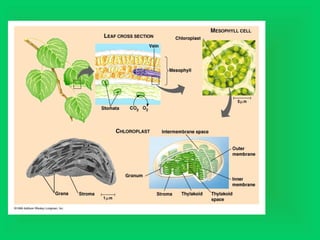
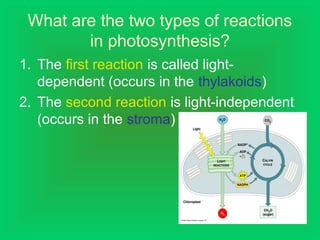
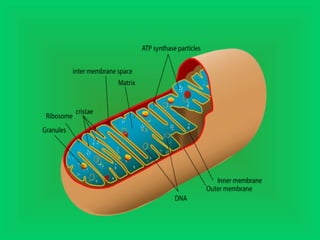
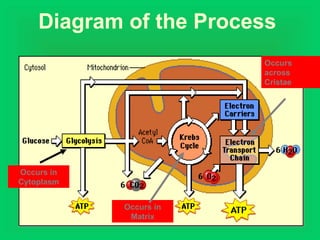
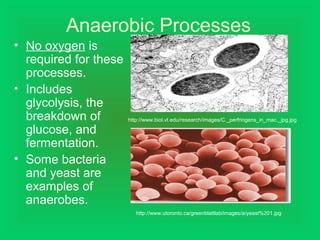
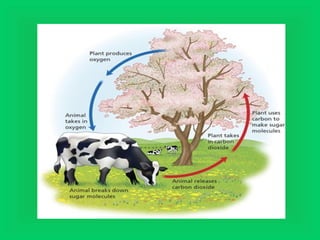
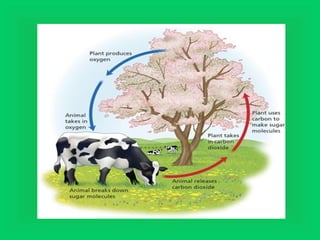
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are complementary processes. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight to produce oxygen and glucose (food). Cellular respiration breaks down glucose to release energy, using oxygen and producing carbon dioxide and water. These processes work together to transfer energy through ecosystems, with photosynthesis capturing solar energy which is then used and released through cellular respiration.