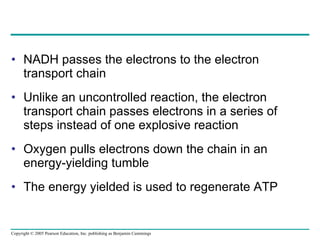
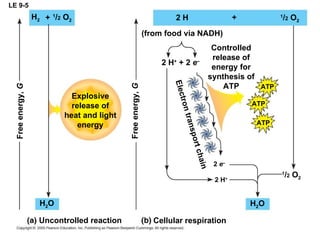
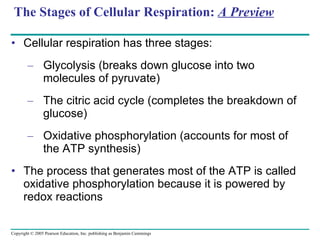
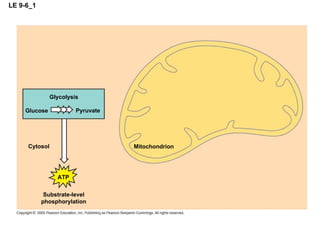
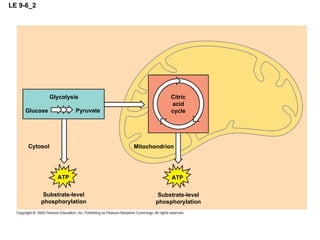
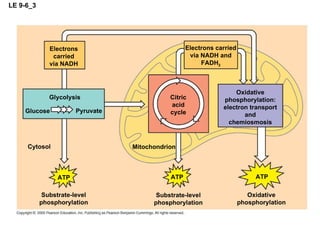
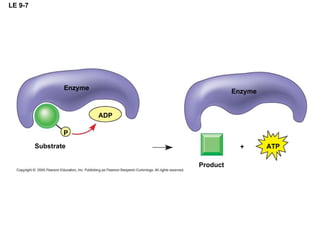
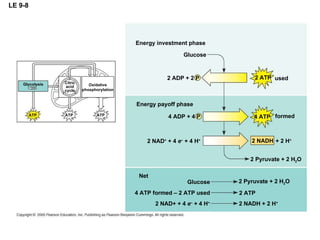
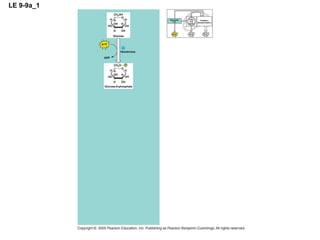
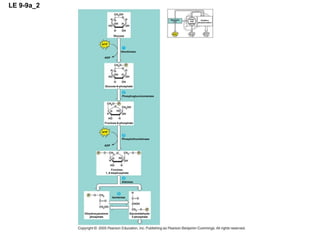
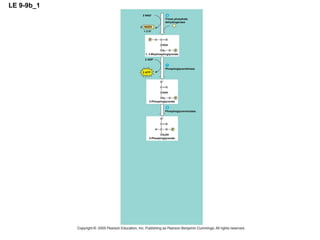
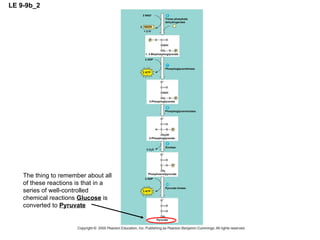
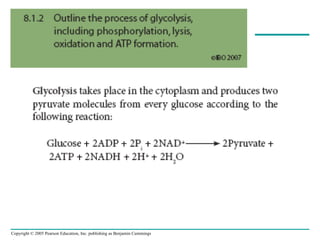
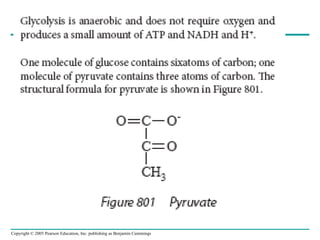
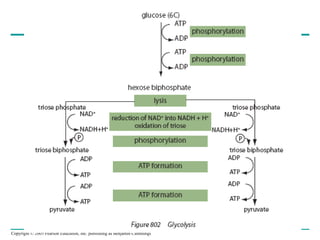
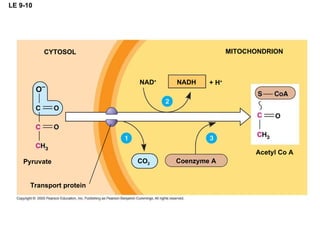
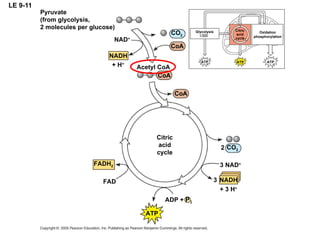
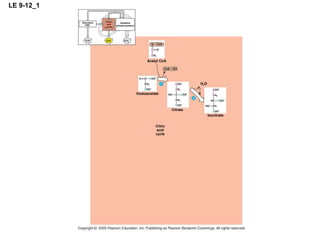
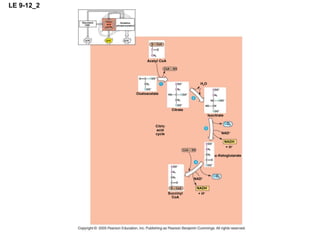
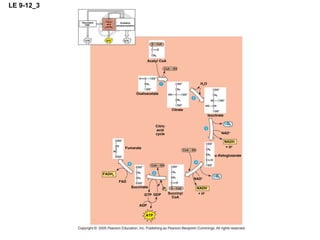
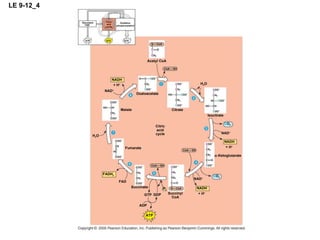
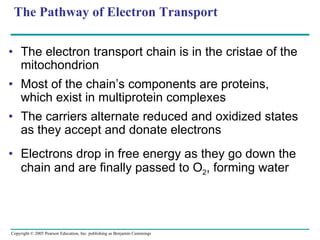
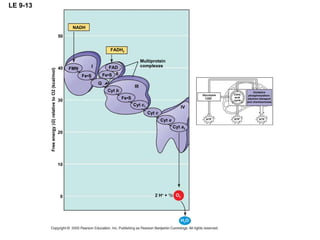
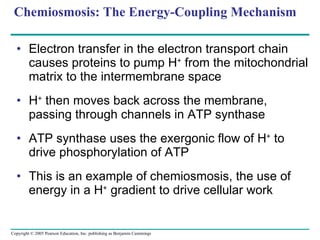
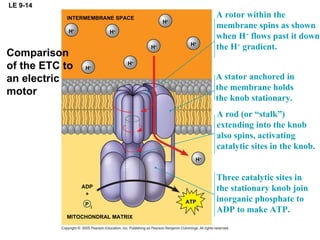
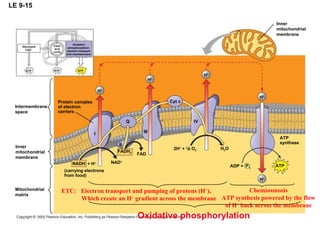
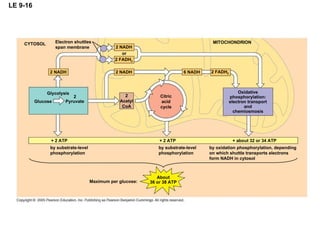
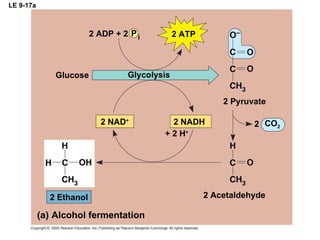
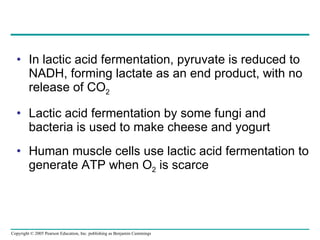
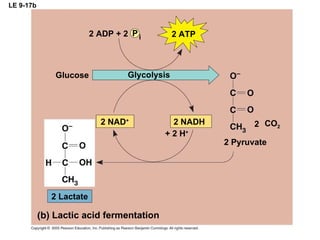
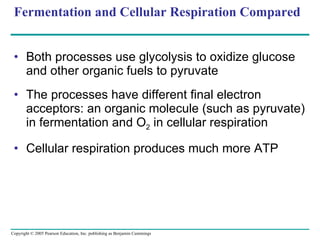
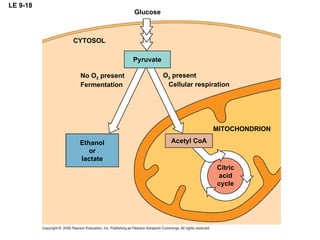
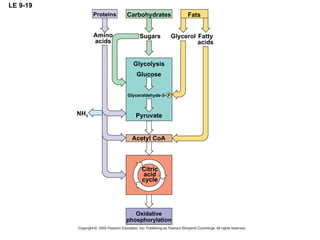
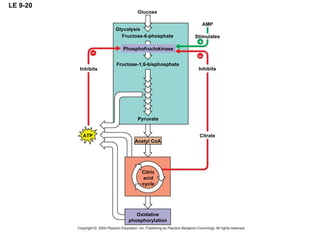
The document summarizes cellular respiration, which consists of three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate and generates a small amount of ATP. The citric acid cycle further oxidizes pyruvate and generates more ATP, NADH, and FADH2. During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed through an electron transport chain where their energy is used to pump protons across a membrane and generate a proton gradient. ATP synthase uses this proton gradient to generate most of the cell's ATP through chemiosmosis.



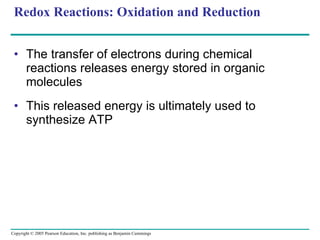
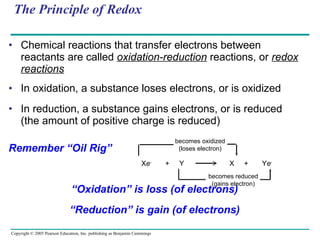


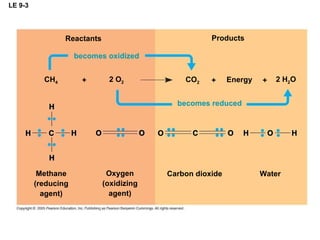
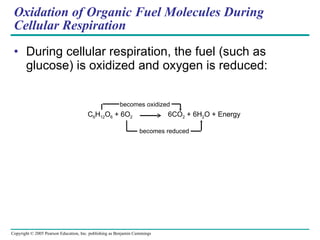
![LE 9-4 NAD + Nicotinamide (oxidized form) Dehydrogenase 2 e – + 2 H + 2 e – + H + NADH H + H + Nicotinamide (reduced form) + 2[ H ] (from food) +](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09lecturesppt-110119000602-phpapp02/85/Cellular-respiration-lecture-14-320.jpg)