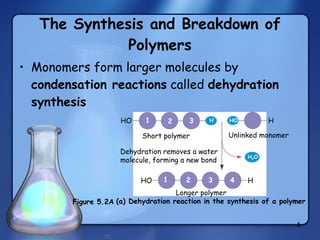
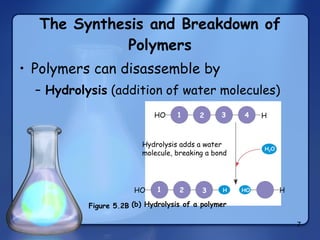
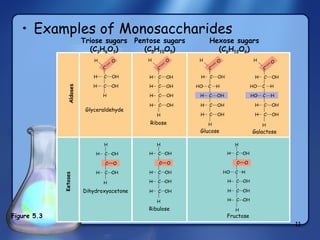
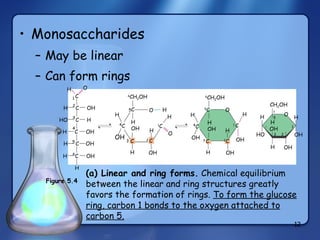
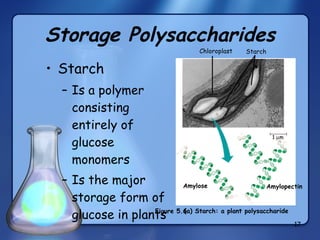
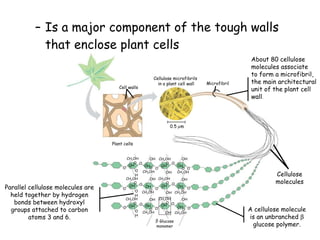
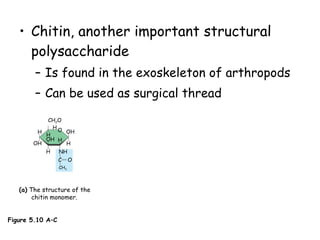
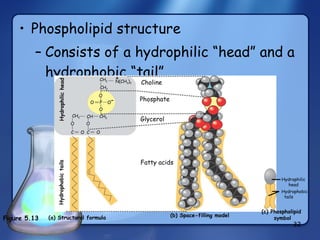
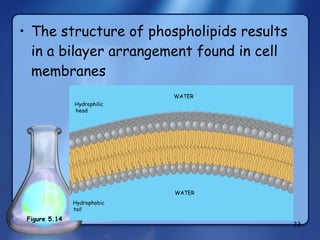
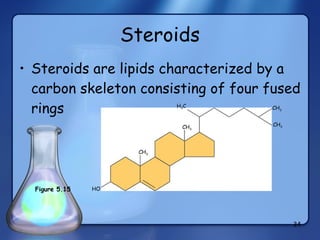
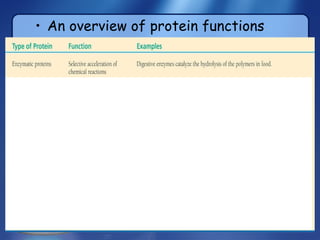
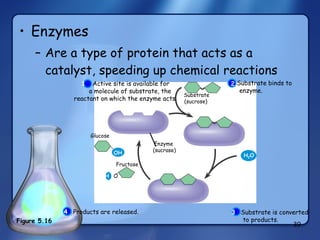
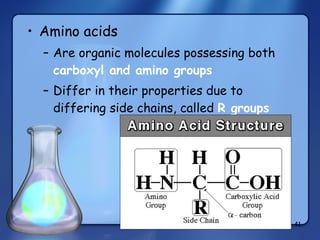
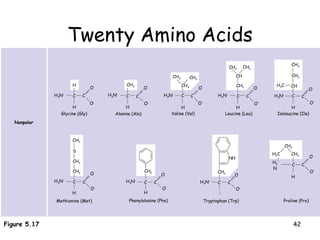
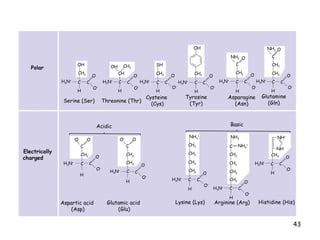
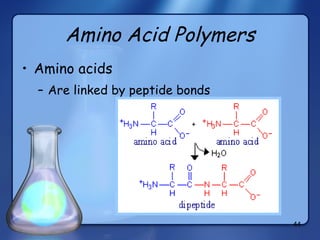
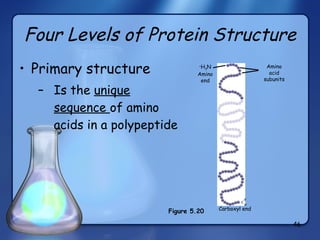
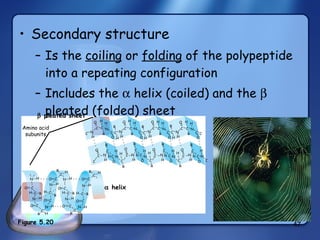
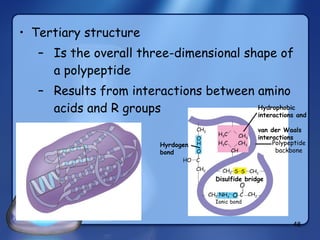
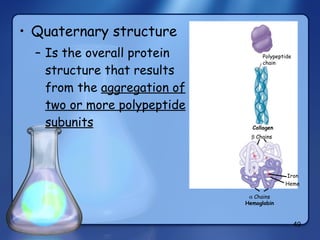
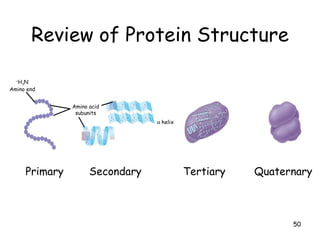
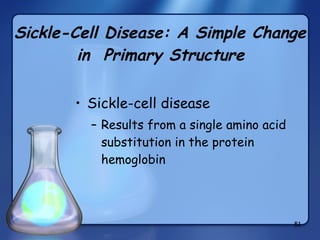
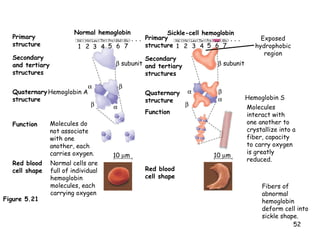
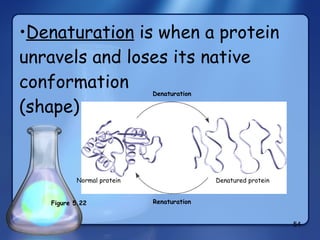
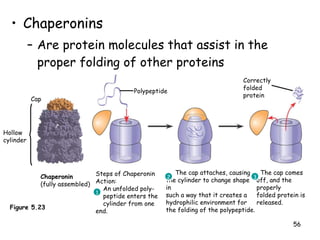
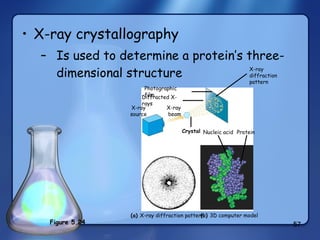
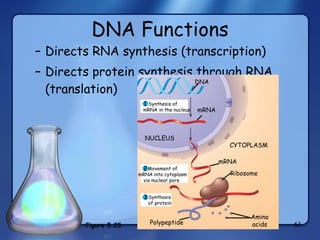
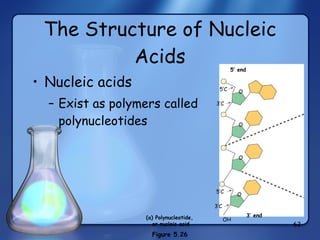
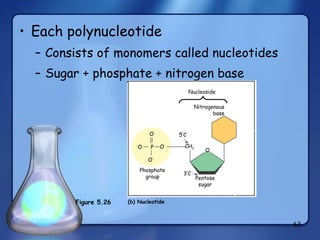
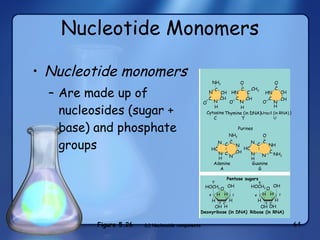
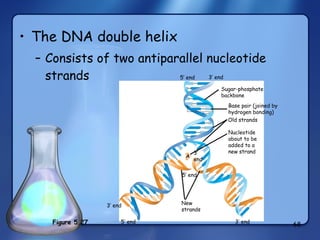
This document summarizes the structure and function of macromolecules. It discusses the four main classes of macromolecules - carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. Carbohydrates include sugars and polymers like starch and cellulose. Sugars are made of monosaccharides that can join to form disaccharides or polysaccharides. Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Lipids include fats, phospholipids, and steroids. Macromolecules are essential to the structure and function of living organisms.