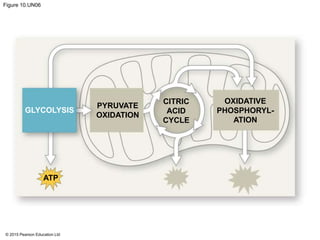
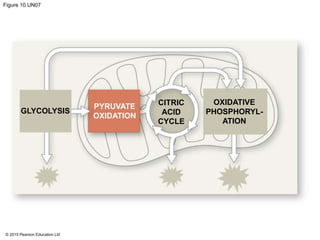
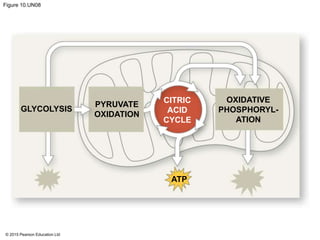
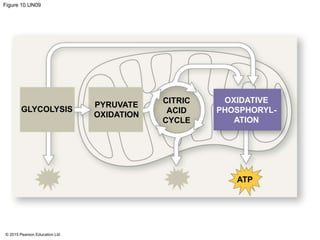
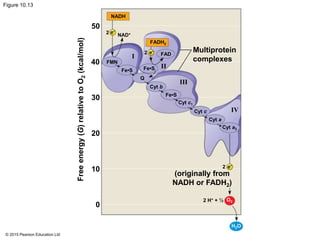
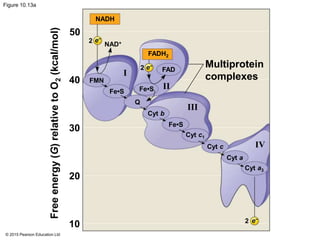
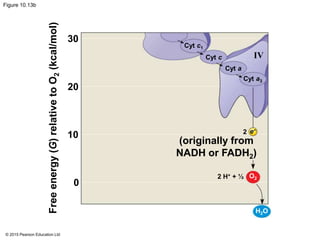
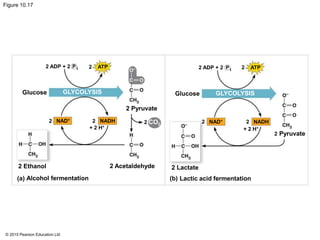
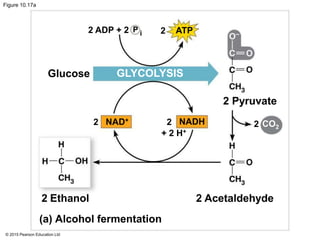
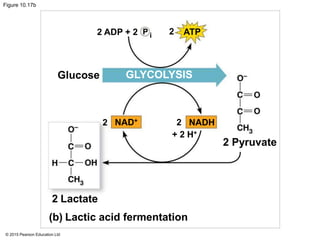
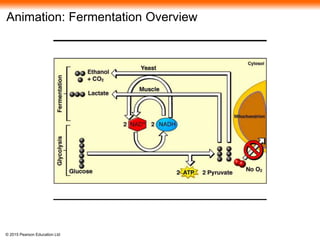
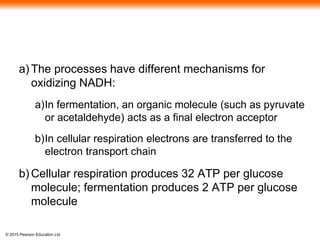
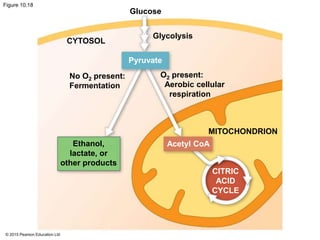
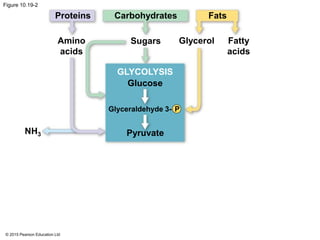
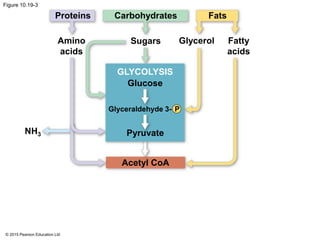
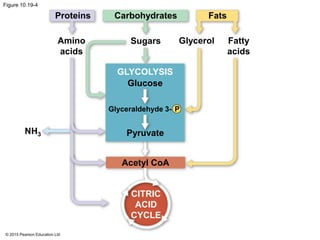
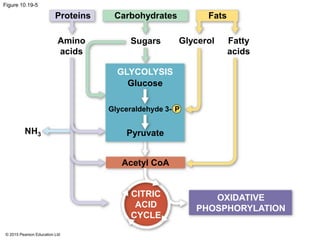
The document provides an overview of cellular respiration and its three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. It discusses how:
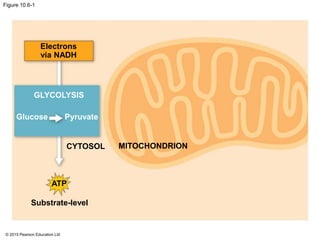
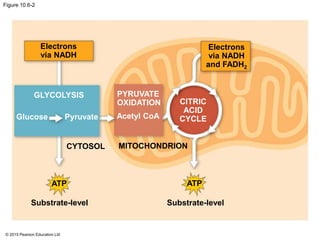
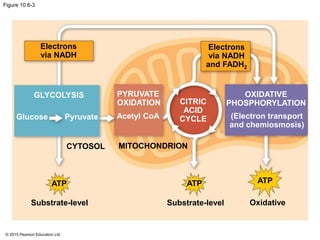
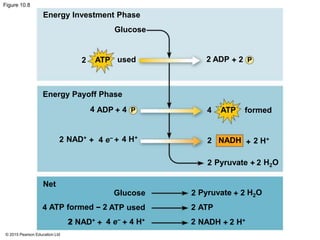
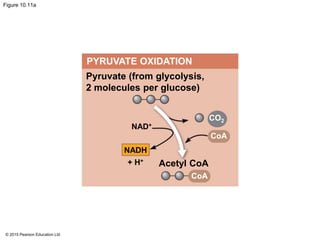
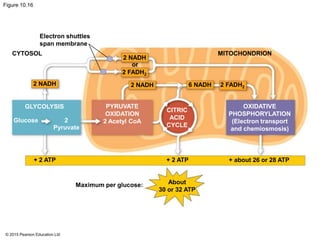
1. Glycolysis breaks down glucose to pyruvate and generates a small amount of ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation.
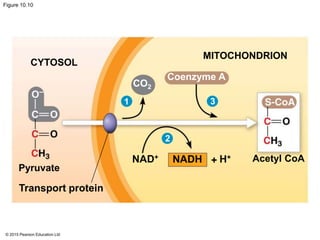
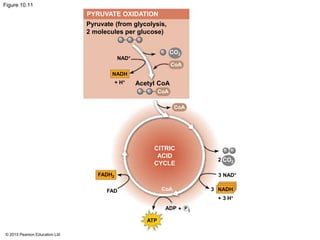
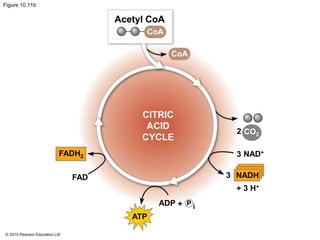
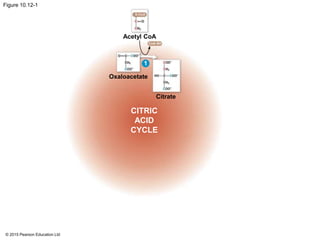
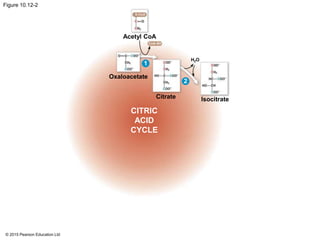
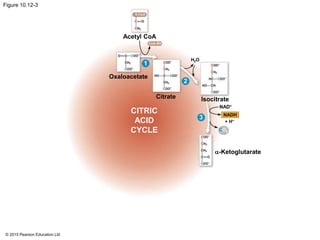
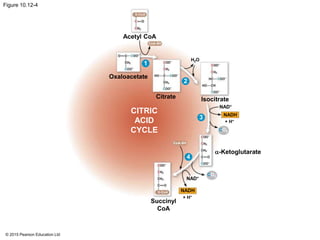
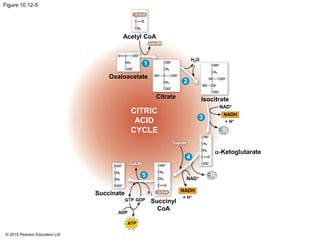
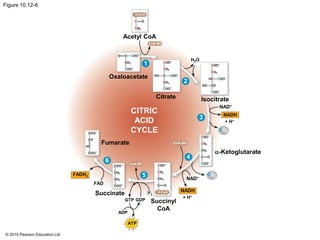
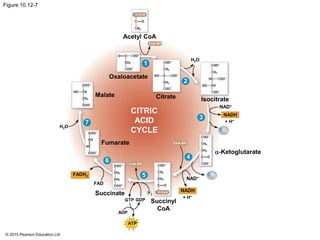
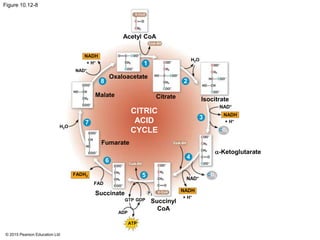
2. Pyruvate then enters the citric acid cycle in the mitochondrion where it is further oxidized, producing NADH, FADH2, and a small amount of ATP.
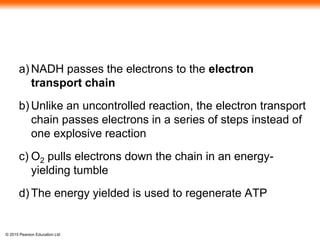
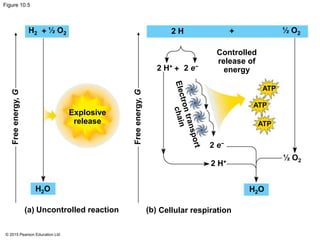
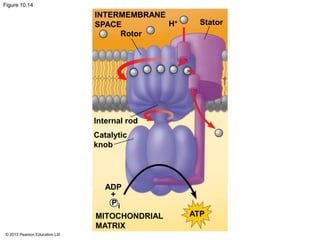
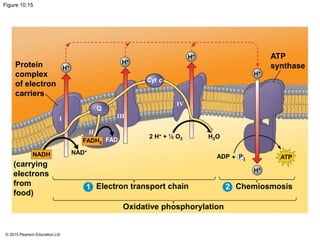
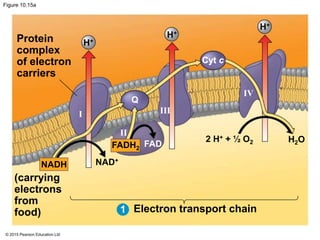
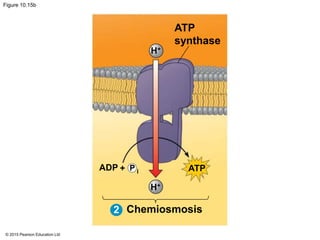
3. The electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed to the electron transport chain during oxidative phosphorylation, where they generate a large amount of ATP through chemiosmosis.










![© 2015 Pearson Education Ltd
Figure 10.4
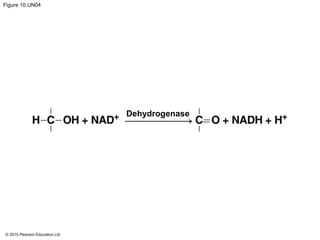
NAD+
2 e− + 2 H+
2[H]
(from food)
Nicotinamide
(oxidized form)
Reduction of NAD+
2 e− + H+
NADH
Nicotinamide
(reduced form)
Oxidation of NADH
H+
H+
Dehydrogenase](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10gelecturepresentation-161130103725/85/10-ge-lecture-presentation-13-320.jpg)