1. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of living things. Microscopes allowed scientists like Hooke and Leeuwenhoek to first observe cells in the 1600s.
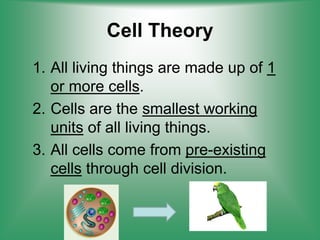
2. The Cell Theory established that all living things are made of cells, cells are the basic functional units of life, and new cells are produced from existing cells.
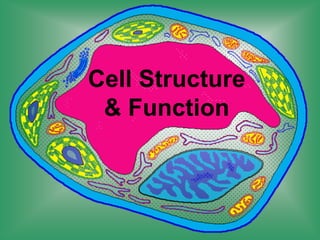
3. Cells can be either prokaryotic without organelles or eukaryotic with organelles like a nucleus. Organelles perform specific functions like mitochondria which produce energy and chloroplasts which facilitate photosynthesis.