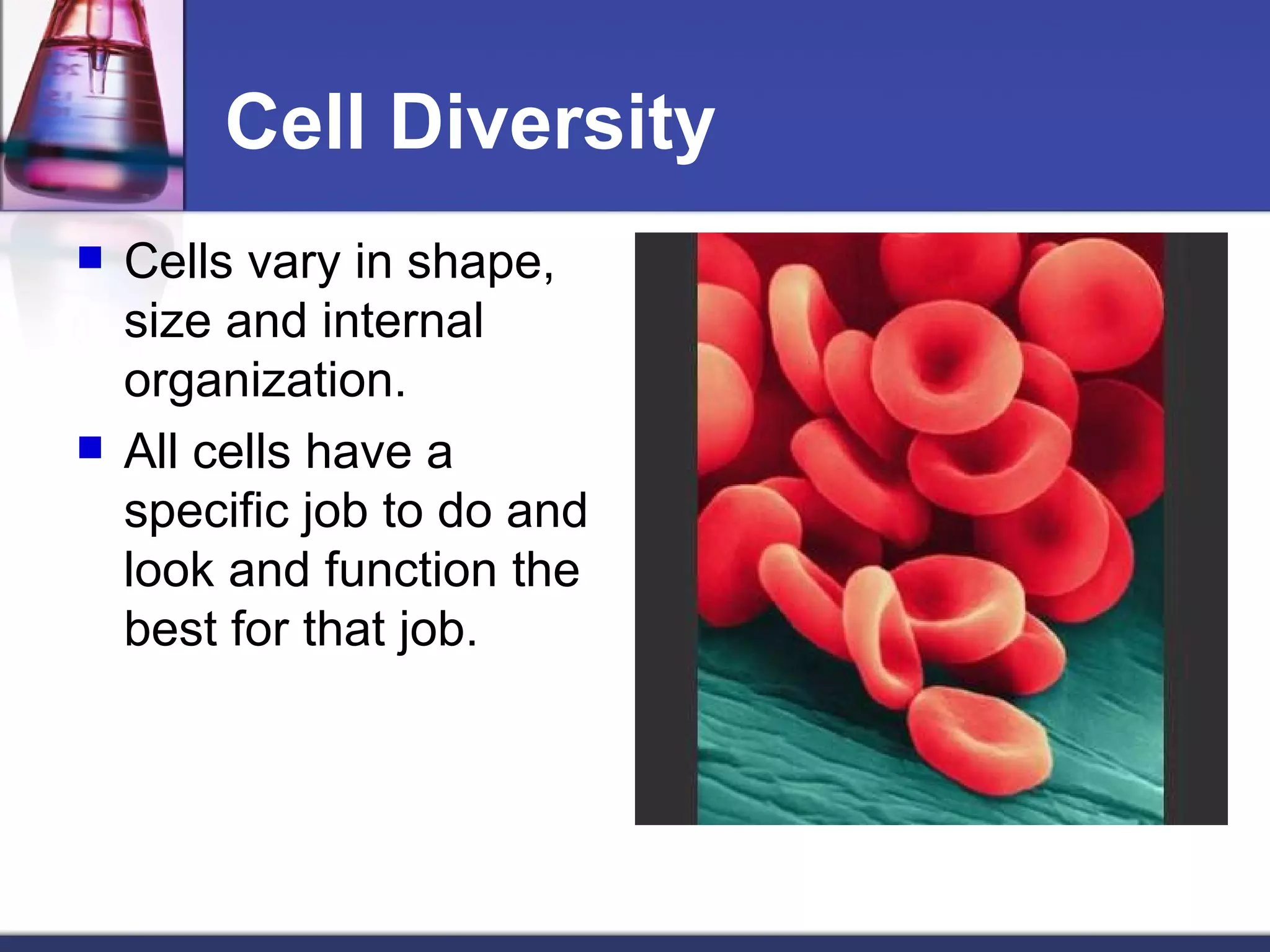
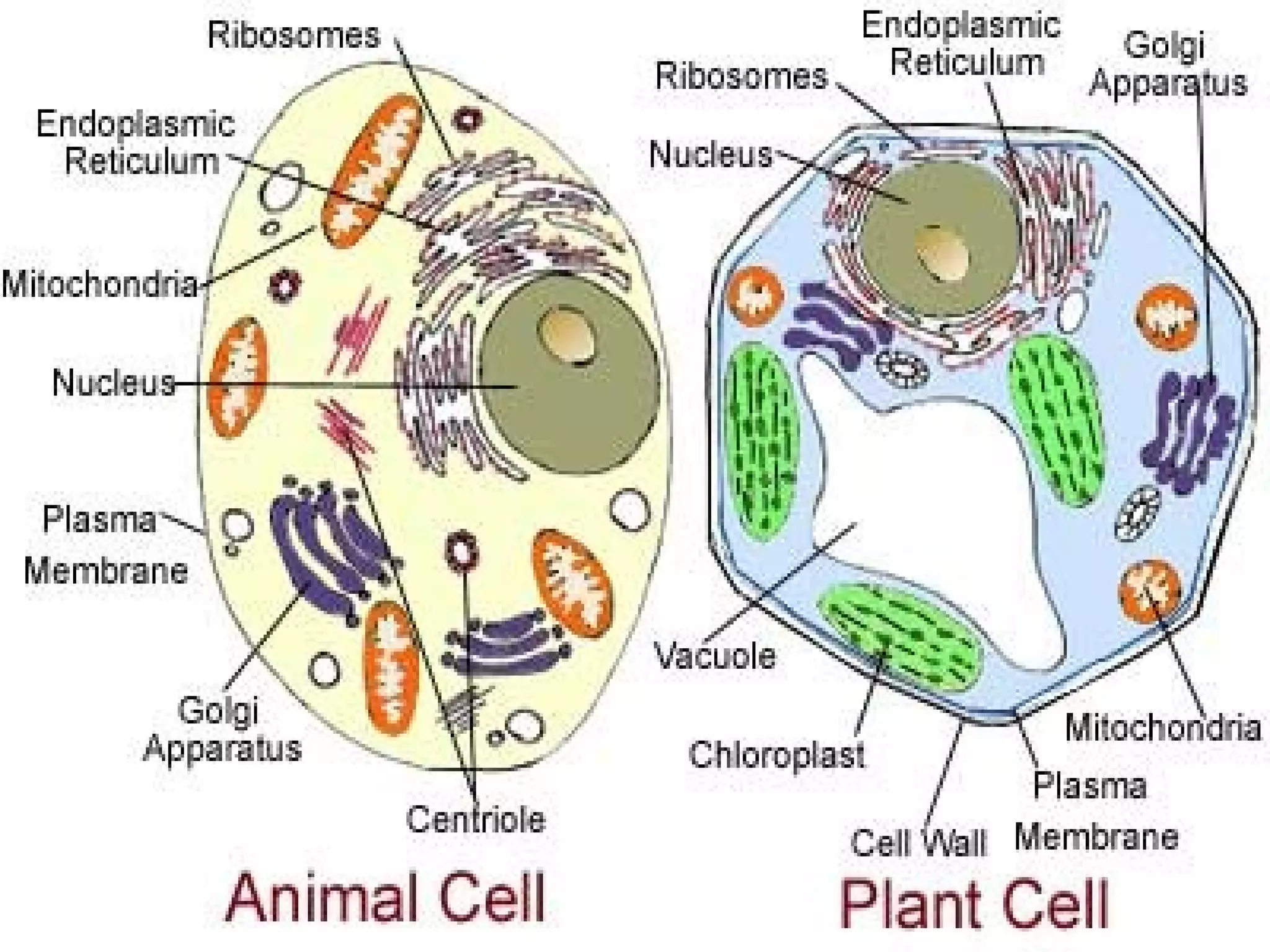
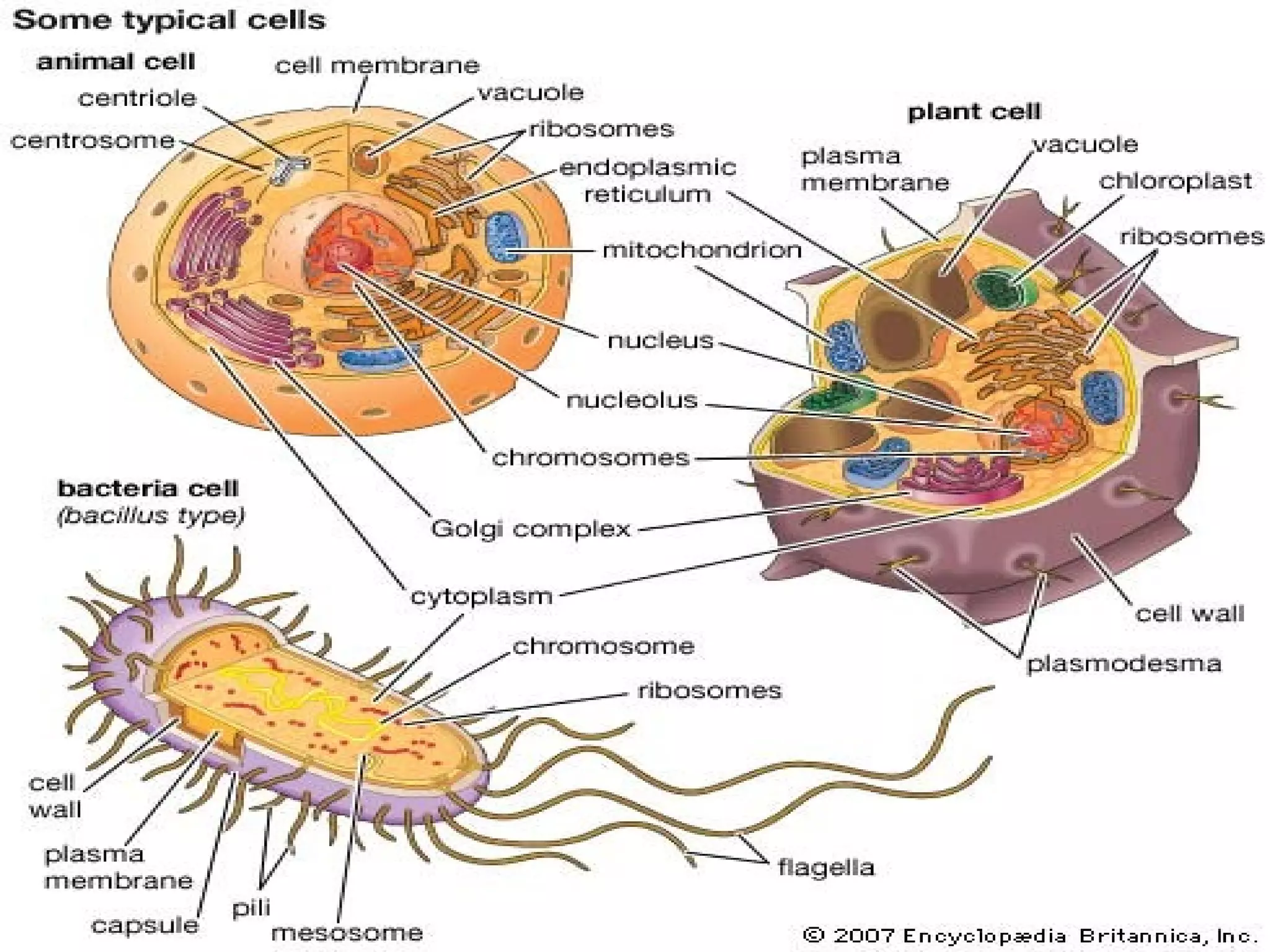
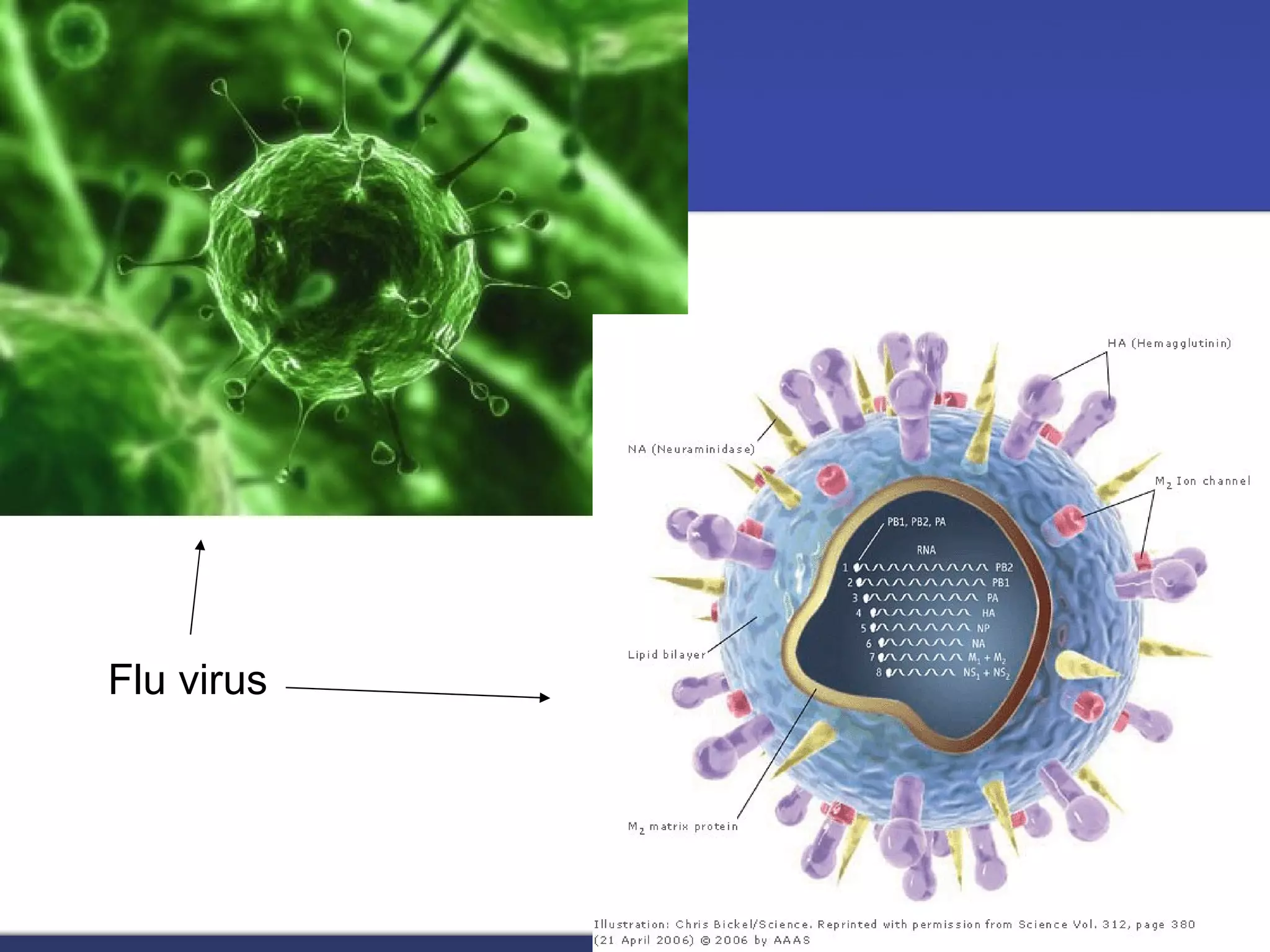
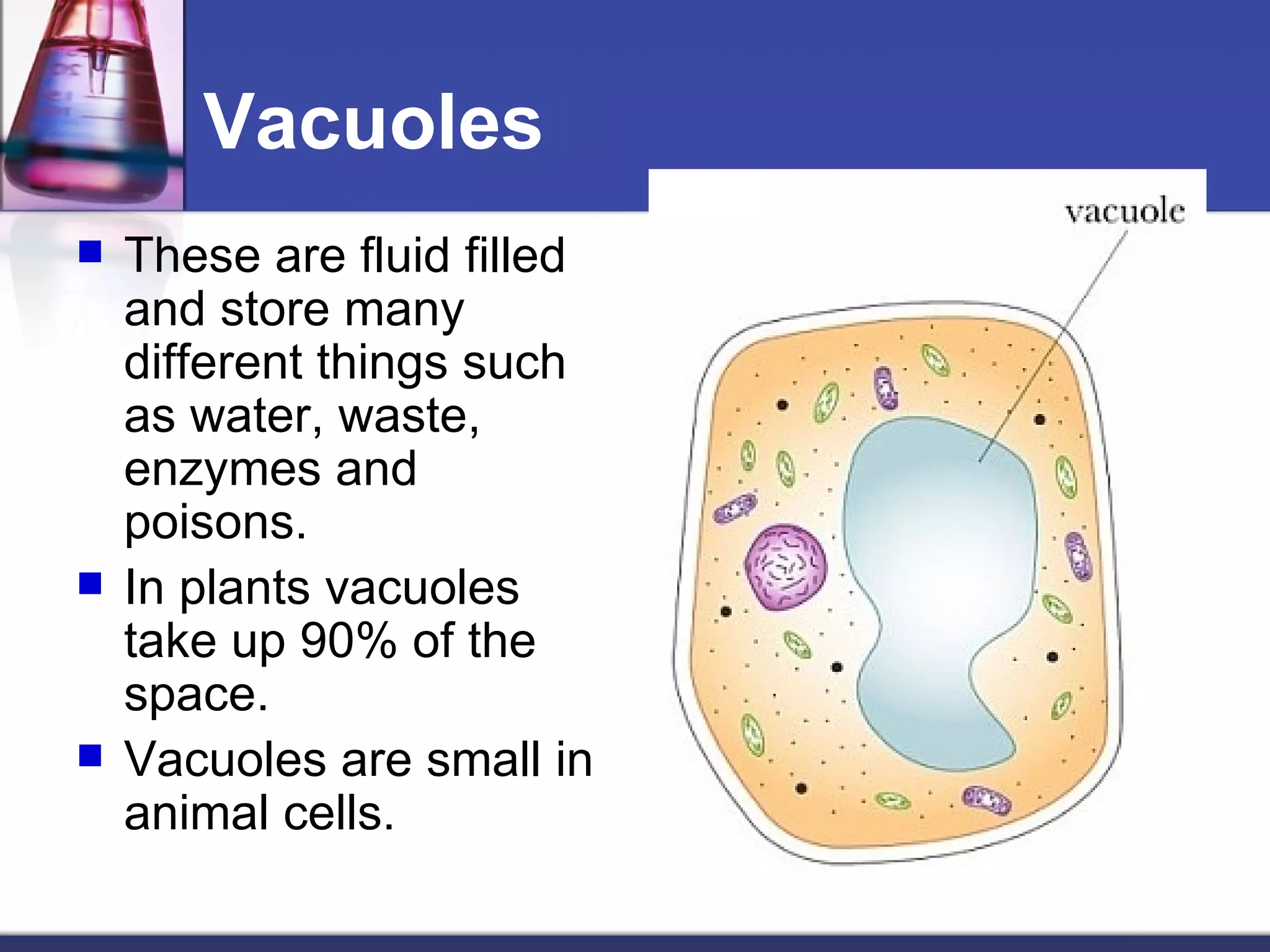
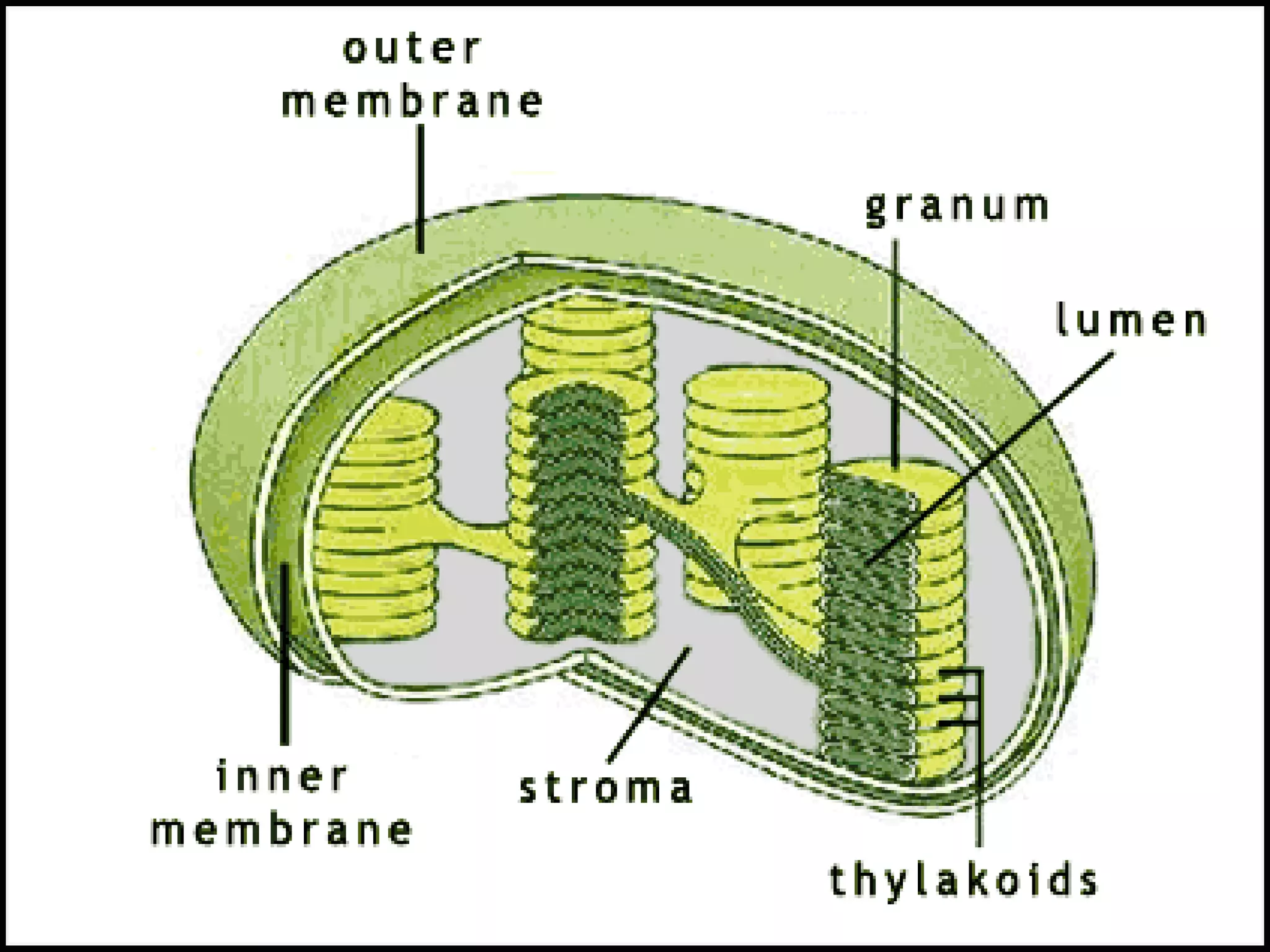
- The document discusses the structure and function of cells, including both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. It describes the key components of the cell and their functions.
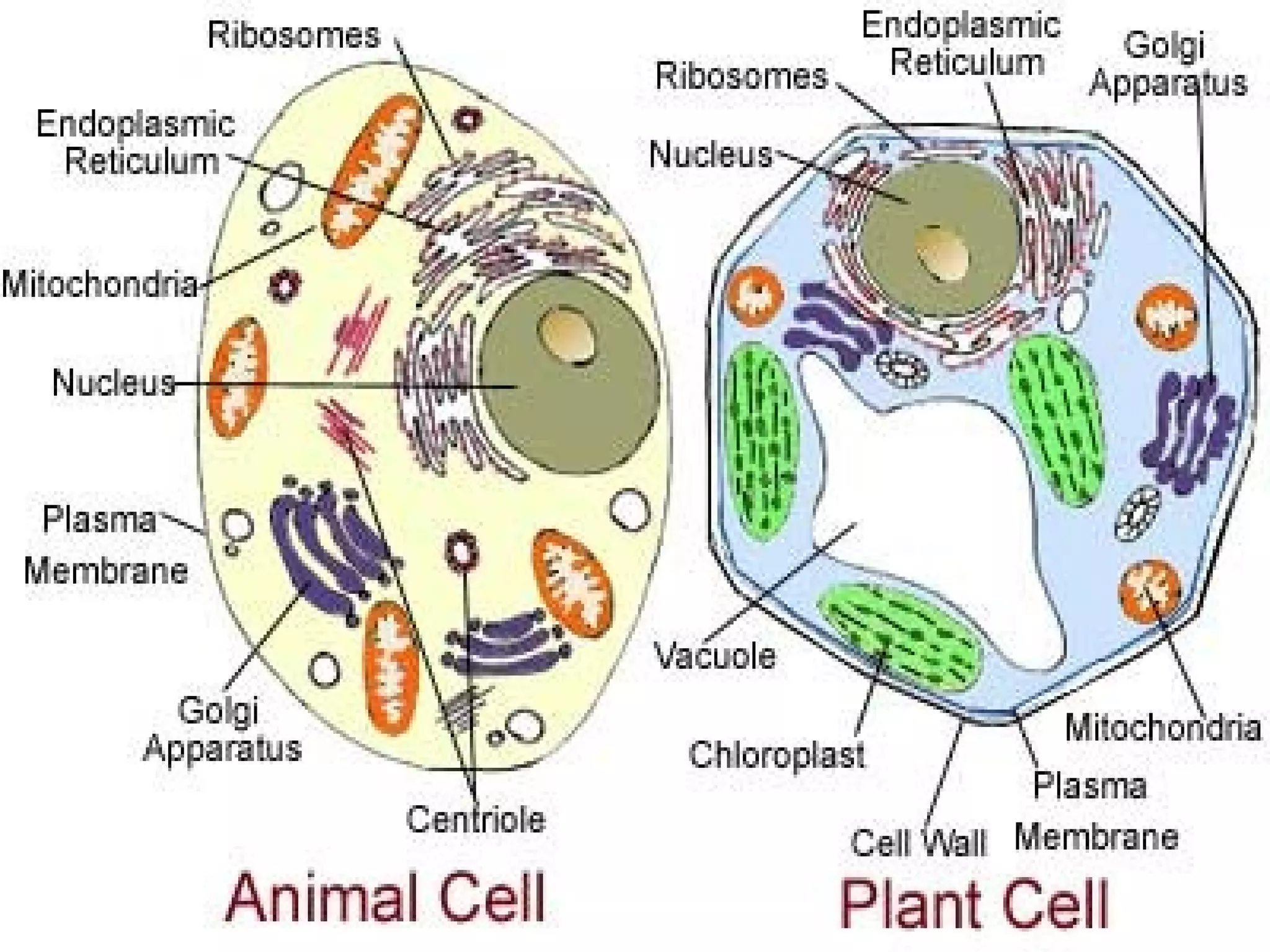
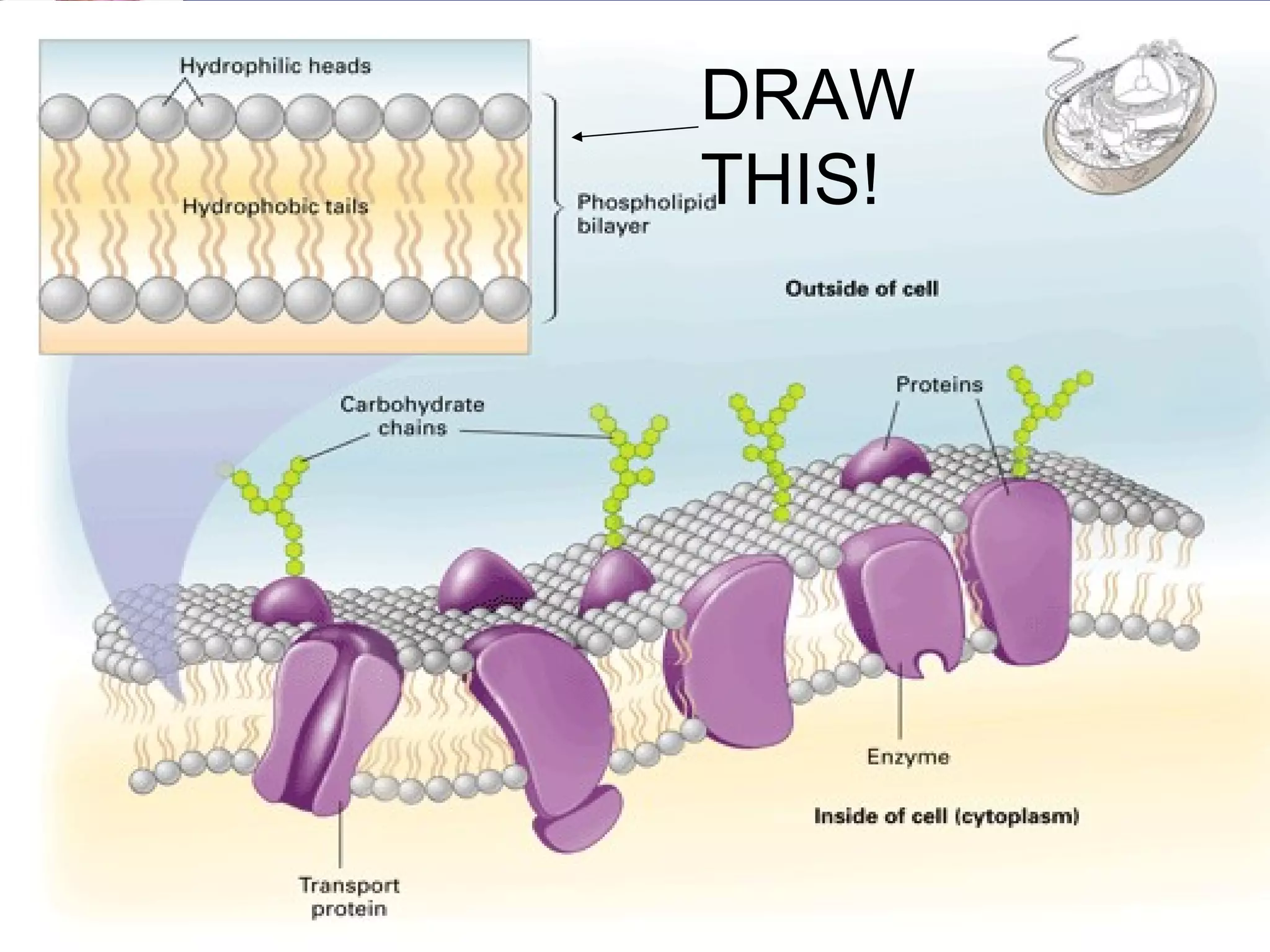
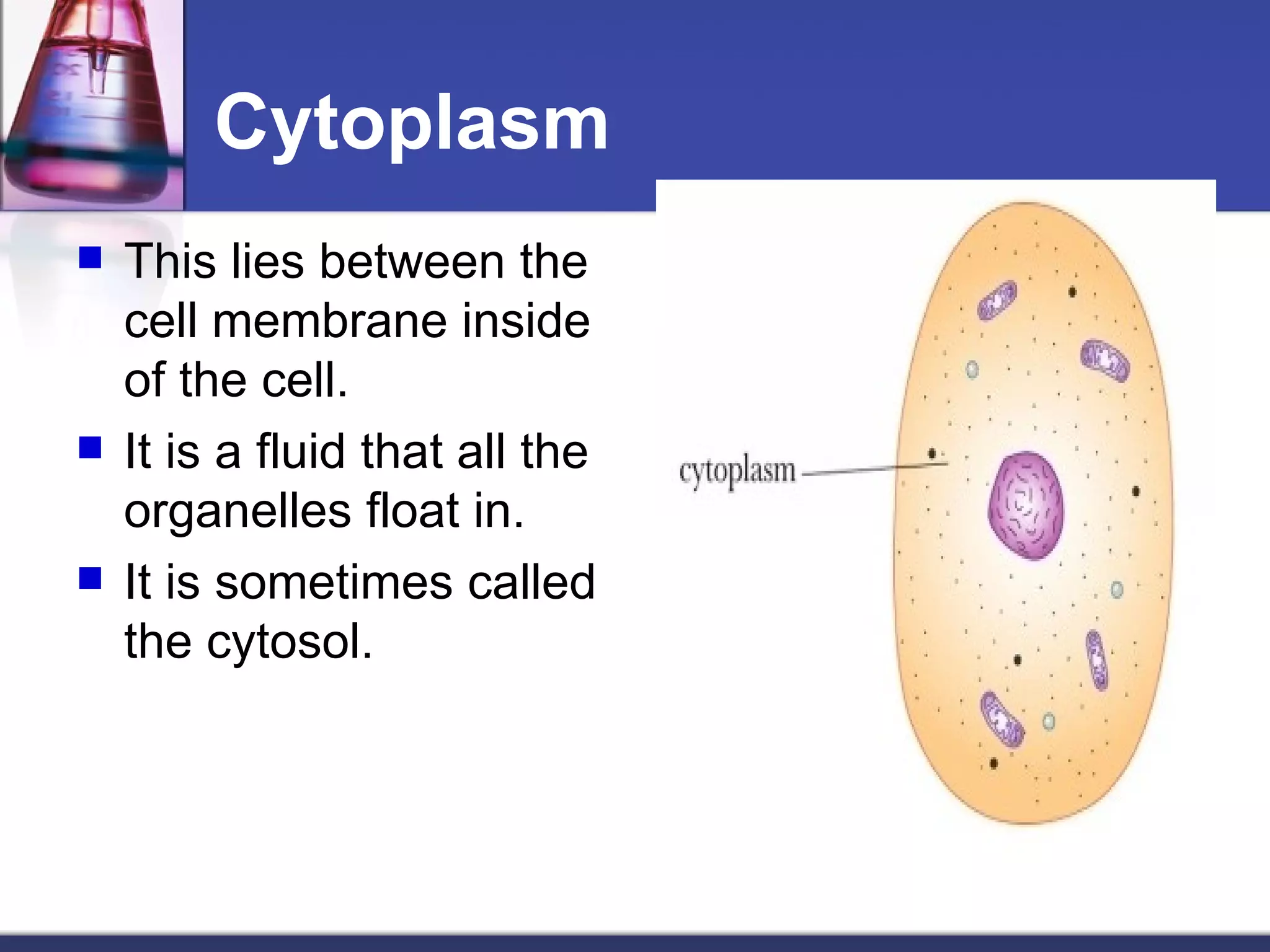
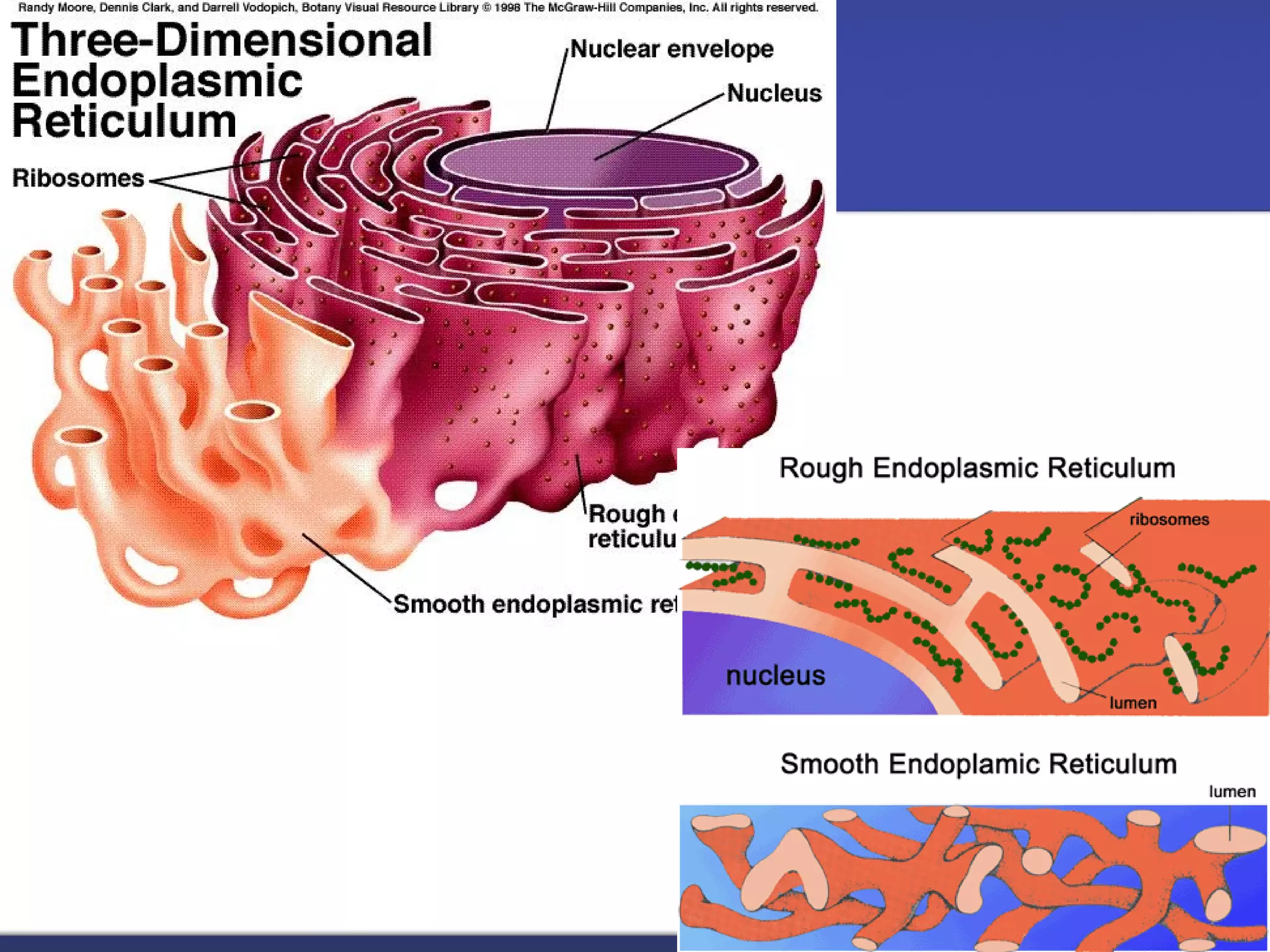
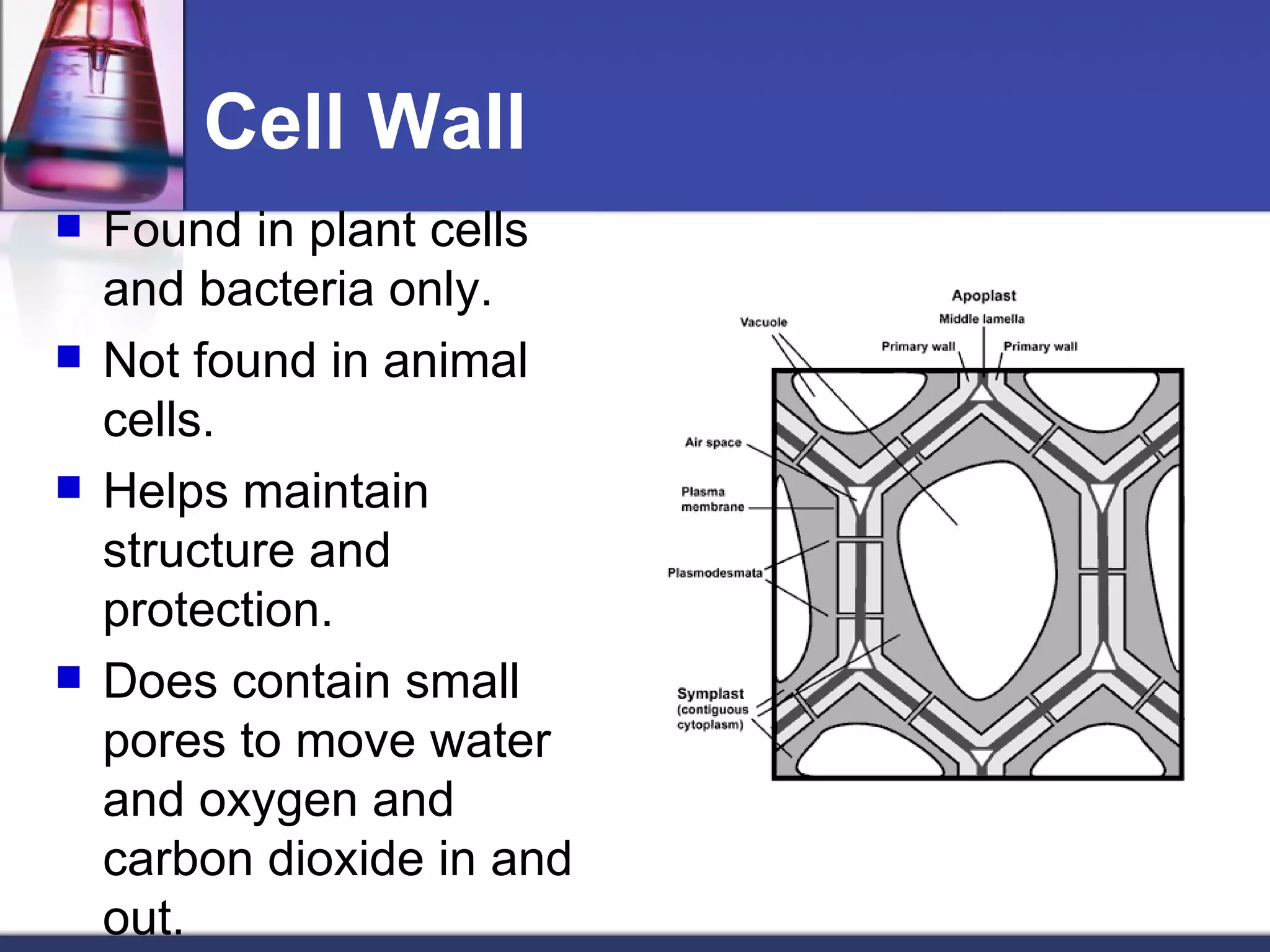
- The main parts of eukaryotic cells are the cell membrane, cytoplasm, organelles like mitochondria and the nucleus. Plant cells additionally contain chloroplasts and a cell wall.
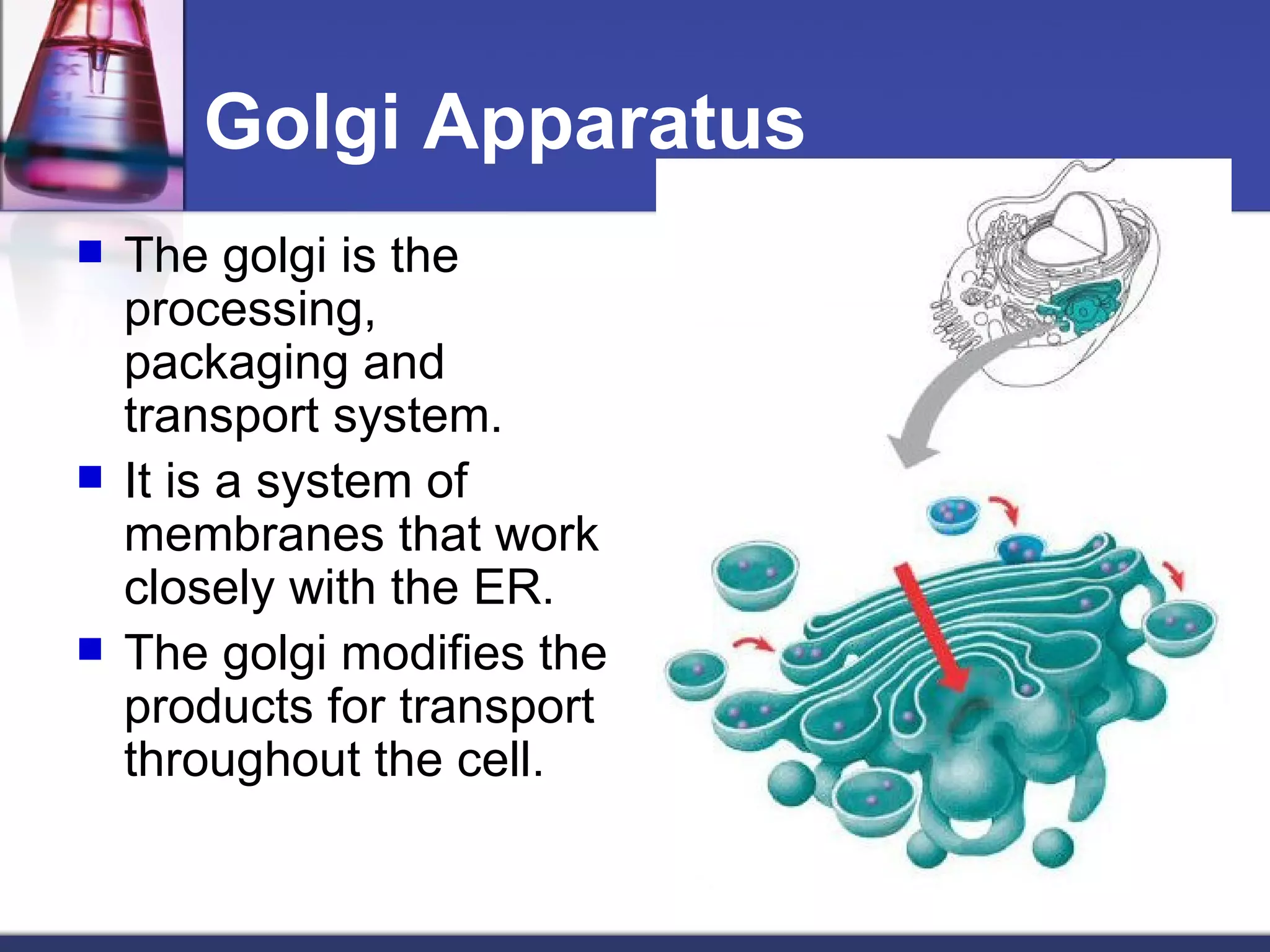
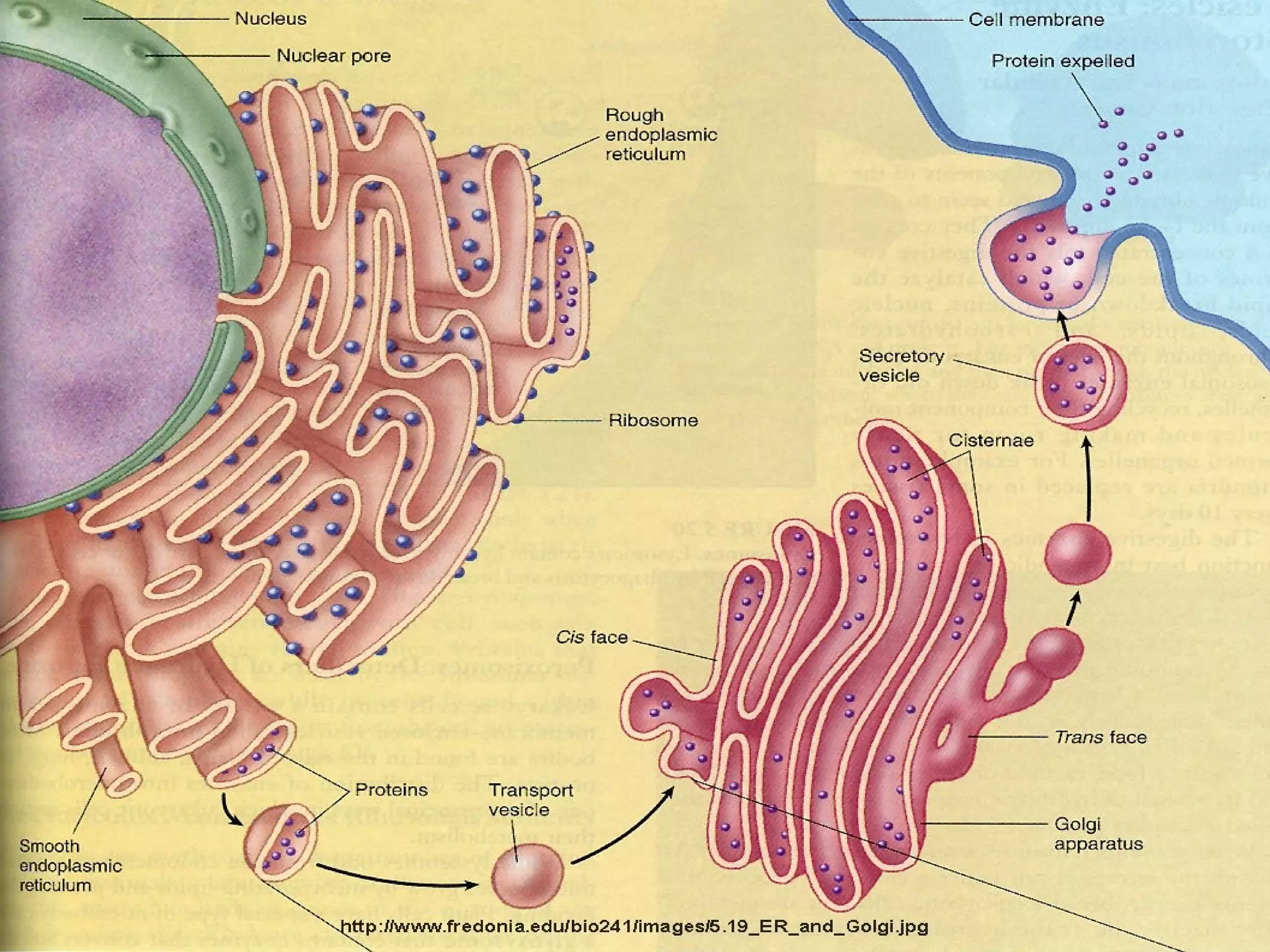
- The structures and organelles work together to carry out essential functions like respiration, protein production, transport and waste removal that allow the cell to survive.