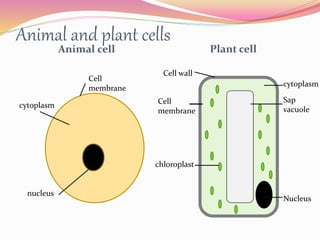
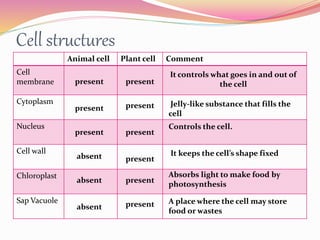
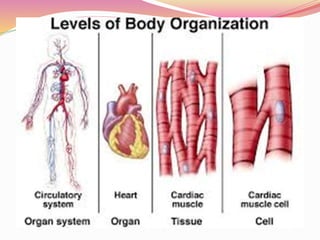
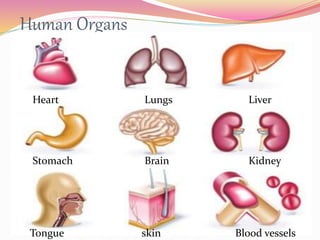
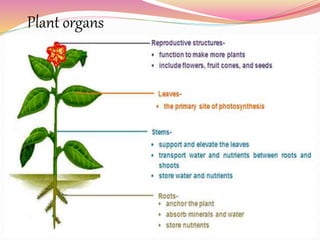
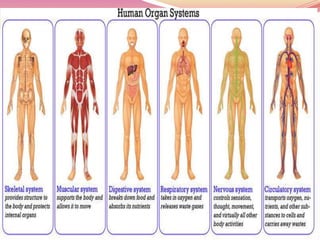
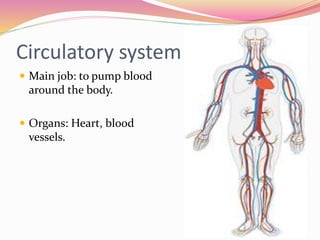
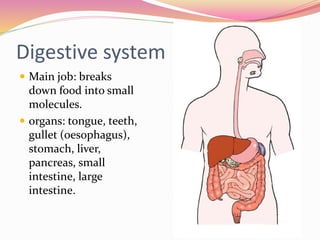
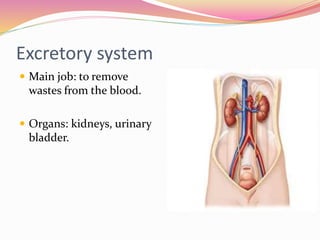
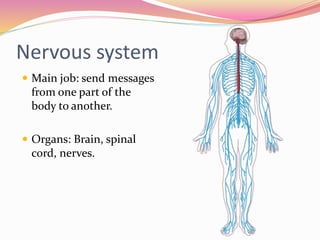
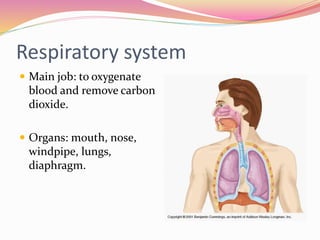
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. Animal cells contain a nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane, while plant cells also have a cell wall and chloroplasts. Cells combine to form tissues, tissues combine to form organs, and organs combine to form organ systems that work together to form a whole organism. The document then discusses the major human organ systems - circulatory, digestive, excretory, nervous, and respiratory - and gives examples of the organs that make up each system.