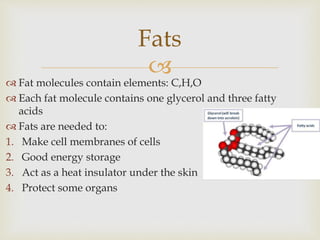
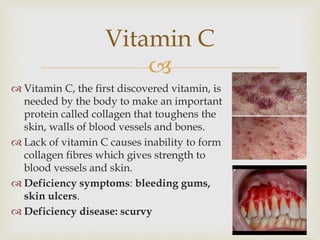
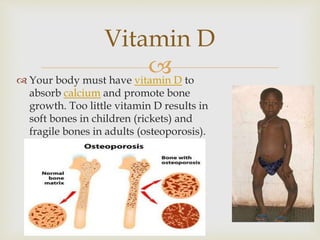
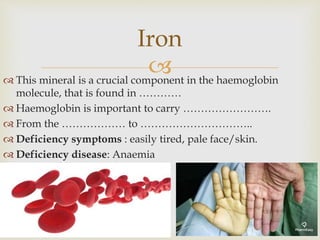
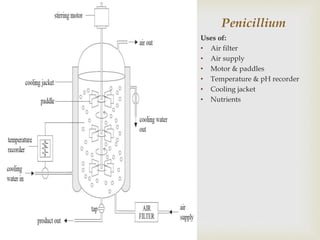
The document discusses carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and microorganisms used in food production. Carbohydrates are made of sugars and provide energy. Proteins are made of amino acids and are needed for enzymes, hemoglobin, and other functions. Fats contain glycerol and fatty acids and provide energy storage and insulation. Vitamins and minerals are micronutrients needed in small amounts to prevent deficiency diseases. Microorganisms like yeast and Lactobacillus are used in fermentation processes in food production.