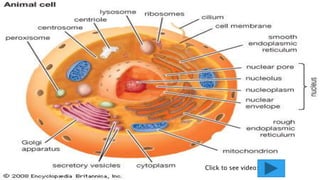
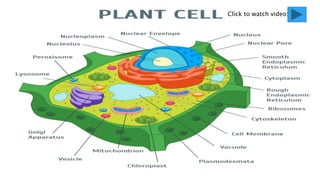
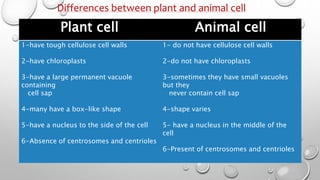
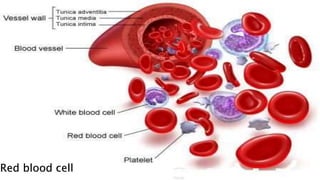
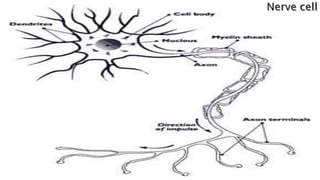
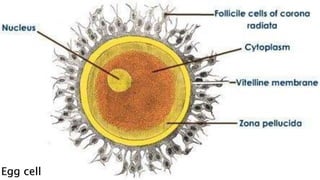
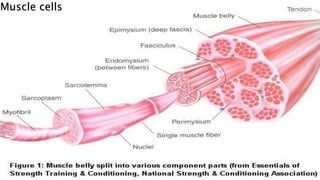
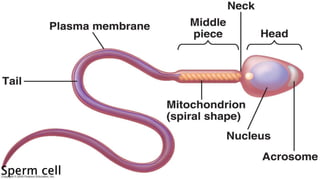
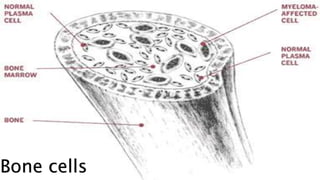
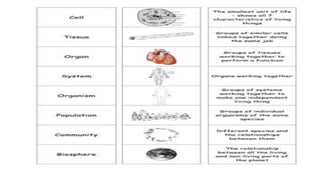
The document provides an overview of biology and cells. It discusses the characteristics of living things, the structures and differences between plant and animal cells, and specialized cell types. It also describes microscopes and their uses in observing cells. The basic unit of life is the cell, which can be unicellular like bacteria or multicellular like humans. Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts while animal cells do not. Microscopes magnify cells in different ways to reveal their structures and organelles.