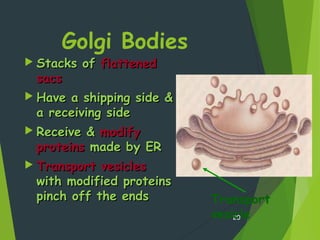
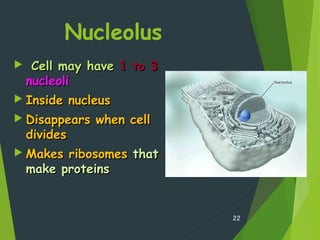
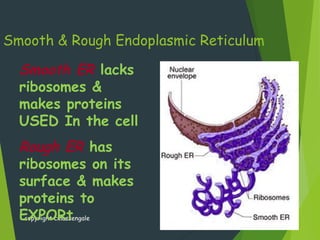
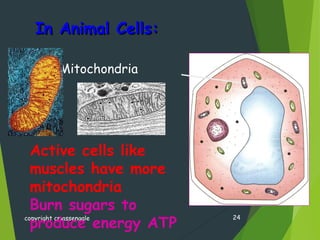
This document provides an overview of cell biology concepts including:
- Biology is the study of living things from cells to organisms. All living things are made of cells, which are the basic unit of structure and function.
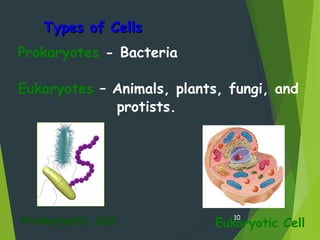
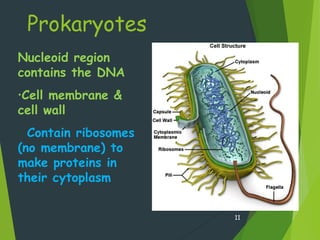
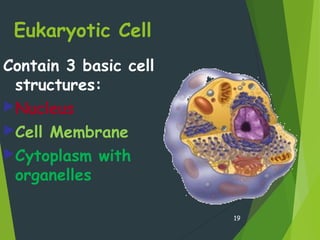
- There are two main types of cells - prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles while prokaryotic cells do not.
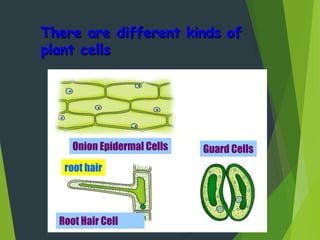
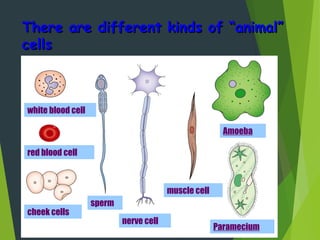
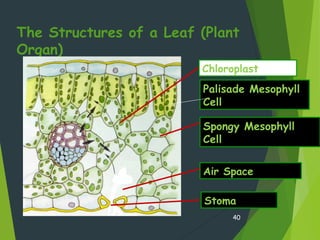
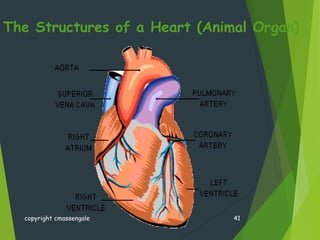
- Organisms can be unicellular, consisting of a single cell, or multicellular, made of many different cell types organized into tissues and organs.
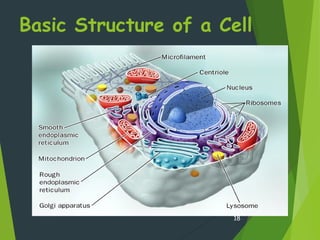
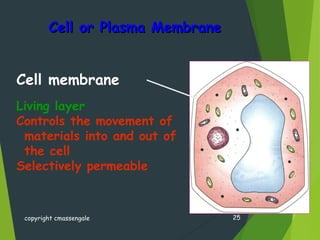
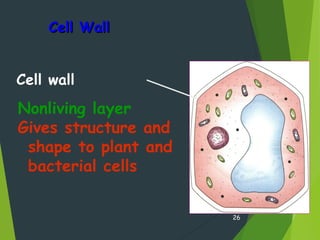
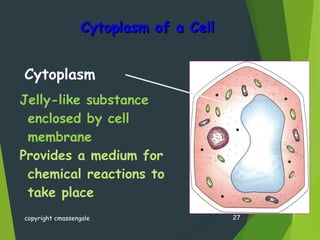
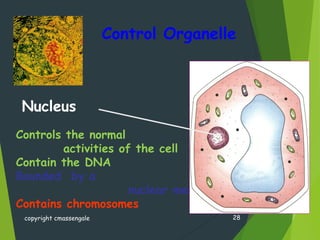
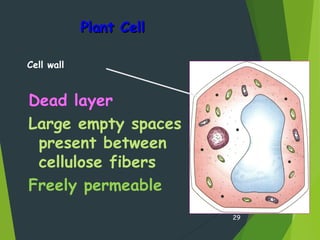
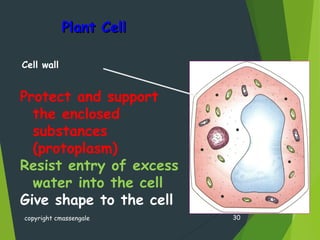
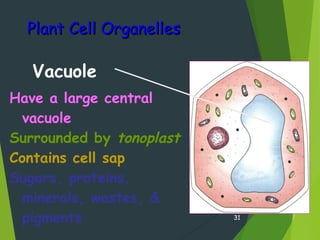
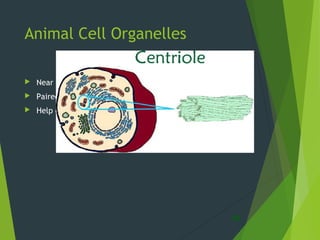
- Key cellular structures include the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, and in plant cells, a cell wall. Organelles such as