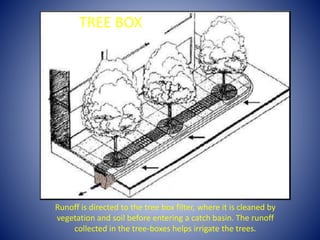
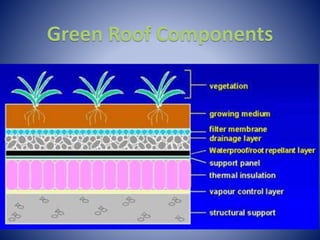
Low Impact Development (LID) techniques like rain barrels, cisterns, rain gardens, tree box filters, permeable pavers, and green roofs can help improve water quality in Sarasota Bay by reducing stormwater runoff. The document discusses various LID strategies and their benefits, then describes how pollution from sources like farms, housing developments, factories, sewage treatment plants, and hazardous waste dumps can harm water quality and aquatic life. It outlines key water quality parameters like dissolved oxygen, temperature, turbidity, phosphate, nitrate, and pH and explains how a fish named Fred is affected as he encounters pollution while swimming down a river.