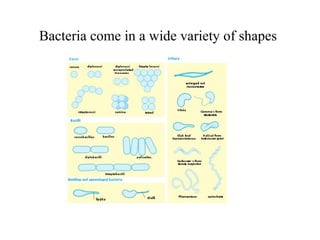
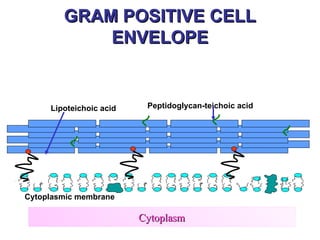
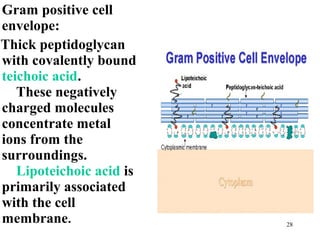
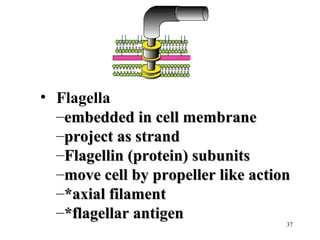
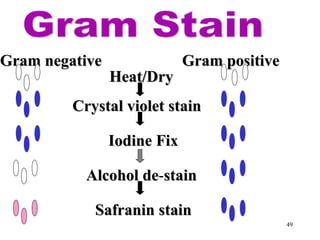
Bacteria have a simple but well-developed cell structure that allows them to survive and carry out essential functions. The three main components of the bacterial cell are the cell envelope, cell membrane, and cytoplasm. The cell envelope provides structure and protection, and its composition differs between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Within the cell are additional structures that carry out key roles such as protein synthesis, DNA replication, and nutrient storage and transport. Some bacteria also possess non-essential structures like flagella, pili, and capsules that contribute to motility, adhesion, and virulence.