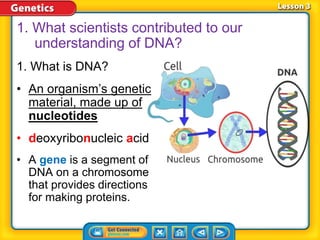
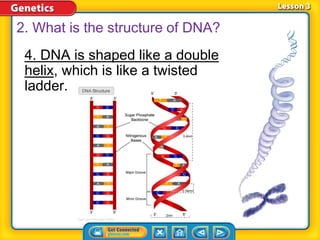
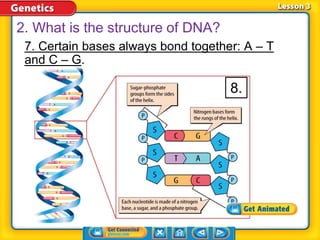
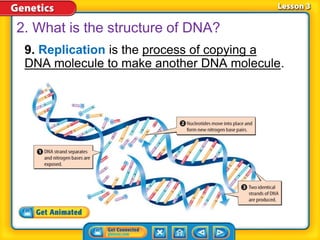
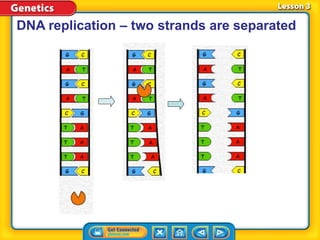
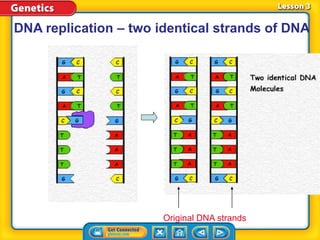
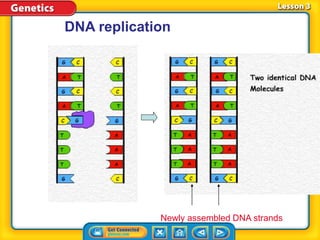
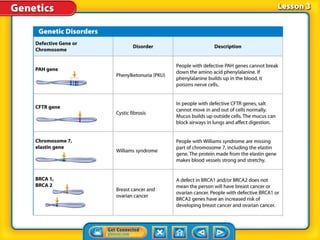
Rosalind Franklin, Maurice Wilkins, and Erwin Chargaff contributed to understanding DNA structure through X-ray diffraction and composition studies. James Watson and Francis Crick determined that DNA has a double helix structure with adenine bonding with thymine and cytosine bonding with guanine. DNA replication is the process where the DNA double helix unwinds and each strand acts as a template to produce two identical DNA molecules. Mutations can occur through insertion, deletion, or substitution of DNA bases and can affect organism traits, sometimes beneficially through increased disease resistance.