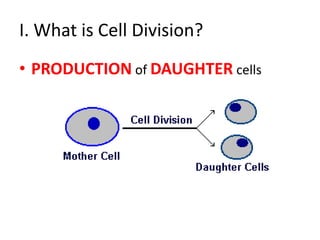
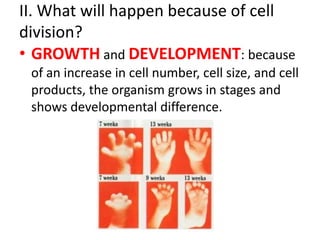
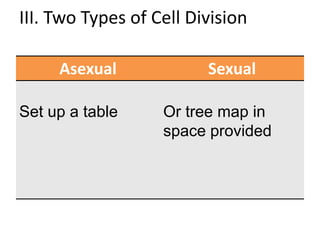
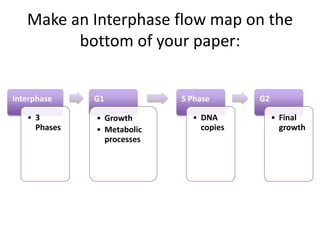
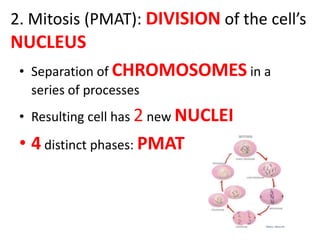
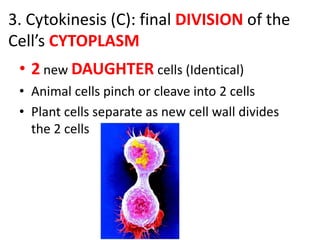
Cell reproduction occurs through cell division which produces daughter cells. There are two types of cell division: asexual and sexual. Asexual division produces two identical daughter cells through mitosis and occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, while sexual division involves meiosis and produces non-identical sperm and egg cells found only in eukaryotes. The cell cycle is the series of events cells undergo before and during cell division, consisting of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis phases.