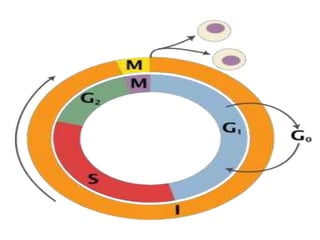
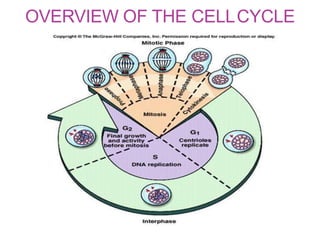
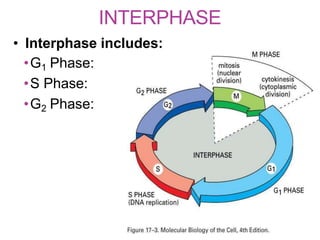
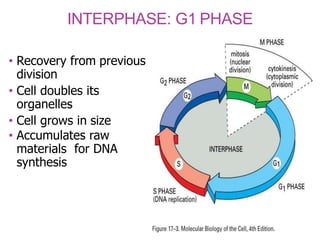
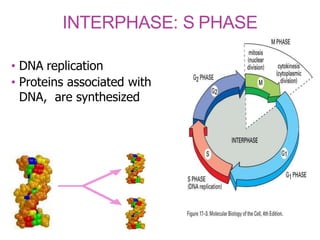
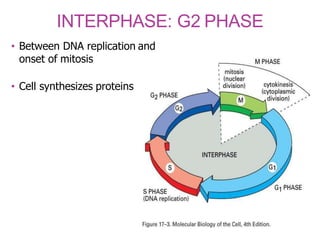
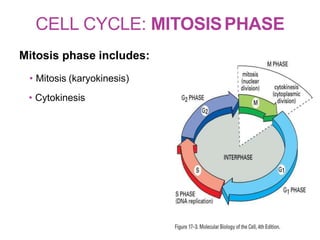
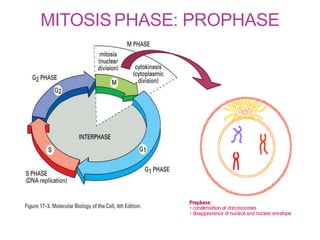
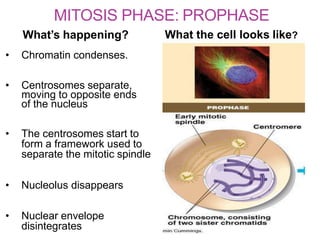
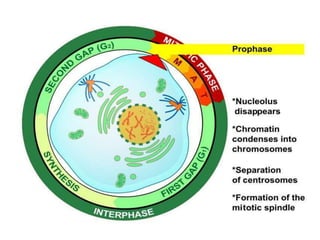
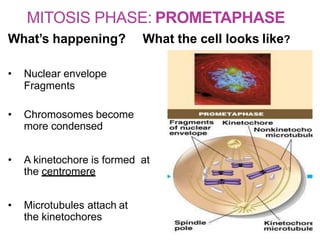
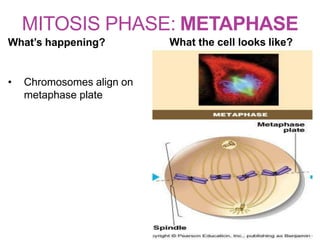
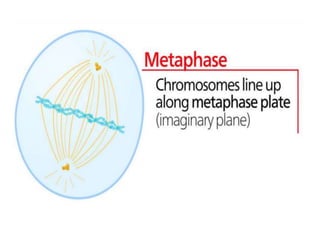
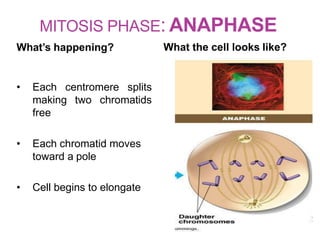
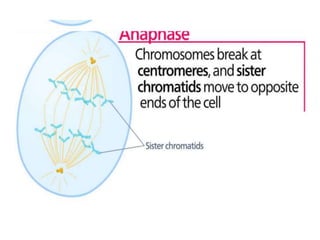
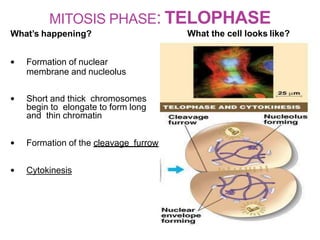
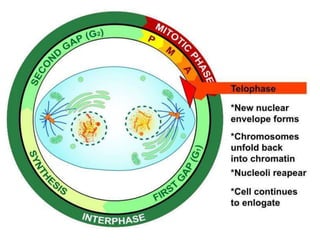
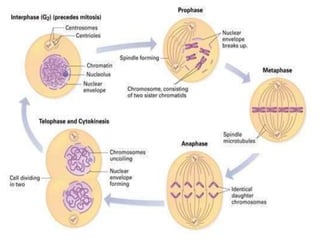
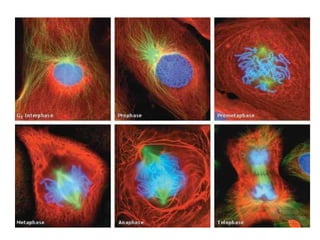
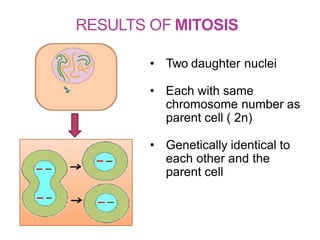
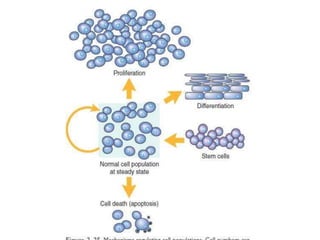
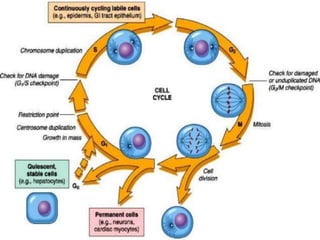
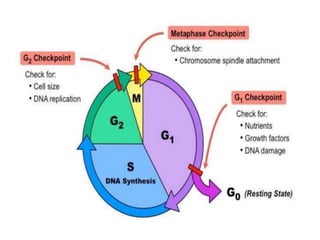
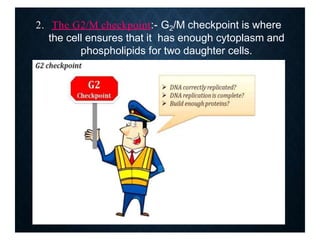
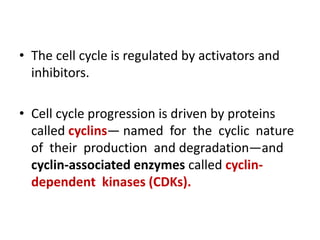
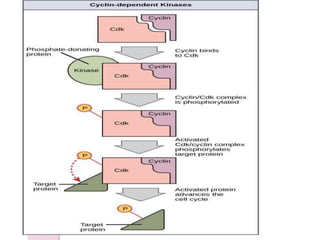
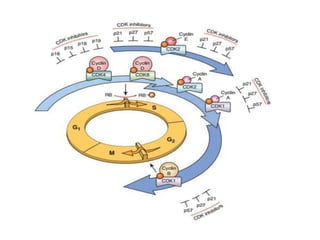
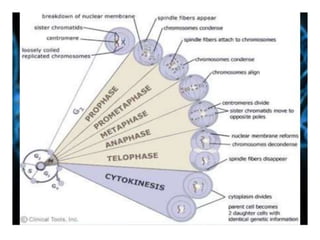
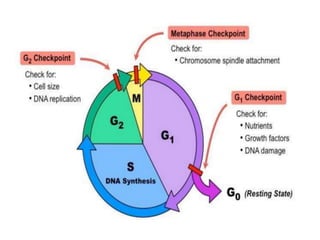
The document discusses the cell cycle and its phases. It begins with an introduction to the cell cycle and its importance in cell division and organism development. It then summarizes the main phases of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells: interphase consisting of G1, S, and G2 phases and the mitotic phase consisting of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis. Checkpoints ensure proper cell division and growth is regulated by cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases.