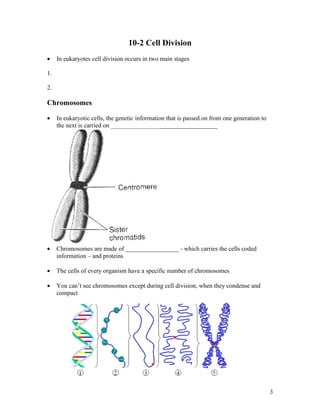
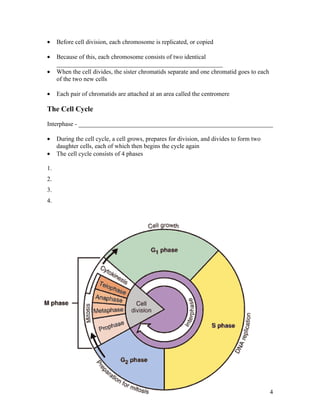
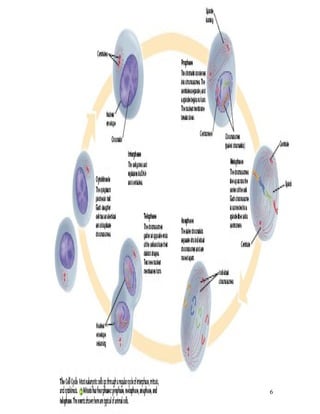
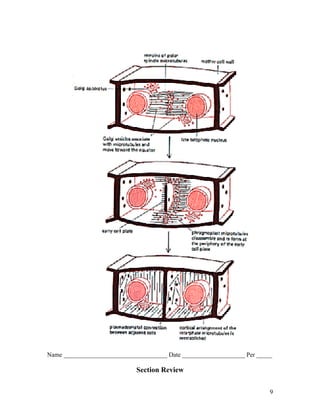
1. Cells normally divide through mitosis or cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells when they become too large. This prevents issues associated with excessive cell size.
2. The cell cycle is regulated by internal and external factors to ensure cells only grow and divide in an orderly fashion. Cancer occurs when cells lose control of their growth and divide uncontrollably.
3. Many cancers have defects in genes like p53 that normally halt cell division when growth conditions are not optimal. Understanding and fixing these regulatory pathways could help cure cancer.