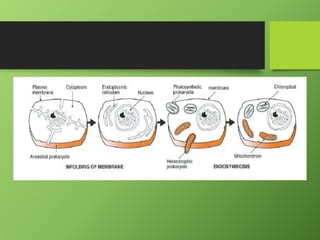
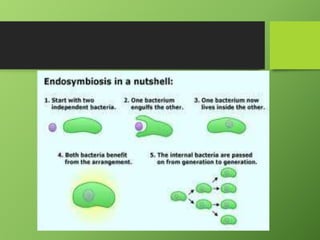
The earliest life on Earth were simple prokaryotic cells that existed around 3.5-3.9 billion years ago. These included stromatolites, primitive photosynthetic bacteria that formed along coastlines. As these prokaryotes became more widespread, they changed the atmosphere to include more oxygen. The first eukaryotic cells evolved around 2.1 billion years ago and included protists like protozoa and algae. Eukaryotic cells developed in two stages: infolding of the cell membrane to form internal structures like the nucleus, and endosymbiosis where mitochondria and chloroplasts originated from engulfed prokaryotic cells and became cellular organelles.