Embed presentation
Downloaded 98 times


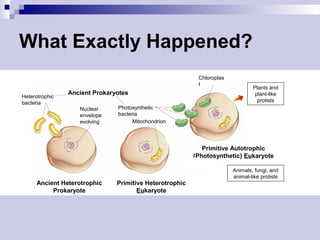

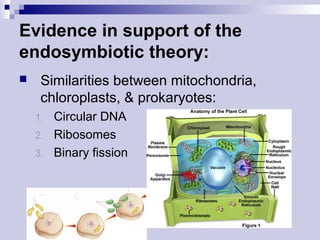


The endosymbiotic theory proposes that eukaryotic cells originated from prokaryotic cells engulfing other prokaryotic cells via endocytosis. Over time, the engulfed cells evolved into membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts. Evidence for this includes similarities between these organelles and prokaryotes like circular DNA, ribosomes, and binary fission. The theory was first proposed by Lynn Margulis and explains the origin of eukaryotic cells and certain organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts.





