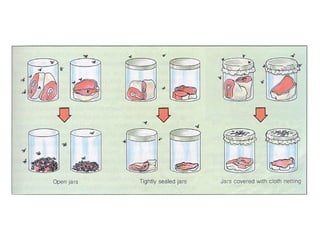
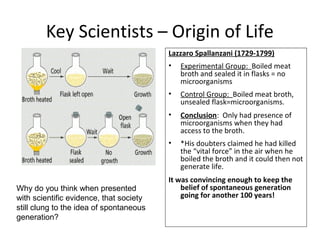
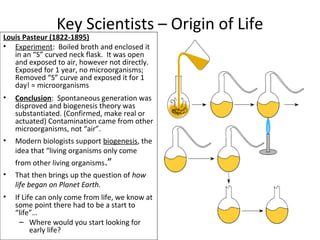
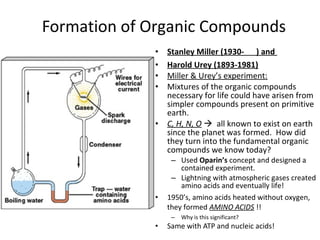
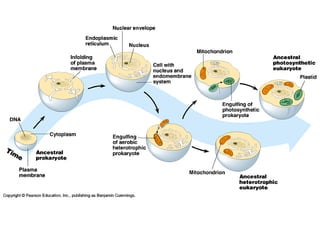
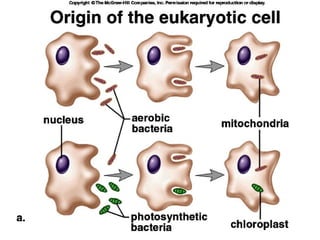
- Early theories proposed that life arose spontaneously from non-living matter, but experiments disproved this. Miller and Urey's experiment showed that amino acids could form from simple gases on the early Earth. Sidney Fox produced early cell-like structures called protocells and microspheres in experiments. Endosymbiotic theory proposes that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as internalized prokaryotes. Early life on Earth was likely anaerobic prokaryotic heterotrophs that evolved into autotrophs as organic compounds became scarce. Archaebacteria and cyanobacteria-like organisms were early photosynthetic life forms.