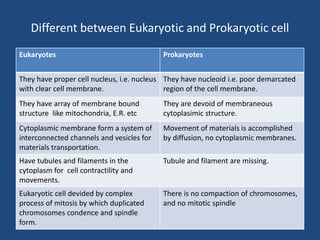
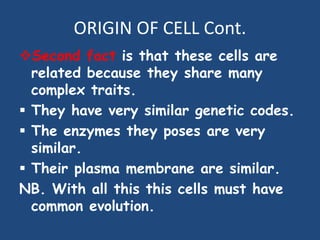
This document provides an overview of a course on cytology and cell physiology. It discusses the basic structure and functions of cells, including the evolution of the cell theory and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Theories on the origin of life and cells are presented, including the serial endosymbiosis theory. Characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are described. The document concludes with assessments for the course.