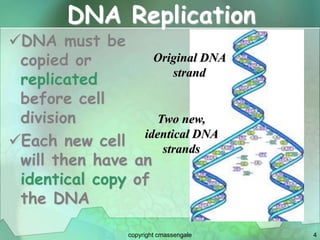
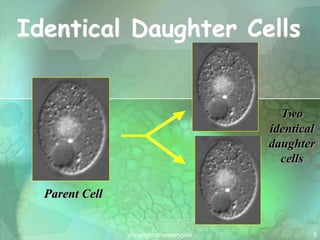
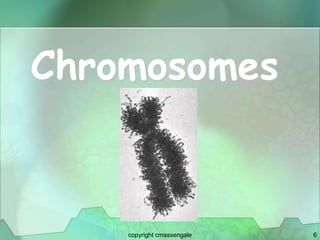
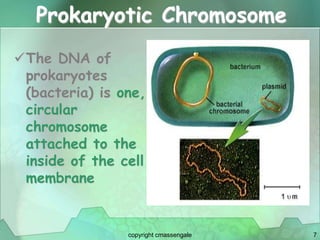
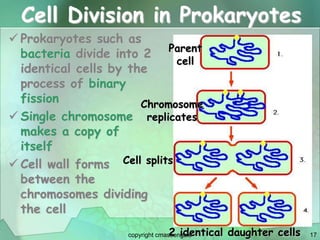
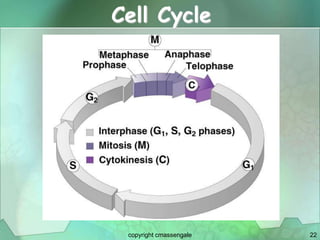
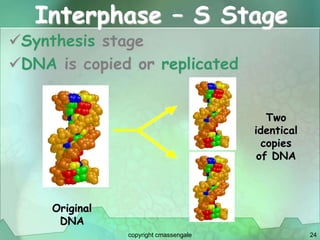
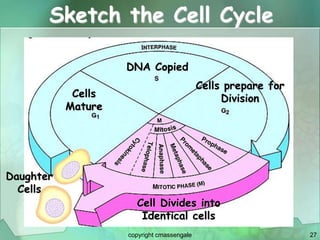
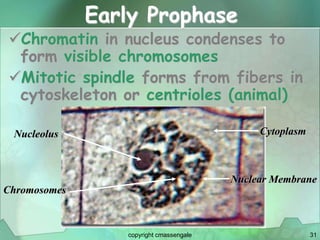
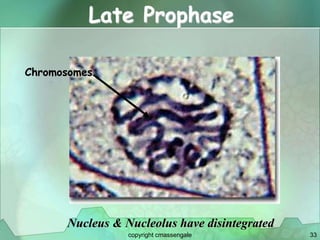
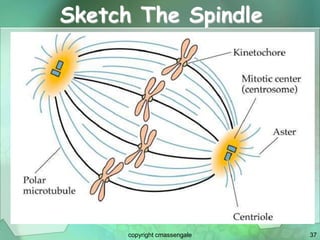
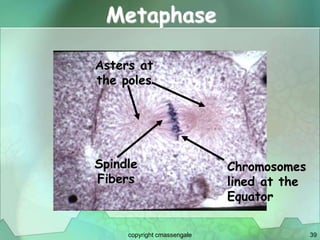
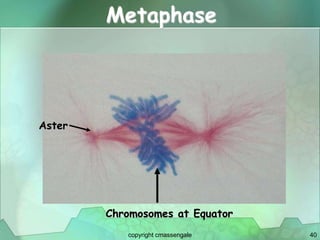
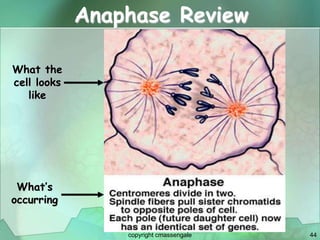
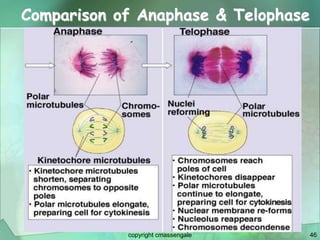
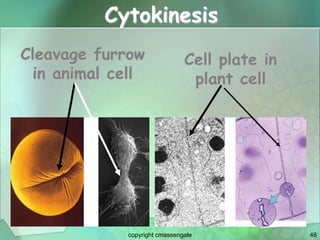
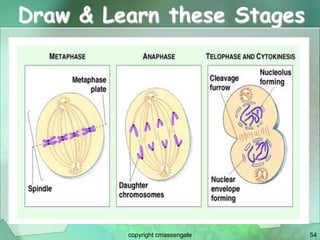
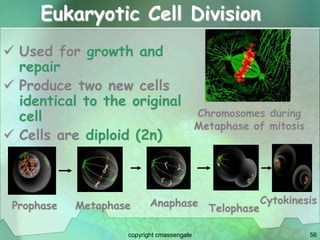
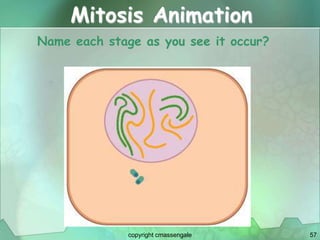
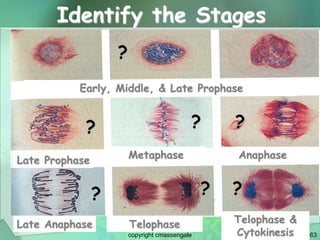
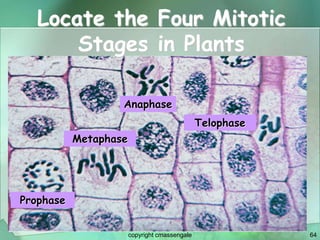
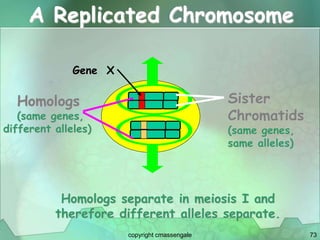
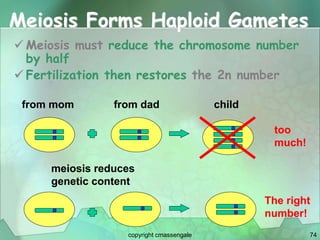
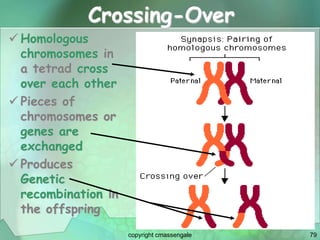
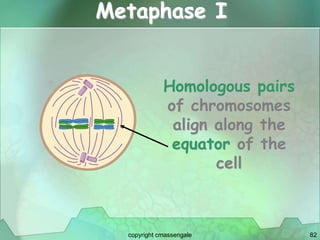
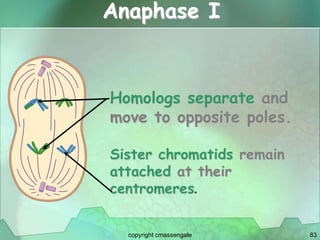
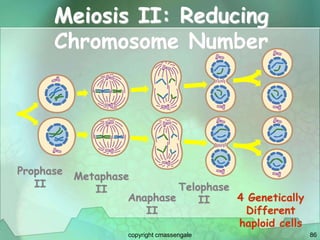
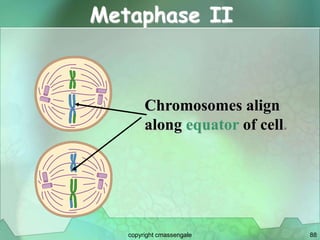
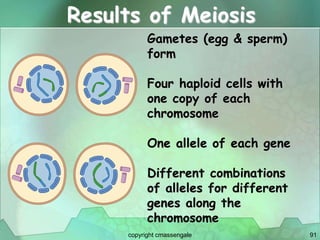
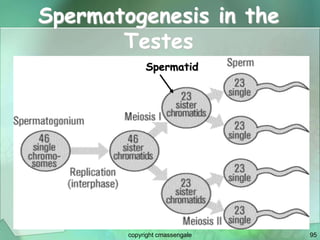
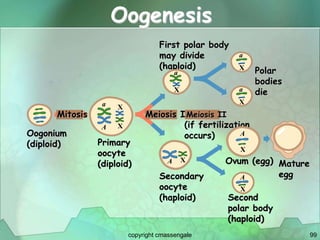
Cellular division involves the replication of DNA and division of the cell into two identical daughter cells. In eukaryotes, this occurs through the process of mitosis, which has four stages - prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Meiosis produces gametes like eggs and sperm through two cell divisions and results in four haploid cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. This ensures fertilization can restore the full chromosome number in offspring.