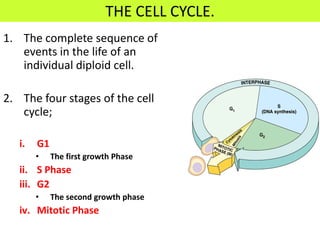
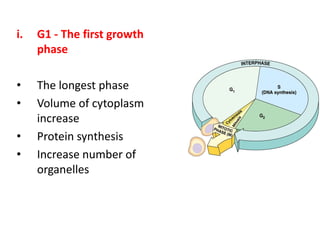
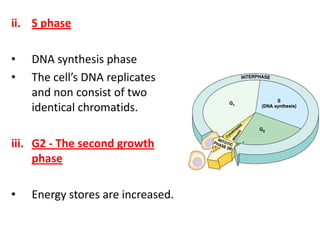
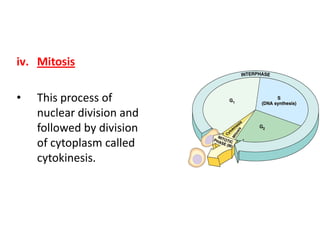
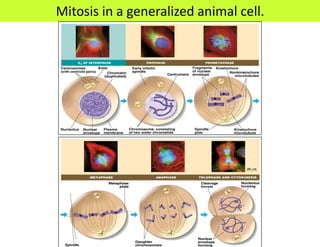
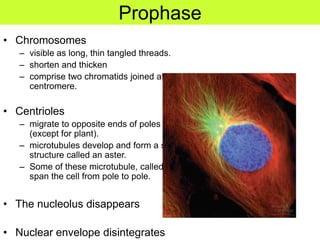
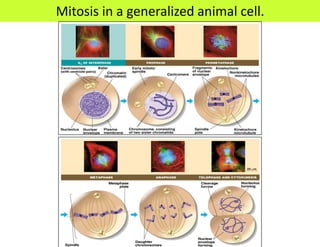
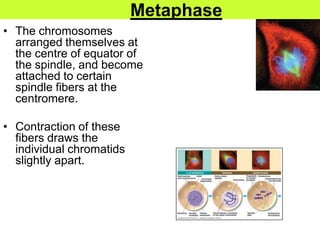
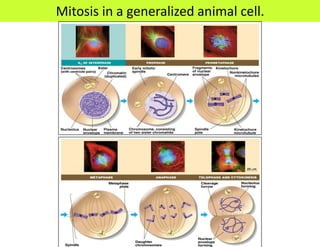
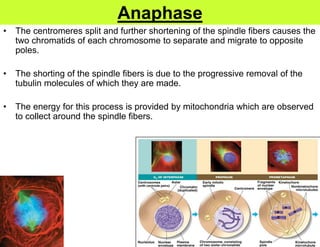
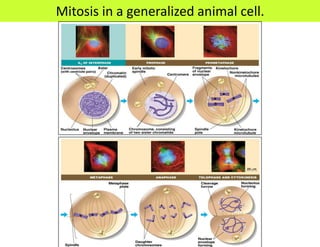
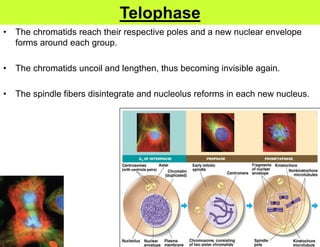
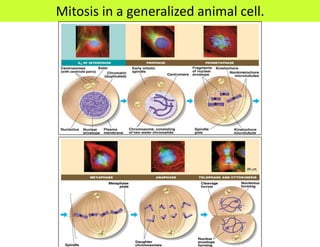
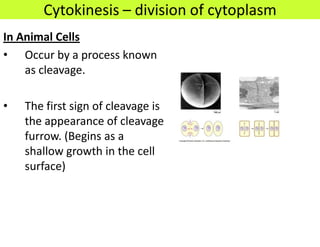
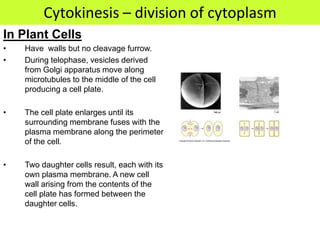
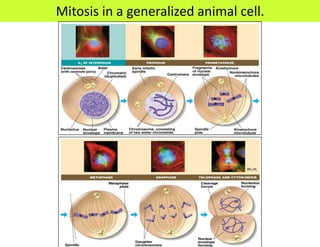
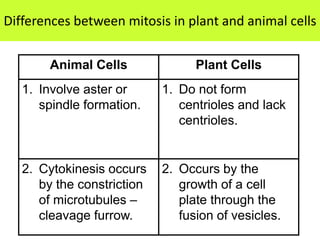
This document defines key terms related to cell division and DNA, describes the main stages of the cell cycle and mitosis, and explains the significance of mitosis. It states that mitosis results in two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell, ensuring genetic stability. It occurs in two phases: nuclear division and cytoplasm division. The four stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Cytokinesis then divides the cytoplasm through cleavage or cell plate formation in animal and plant cells respectively.