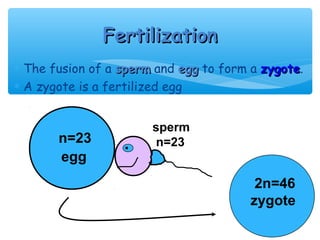
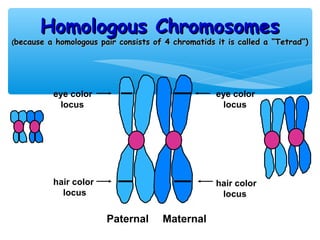
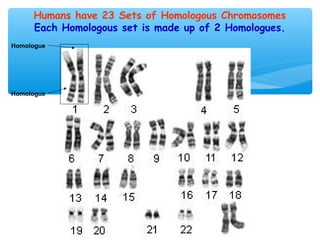
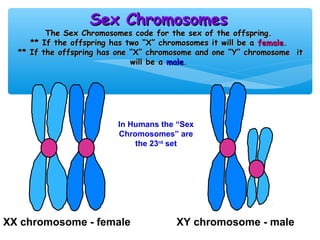
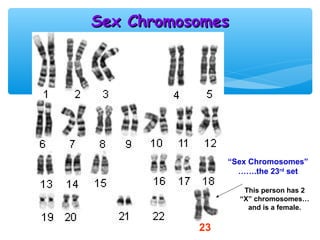
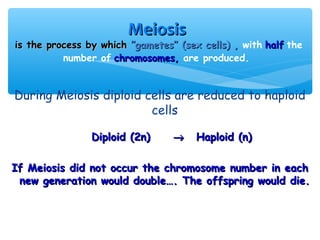
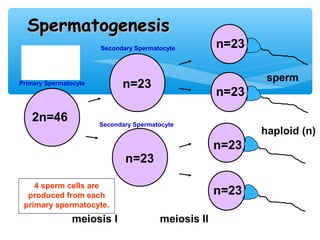
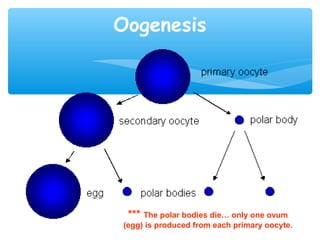
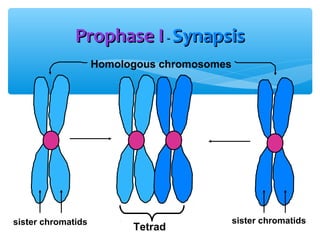
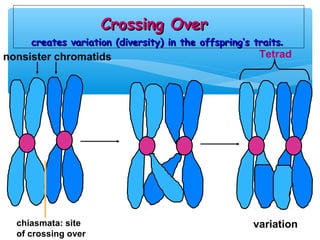
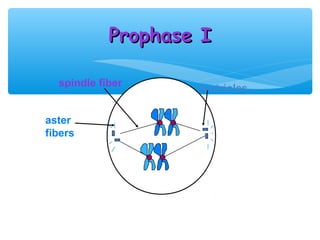
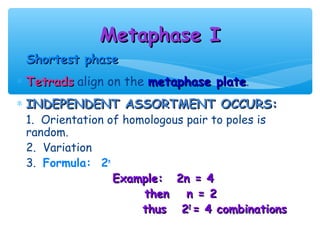
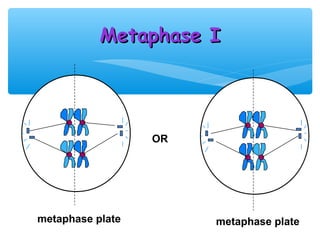
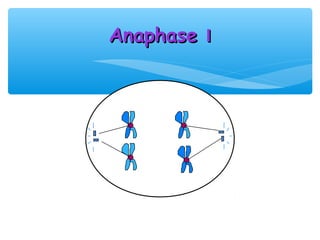
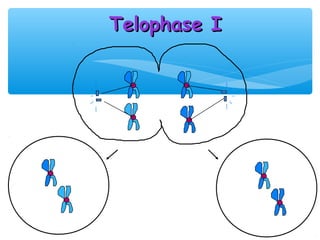
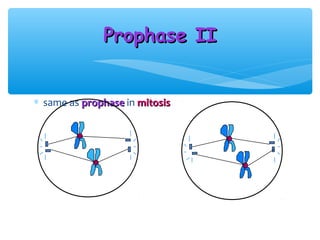
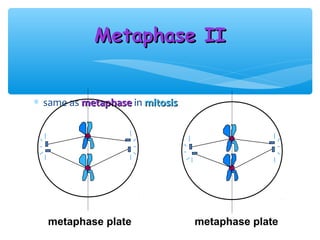
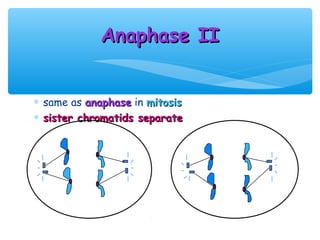
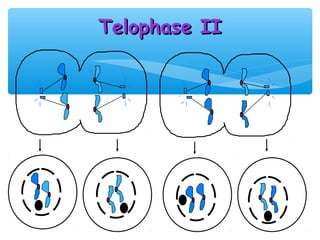
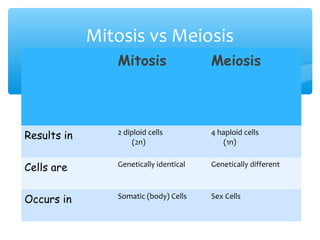
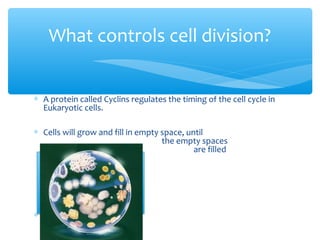
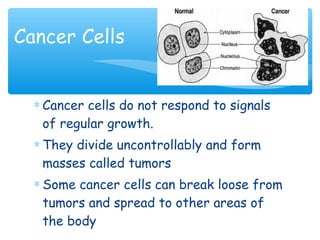
Meiosis is the process by which gametes are produced with half the normal number of chromosomes. During meiosis, diploid cells undergo two cell divisions to produce four haploid cells. The key events of meiosis include homologous chromosome pairing, crossing over between nonsister chromatids, and independent assortment of homologous chromosomes during metaphase I. This results in genetic variation among gametes and offspring.