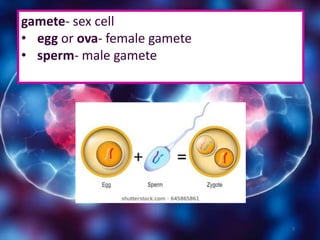
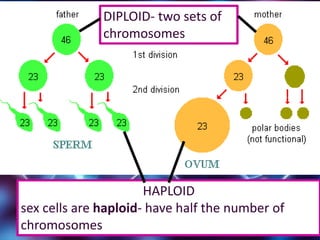
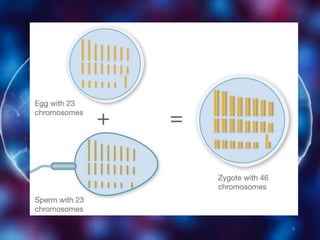
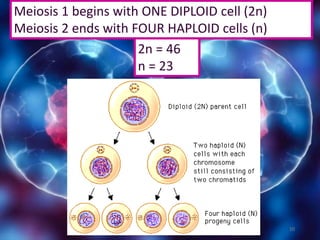
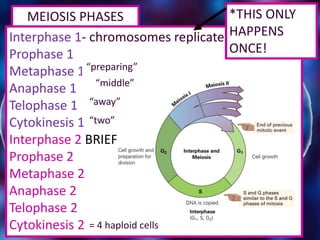
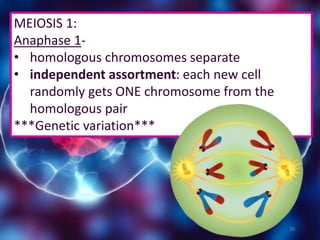
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces gametes or sex cells with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. It involves two divisions and results in four daughter cells each with a single set of chromosomes. This ensures that offspring will receive one set of chromosomes from each parent, maintaining the chromosome number from generation to generation. The key phases and events of meiosis include homologous chromosome pairing, crossing over, independent assortment of chromosomes into new cells, and two cell divisions that ultimately produce four haploid gametes.