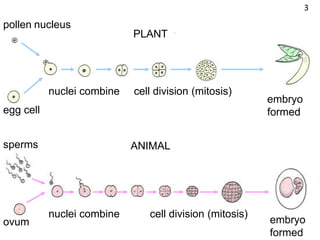
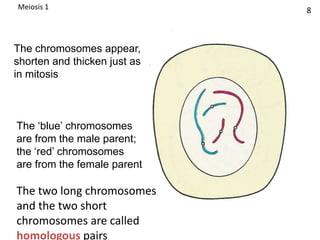
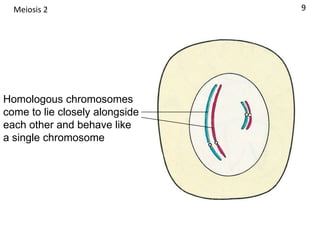
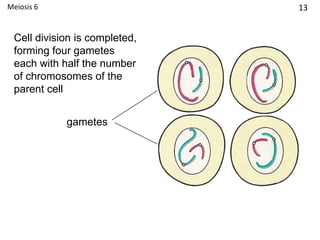
Meiosis is a type of cell division that results in gametes like sperm and egg cells, which have half the number of chromosomes as regular body cells. This ensures that when the gametes fuse during fertilization, the resulting zygote will have the normal chromosome number. Specifically, during meiosis the parent cell's chromosomes are divided into two daughter cells, reducing the number from 46 chromosomes to 23. Then a second round of division takes place, dividing the cells again and reducing the number to a total of 4 gametes each with 23 chromosomes. This ensures the zygote formed during fertilization has 46 chromosomes, the same as the parents.