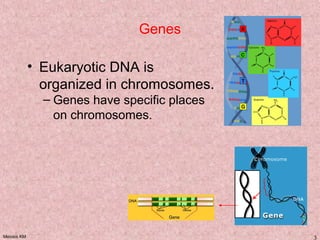
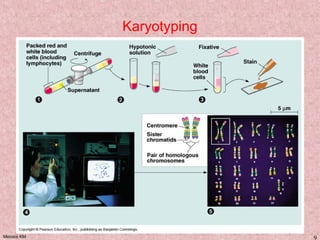
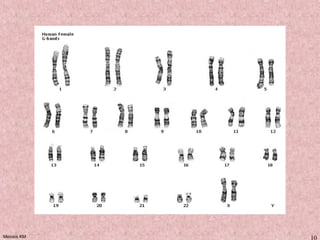
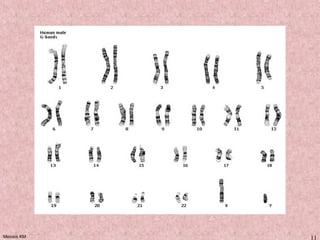
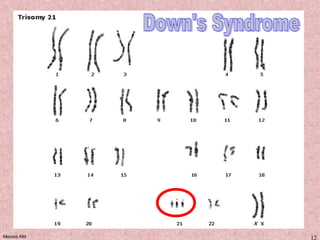
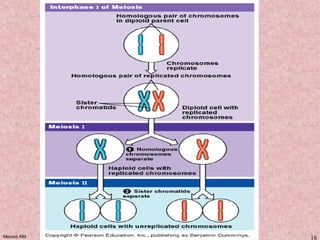
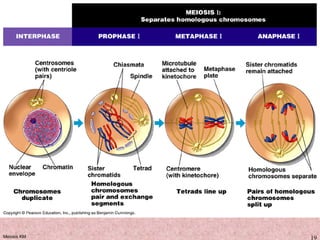
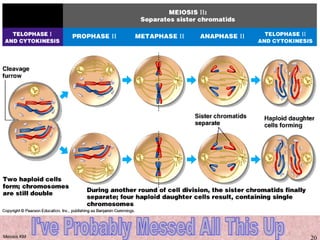
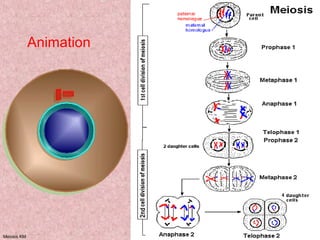
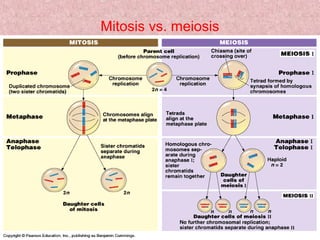
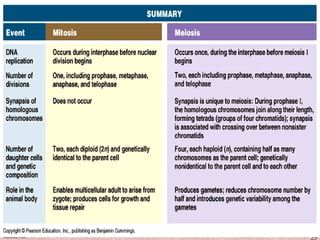
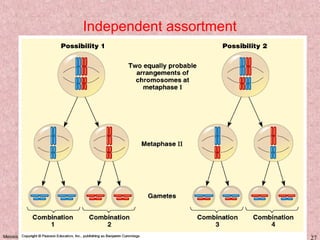
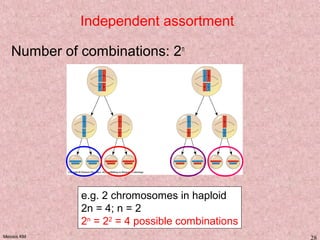
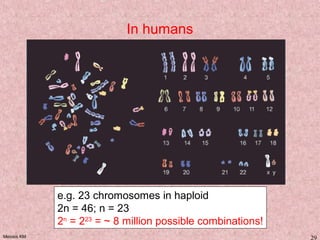
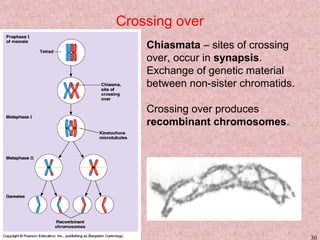
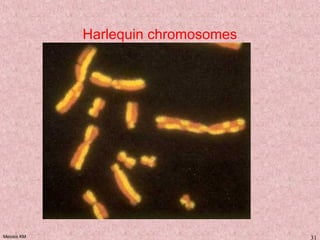
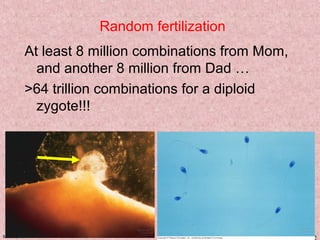
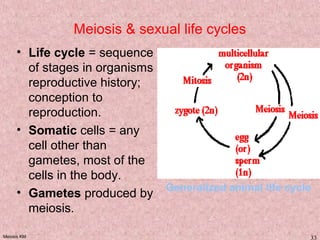
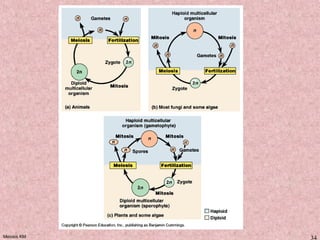
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces gametes, such as sperm and egg cells, with half the normal number of chromosomes. It involves two rounds of division instead of one, as in mitosis. The first division separates the homologous chromosome pairs, while the second divides the sister chromatids. This ensures the gametes have a single set of chromosomes and genetic variation is introduced through independent assortment and crossing over. Fusion of male and female gametes in fertilization restores the diploid number.