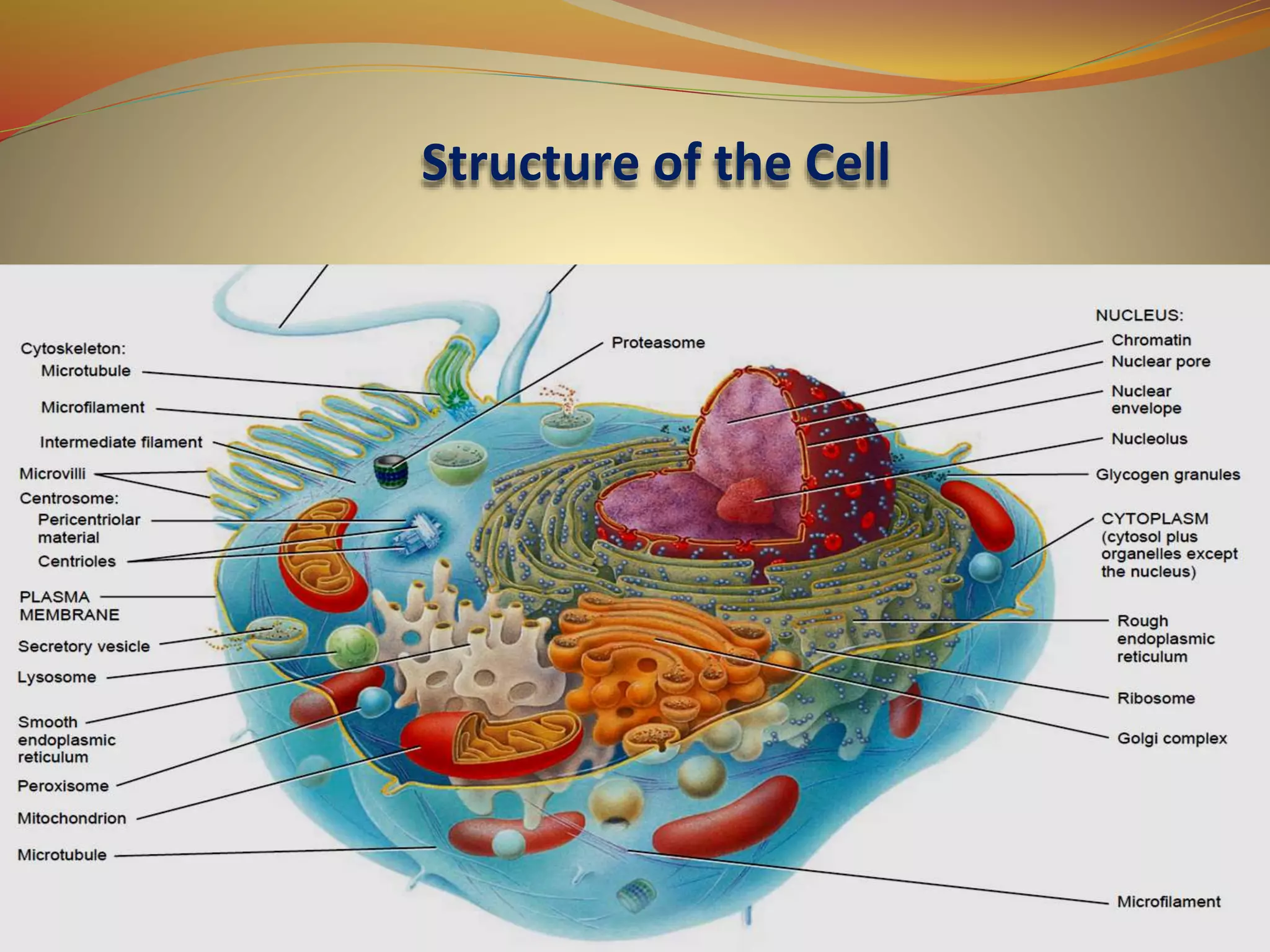
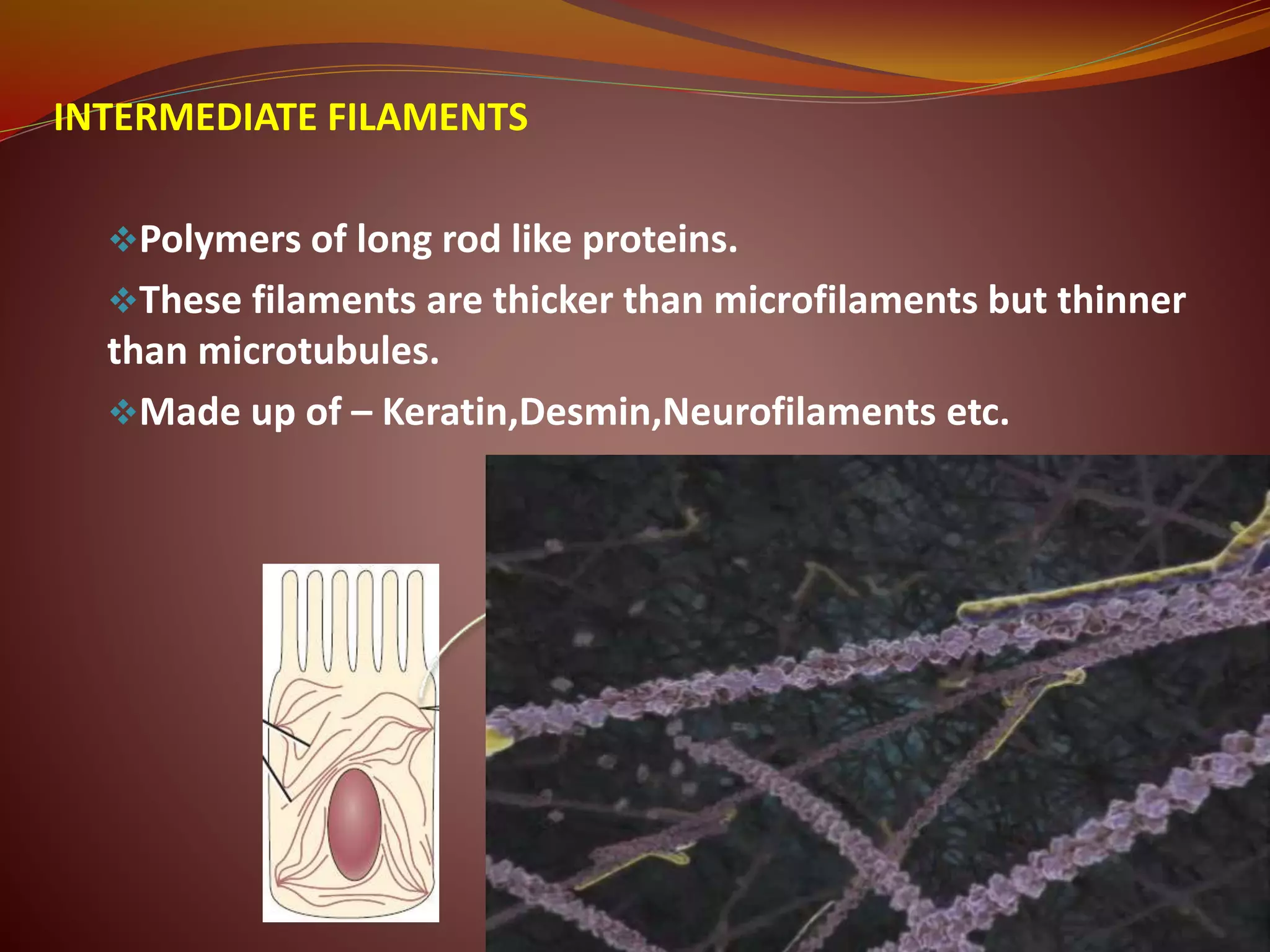
The document provides information on cell biology. It begins by defining the cell as the fundamental unit of life and describes the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It then discusses several organelles found within cells including the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, peroxisomes, cytosol, and cytoskeleton. It explains the structure and functions of the cell membrane, including the fluid mosaic model. Finally, it briefly outlines different mechanisms of transport across the cell membrane including passive transport, active transport, and bulk transport.
















































![Transport across Cell membrane
Uniport
Cotransport
Mechanisms –
Passive transport.
Simple diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Active transport.
Primary Active Transport
Secondary Active Transport
Bulk Transport [MACROMOLECULES]
Exocytosis.
Endocytosis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellbiology-140912042746-phpapp02/75/CELL-BIOLOGY-51-2048.jpg)





















