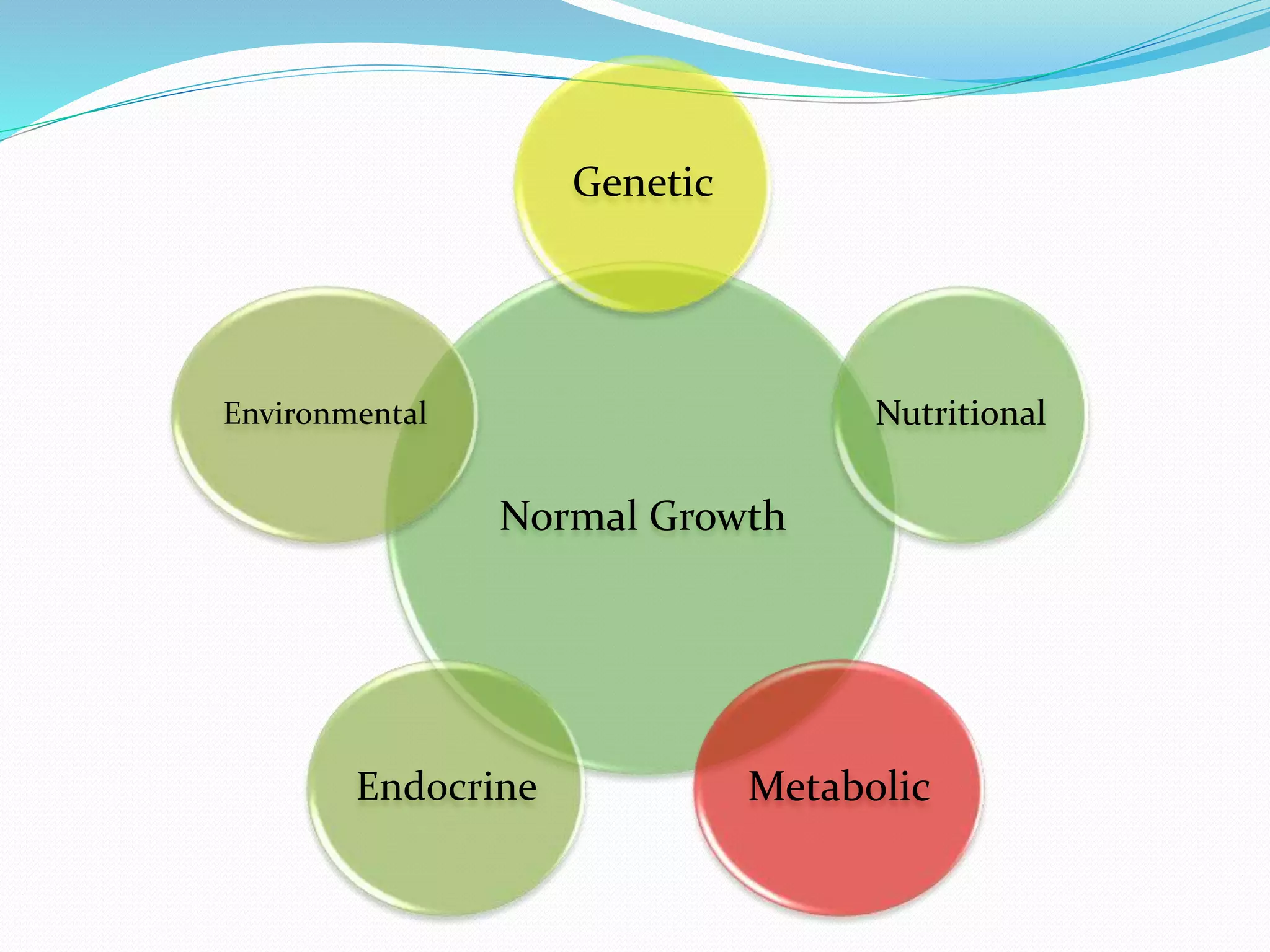
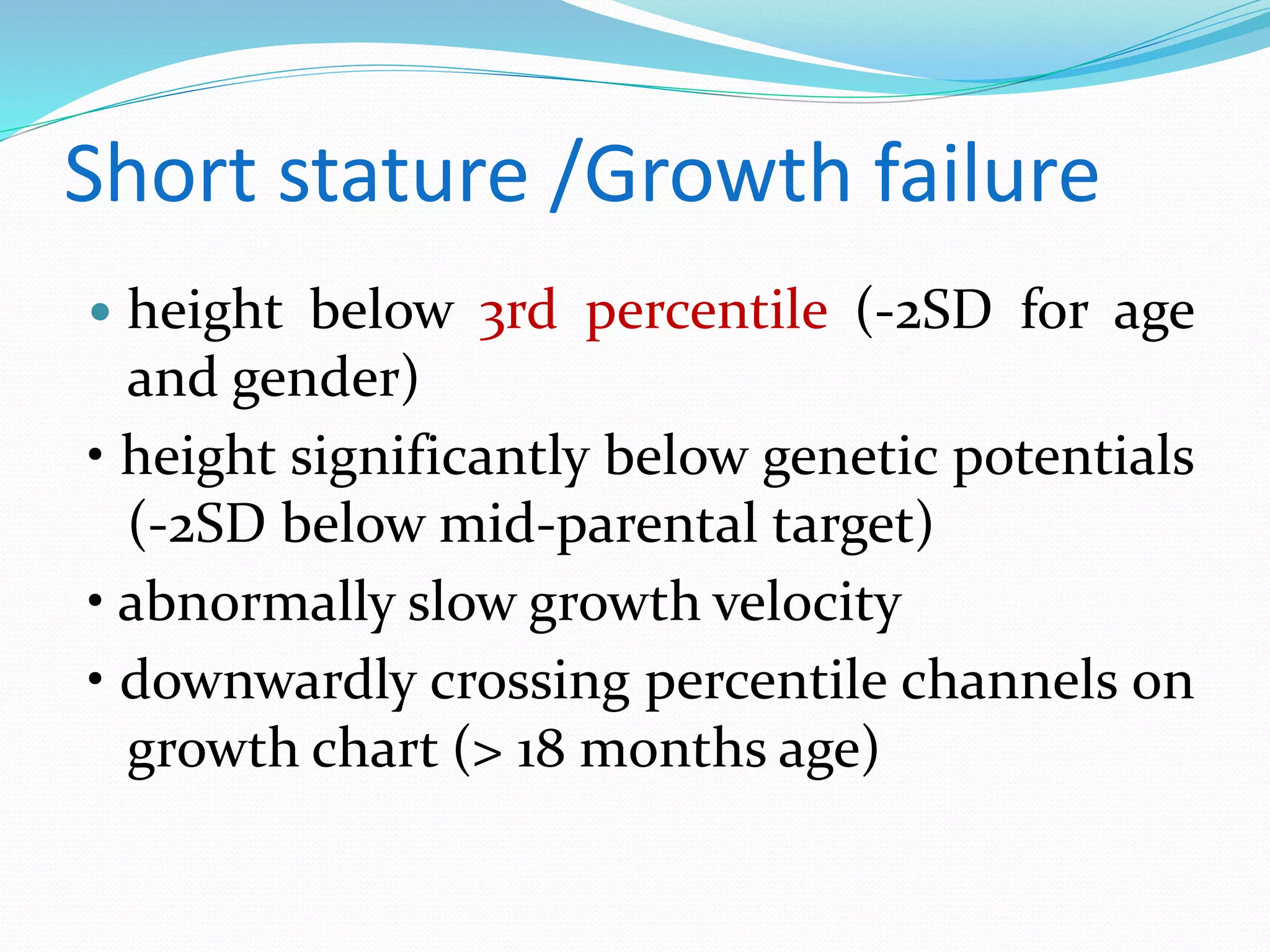
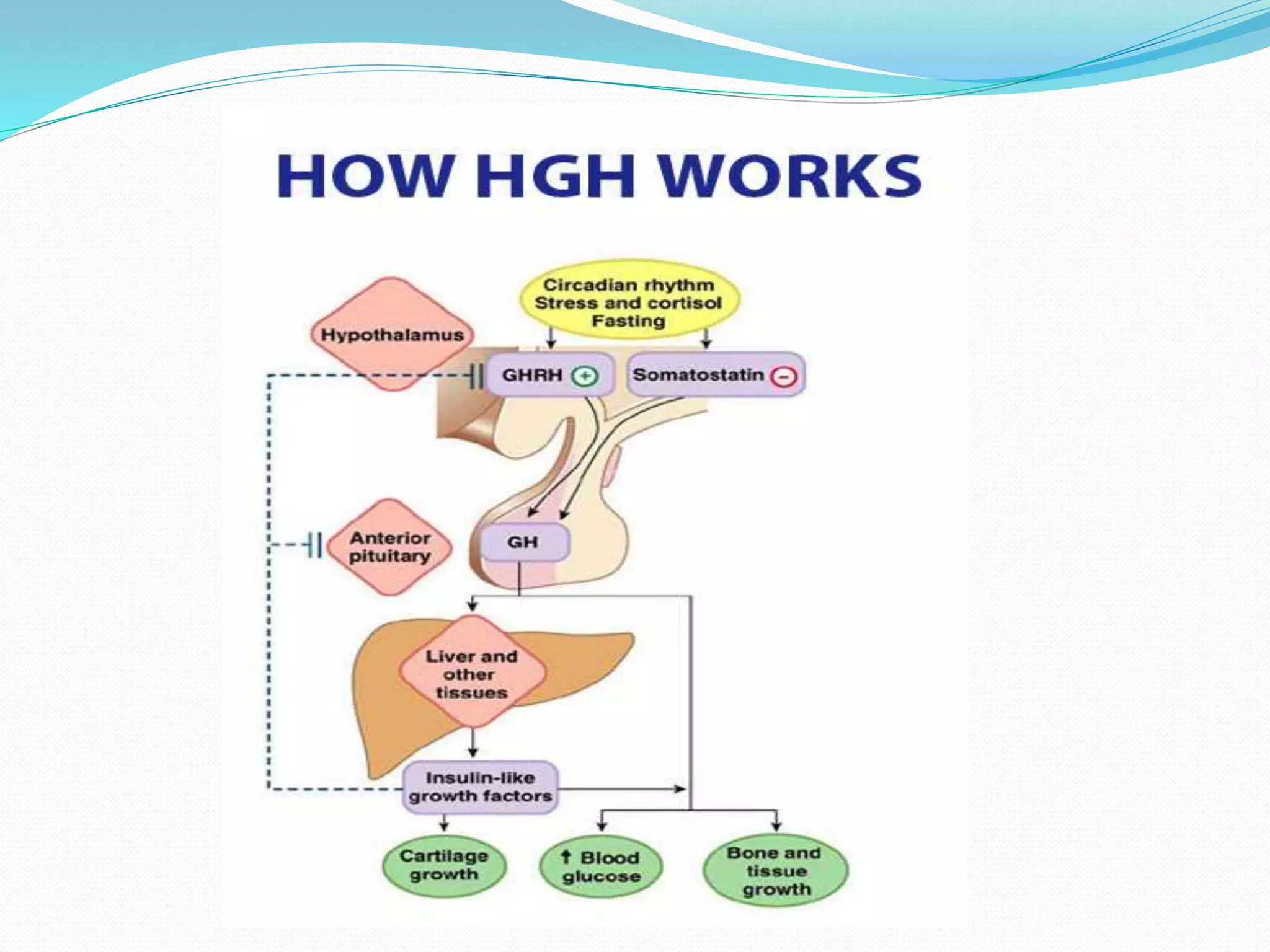
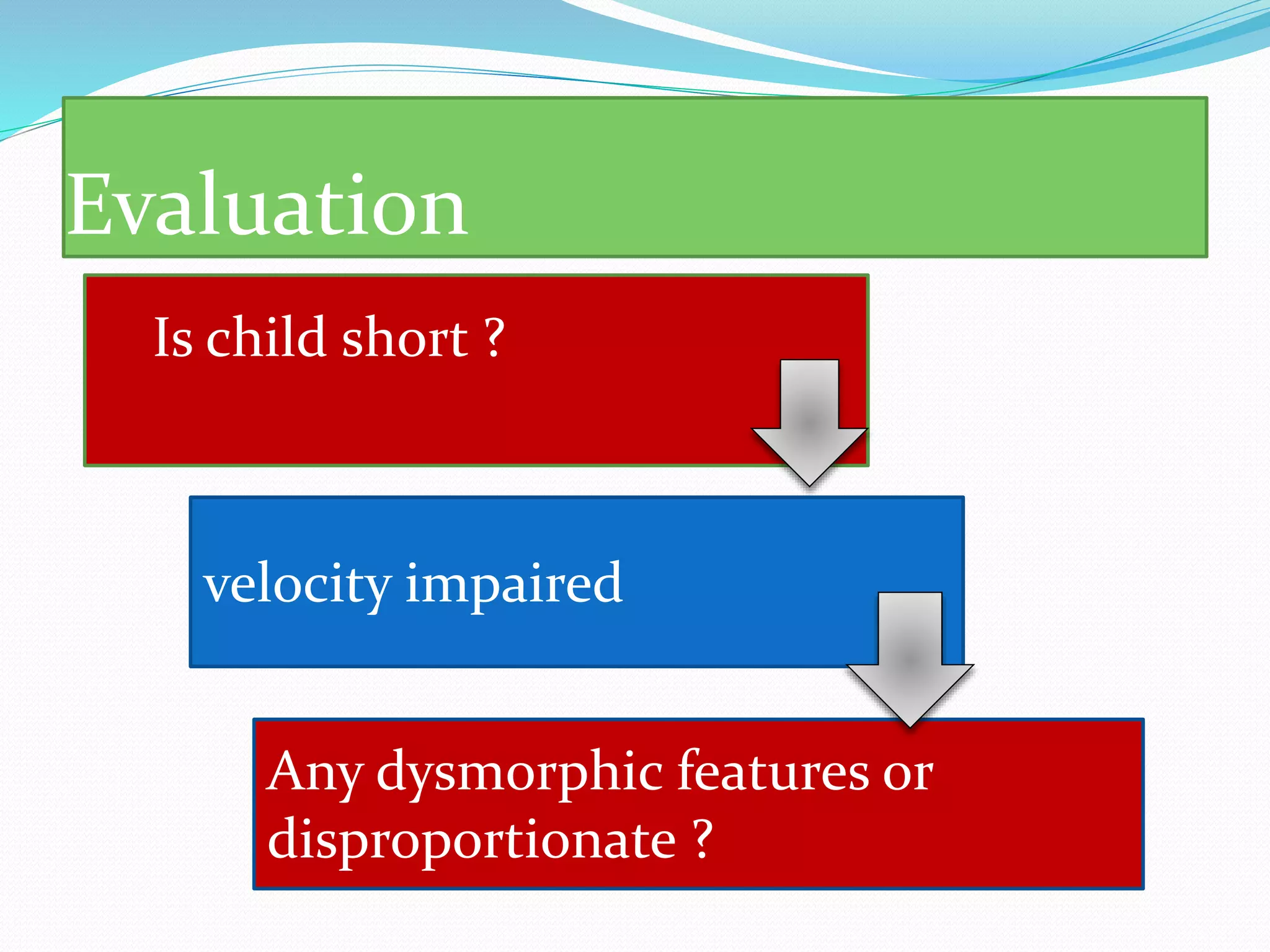
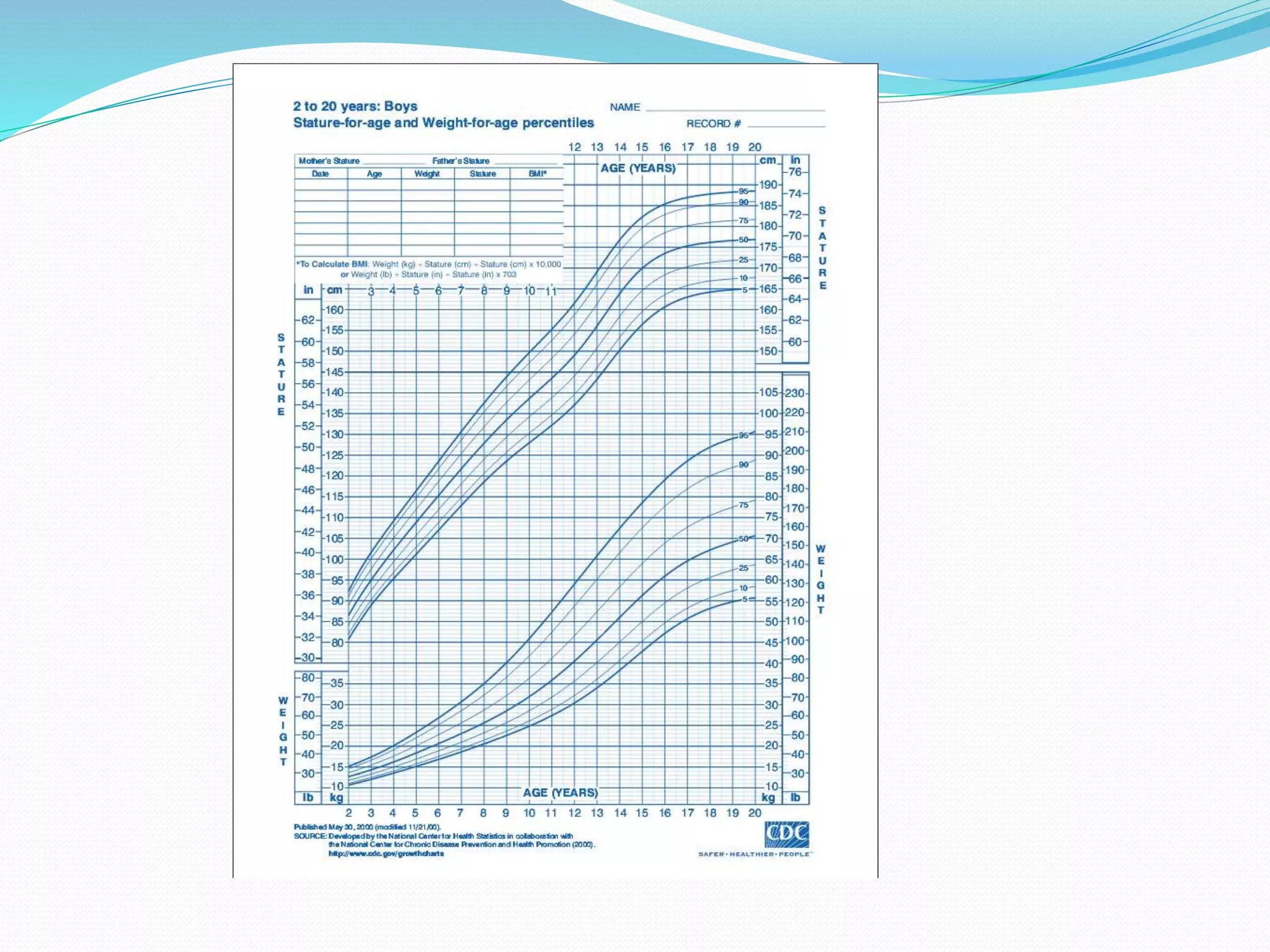
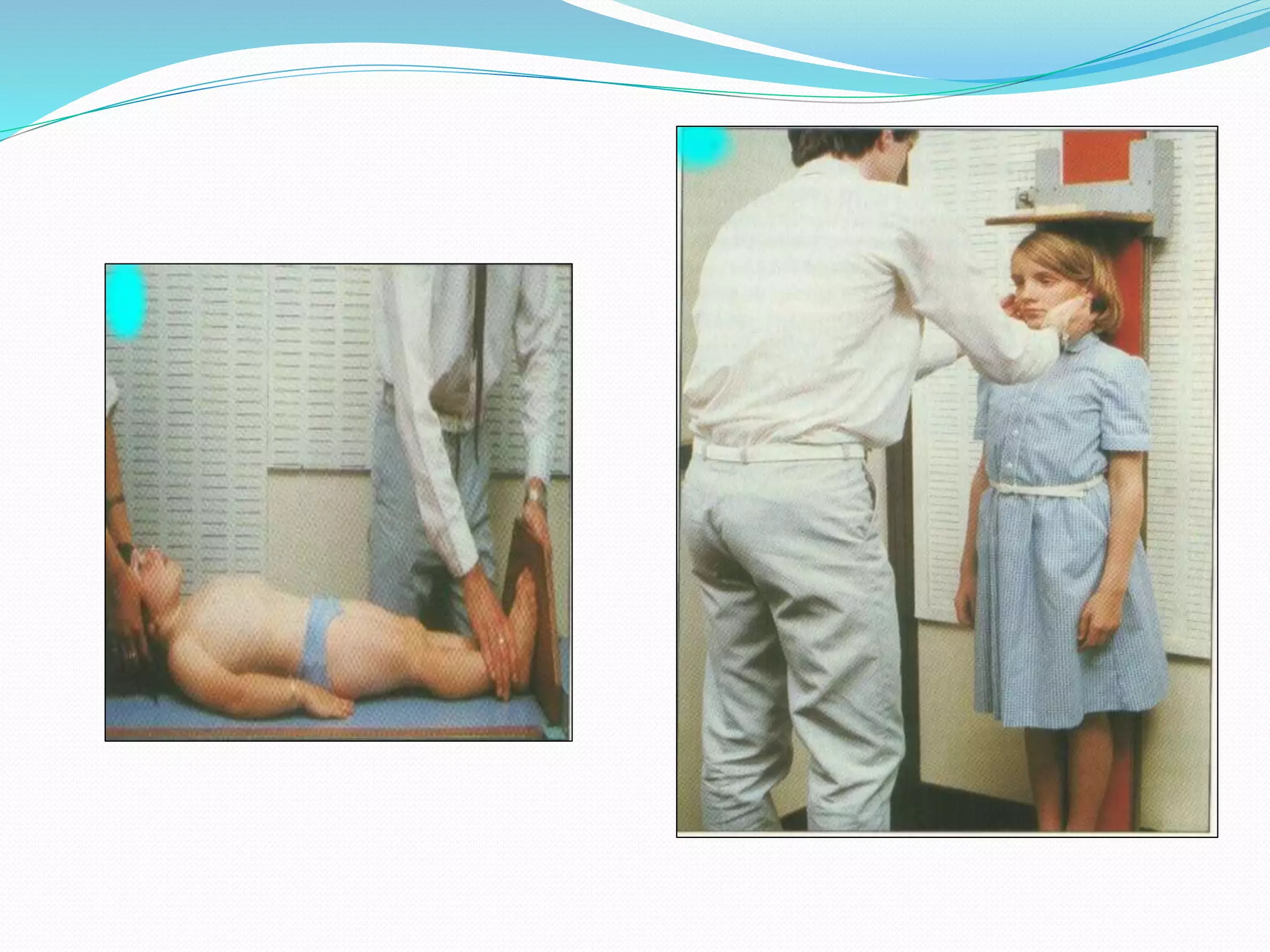
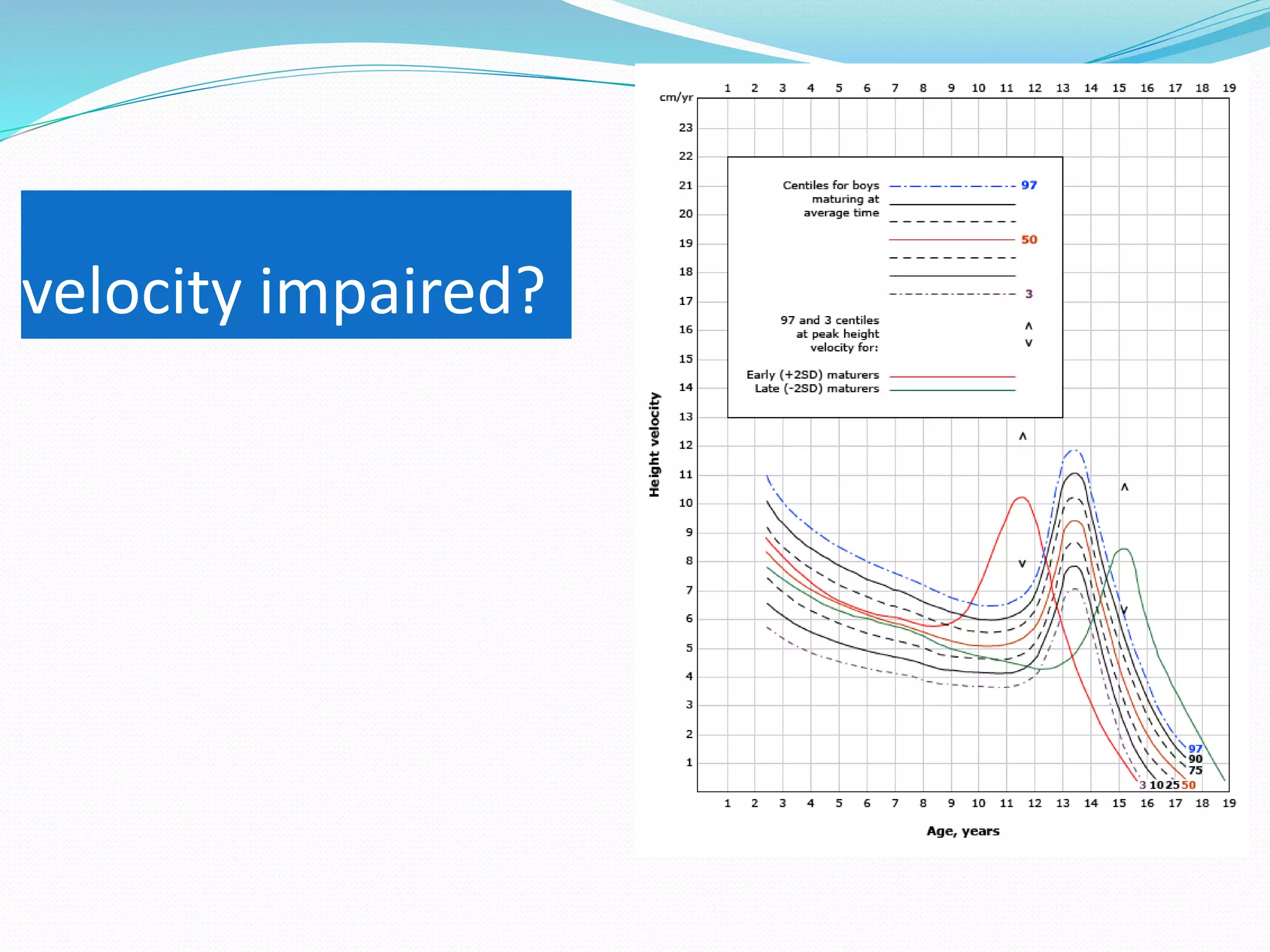
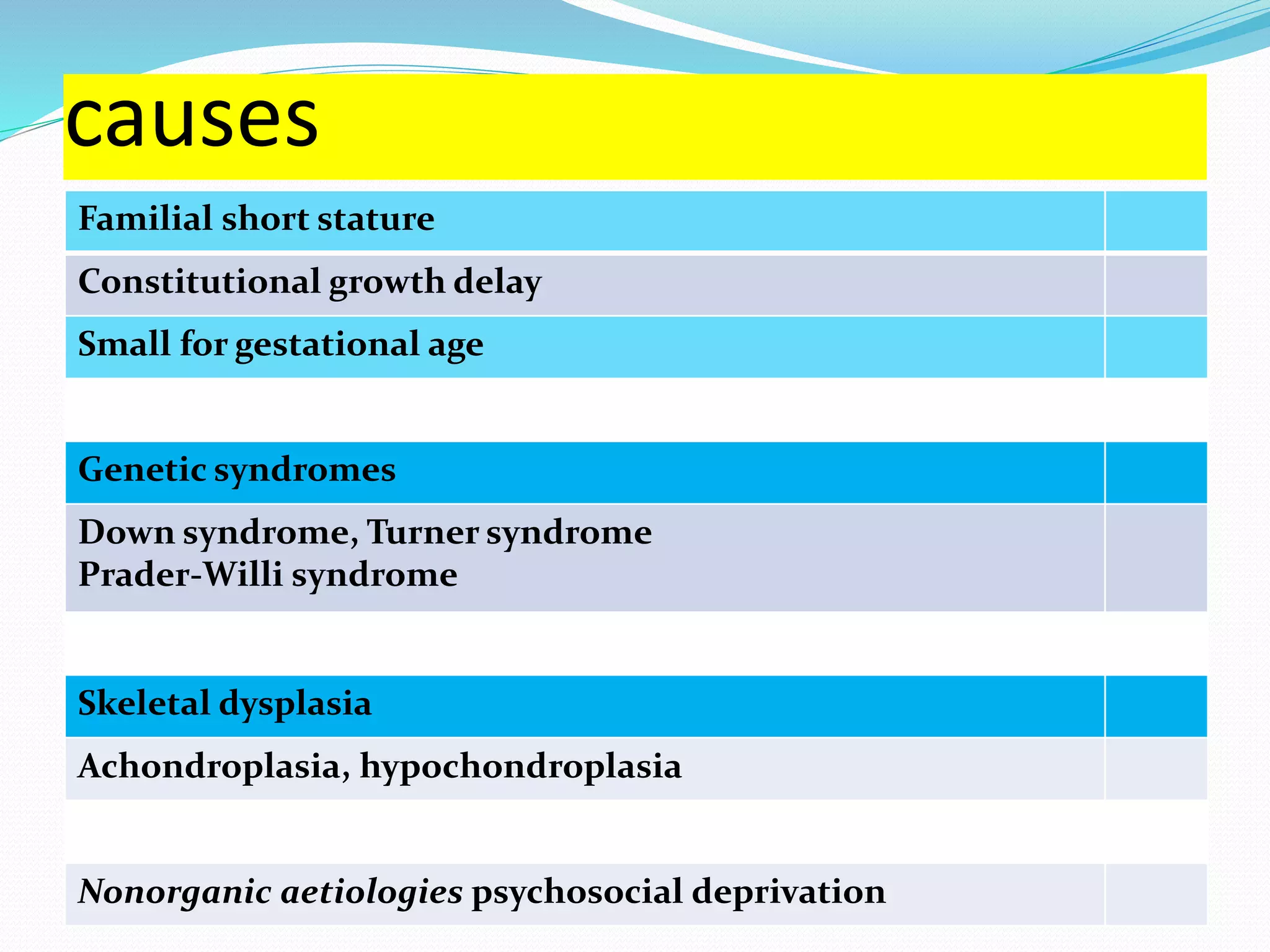
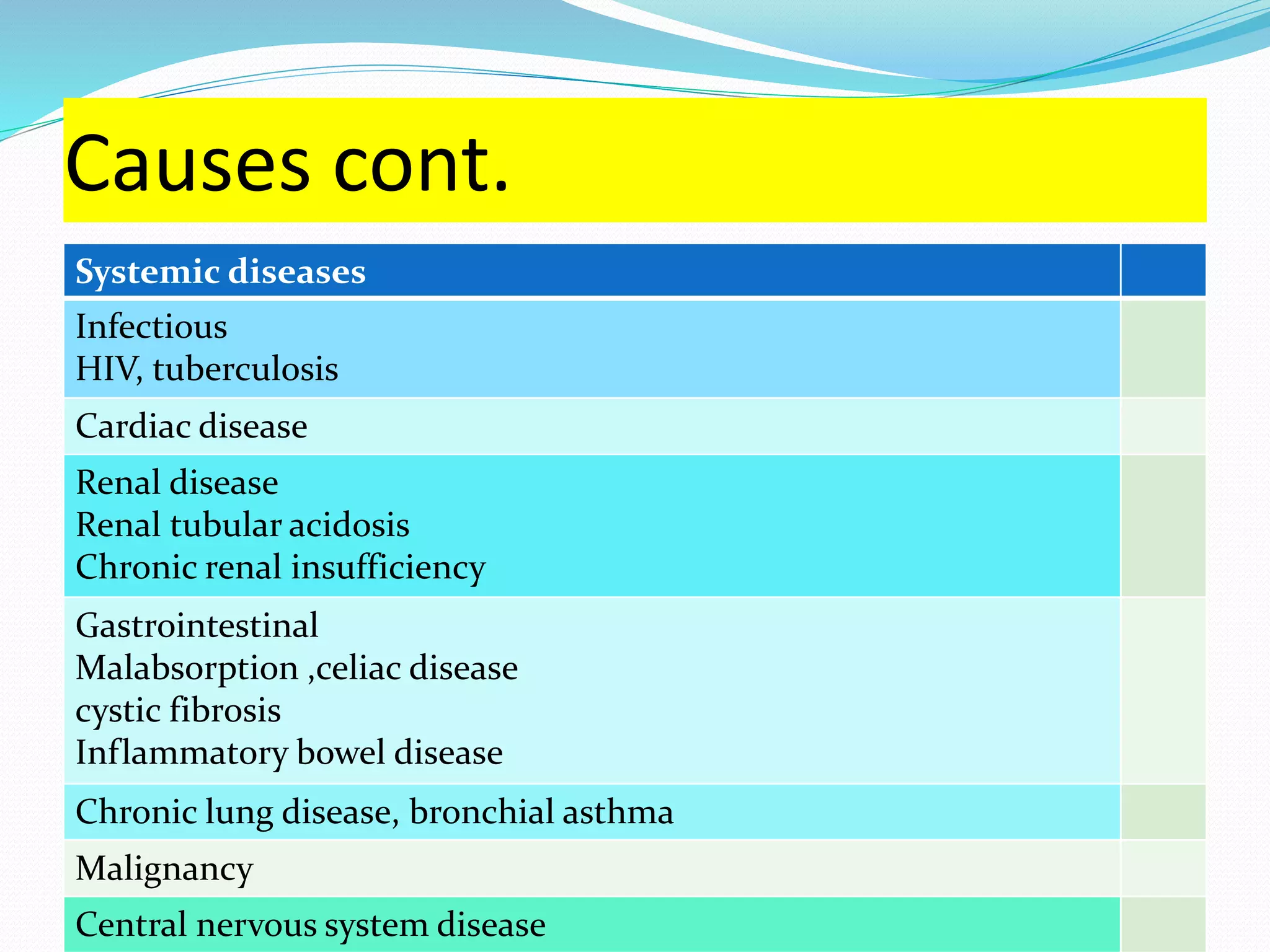
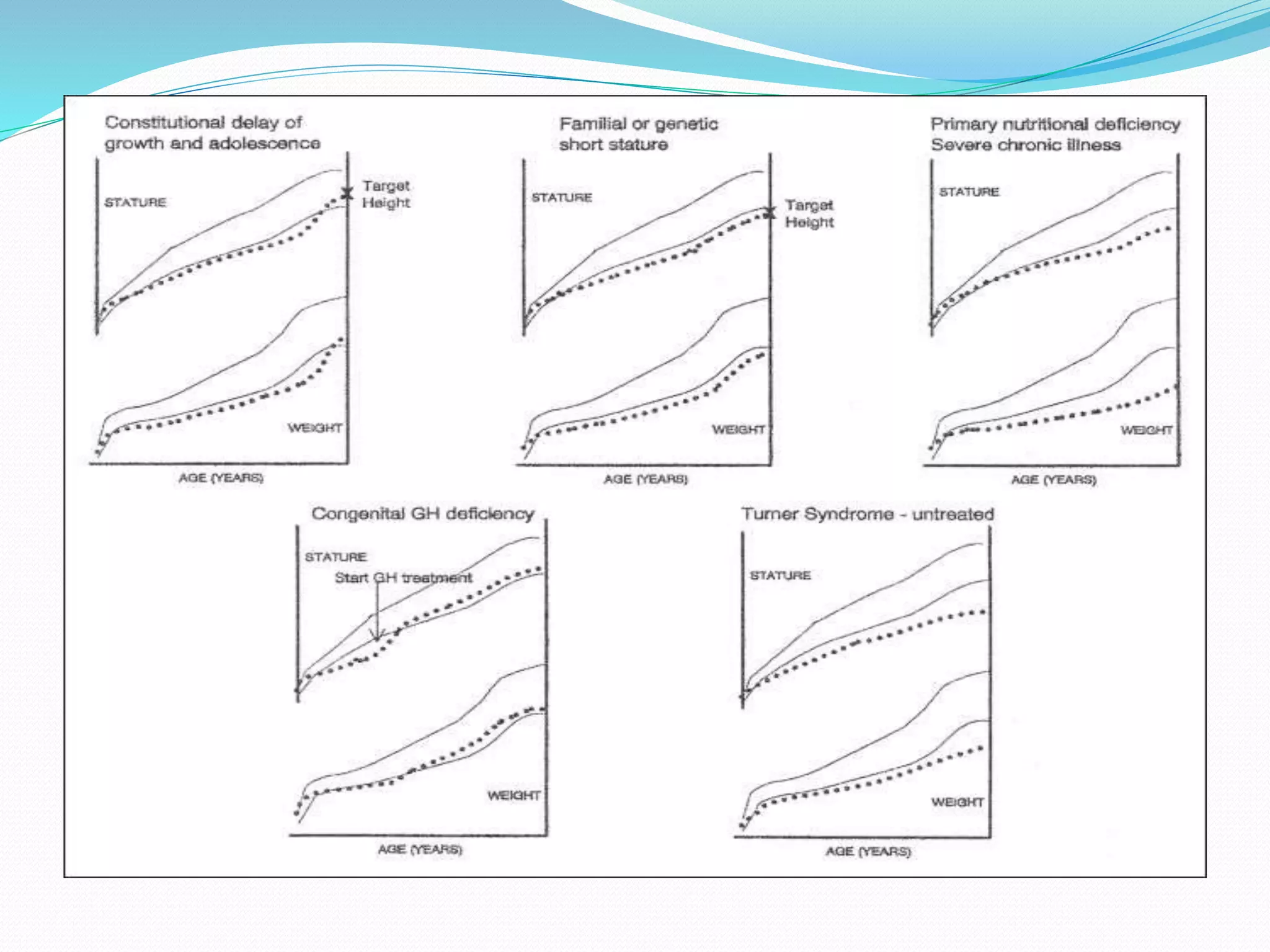
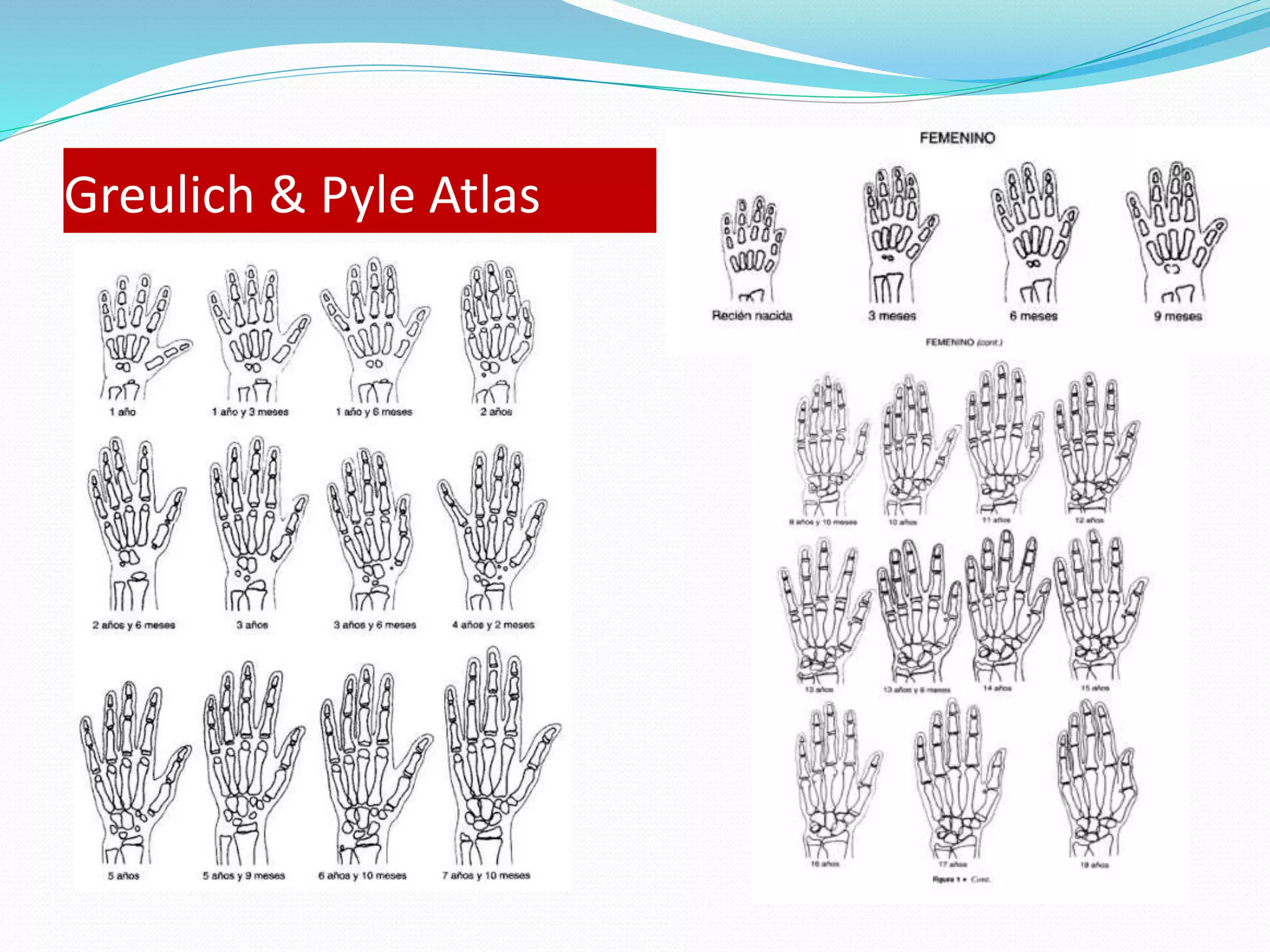
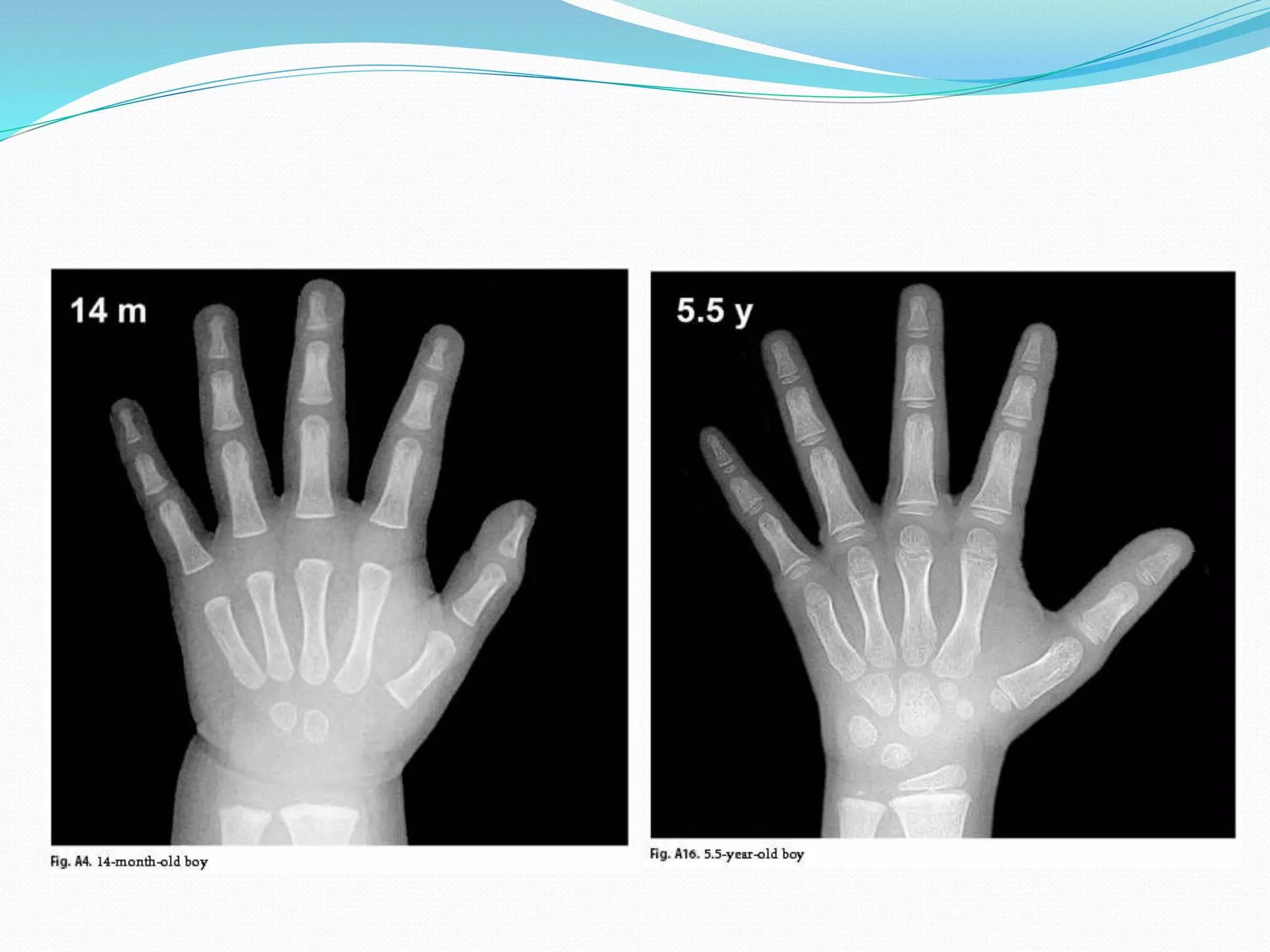
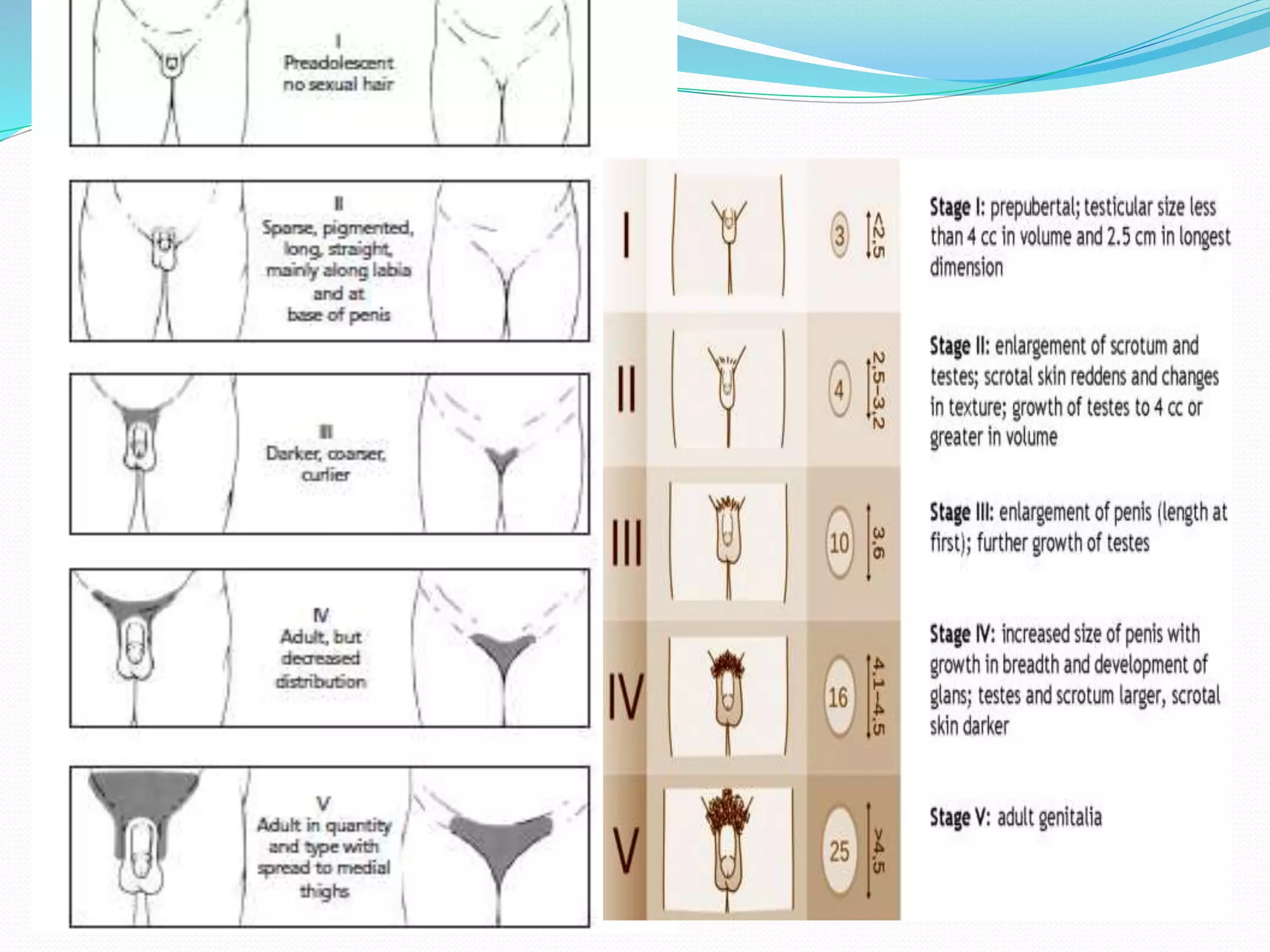
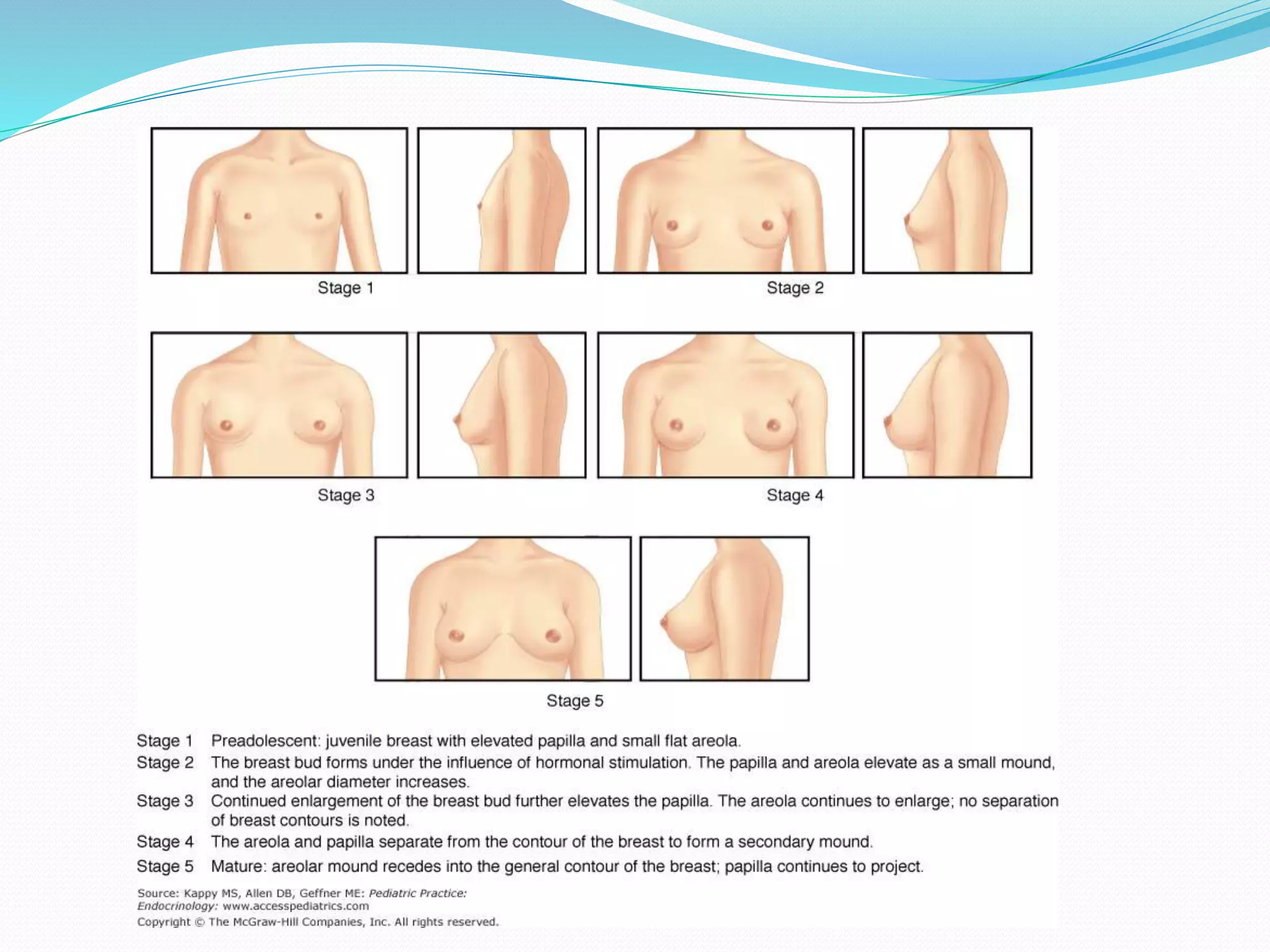
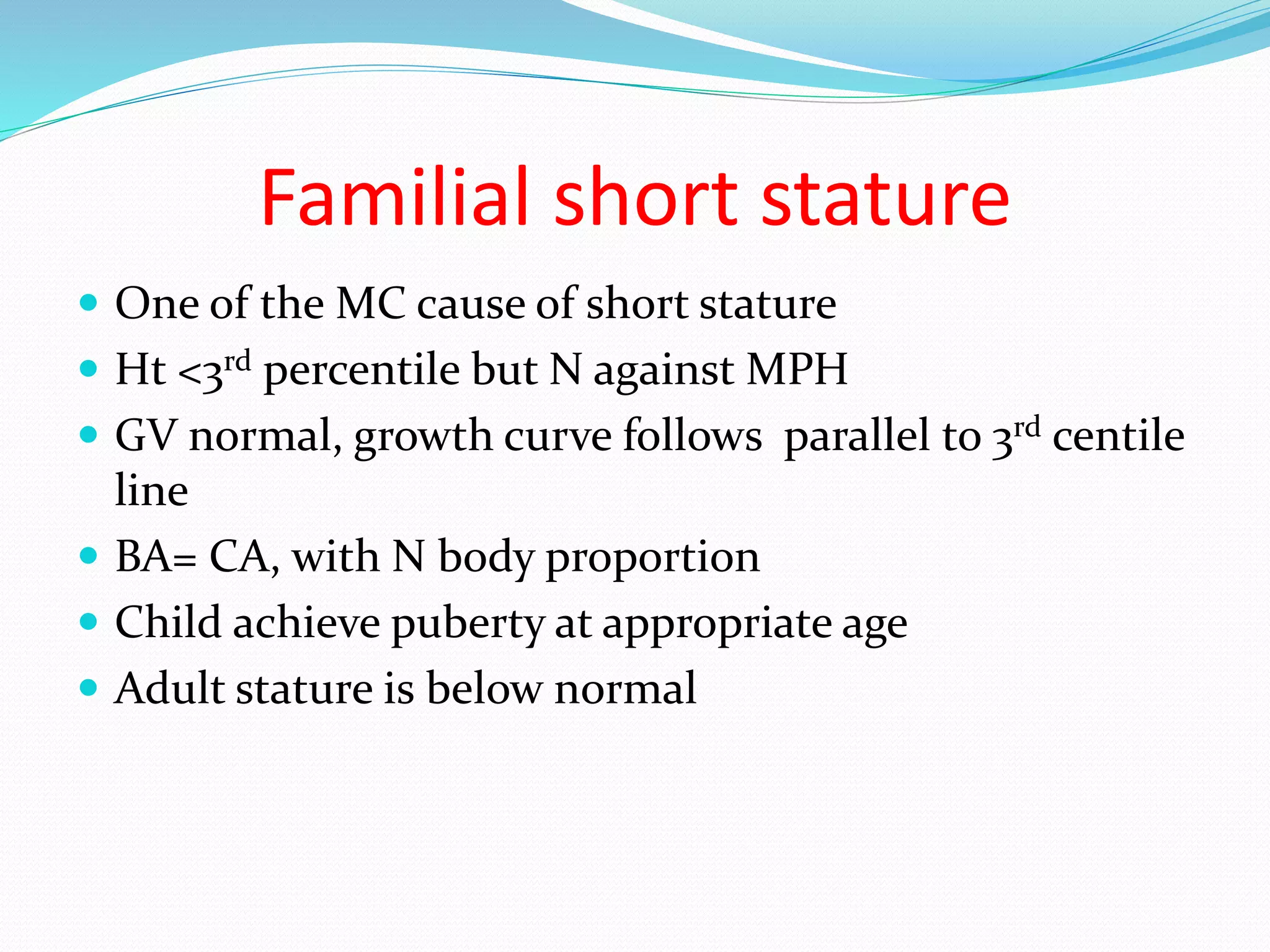
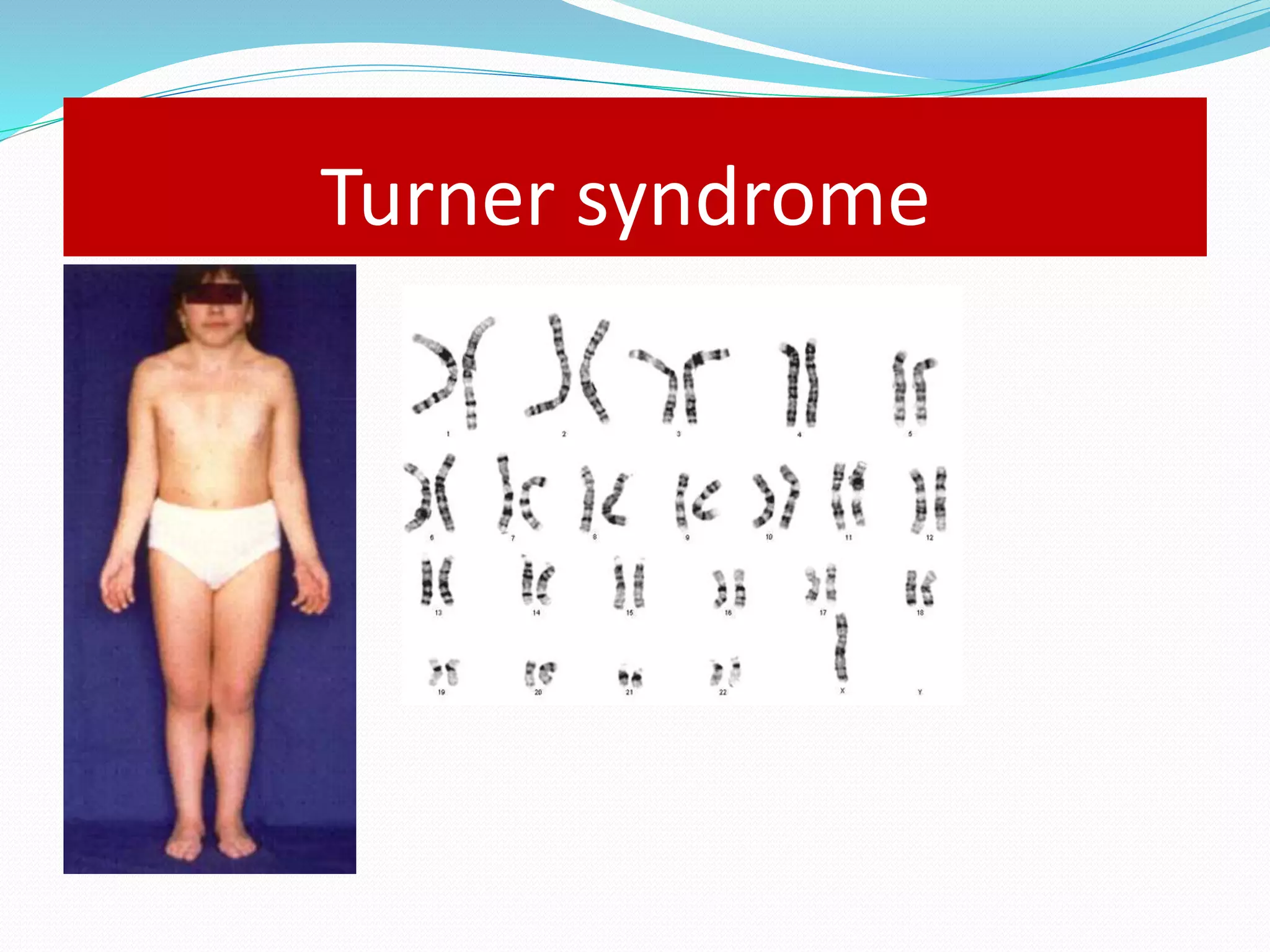
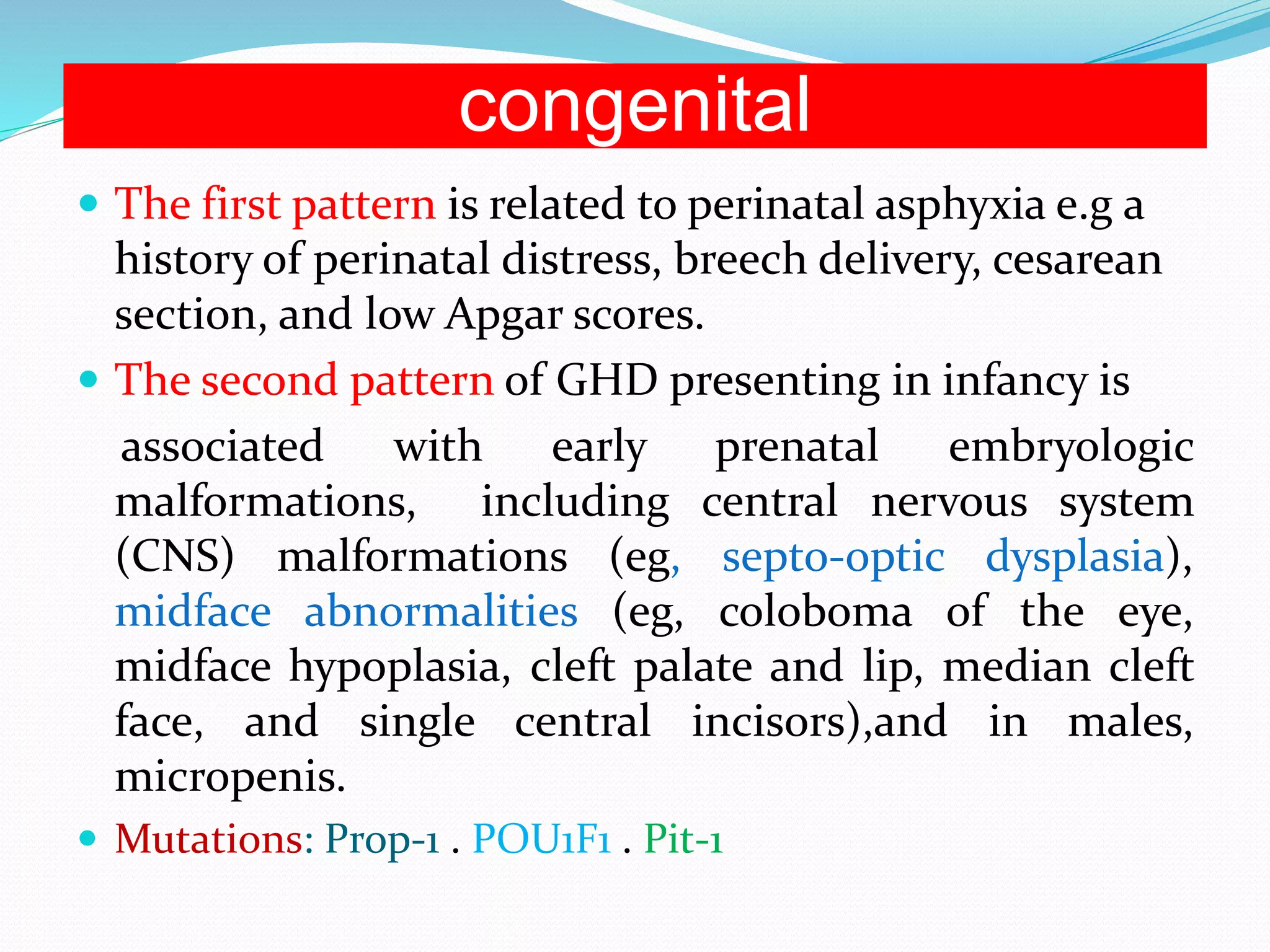
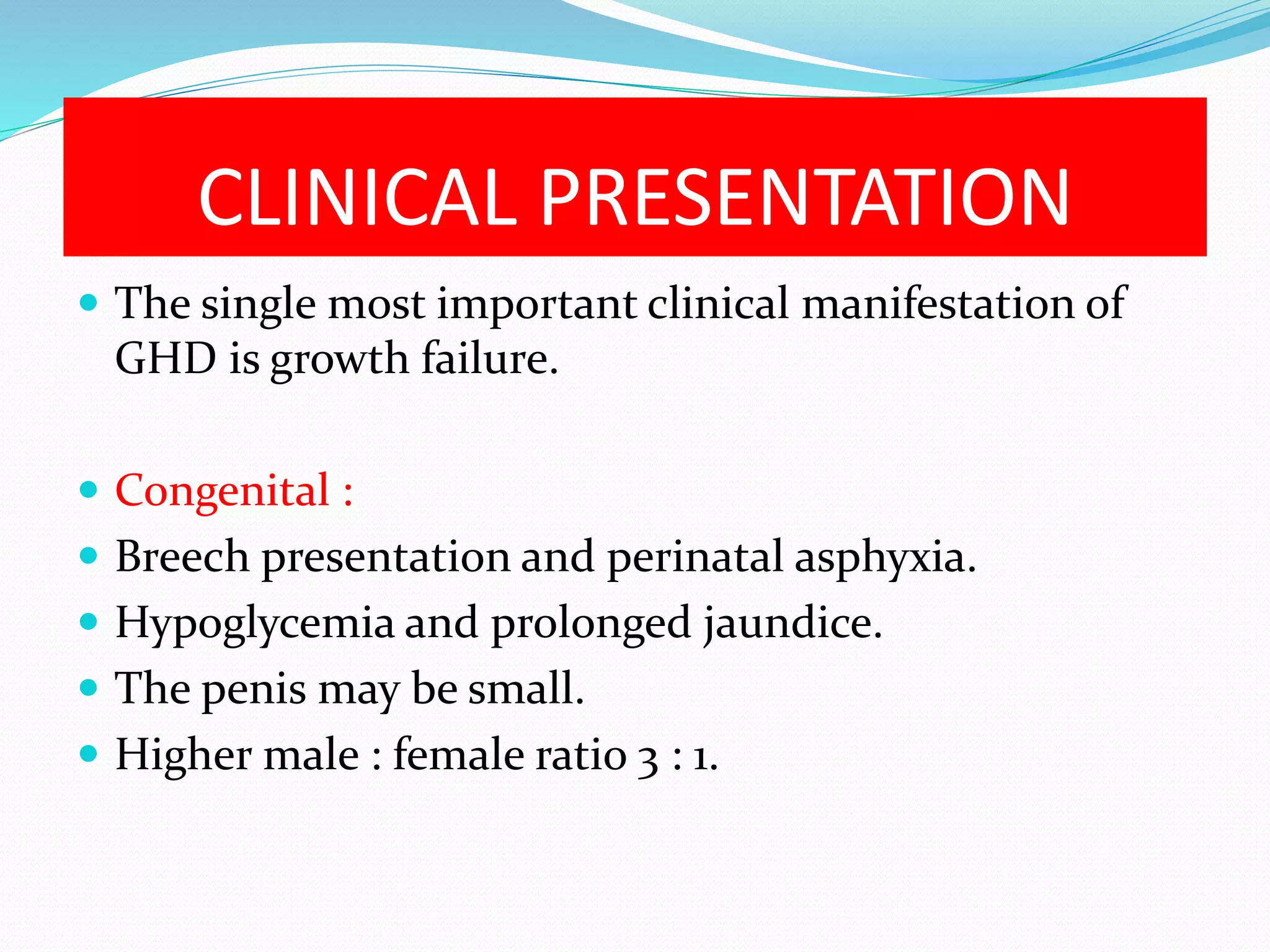
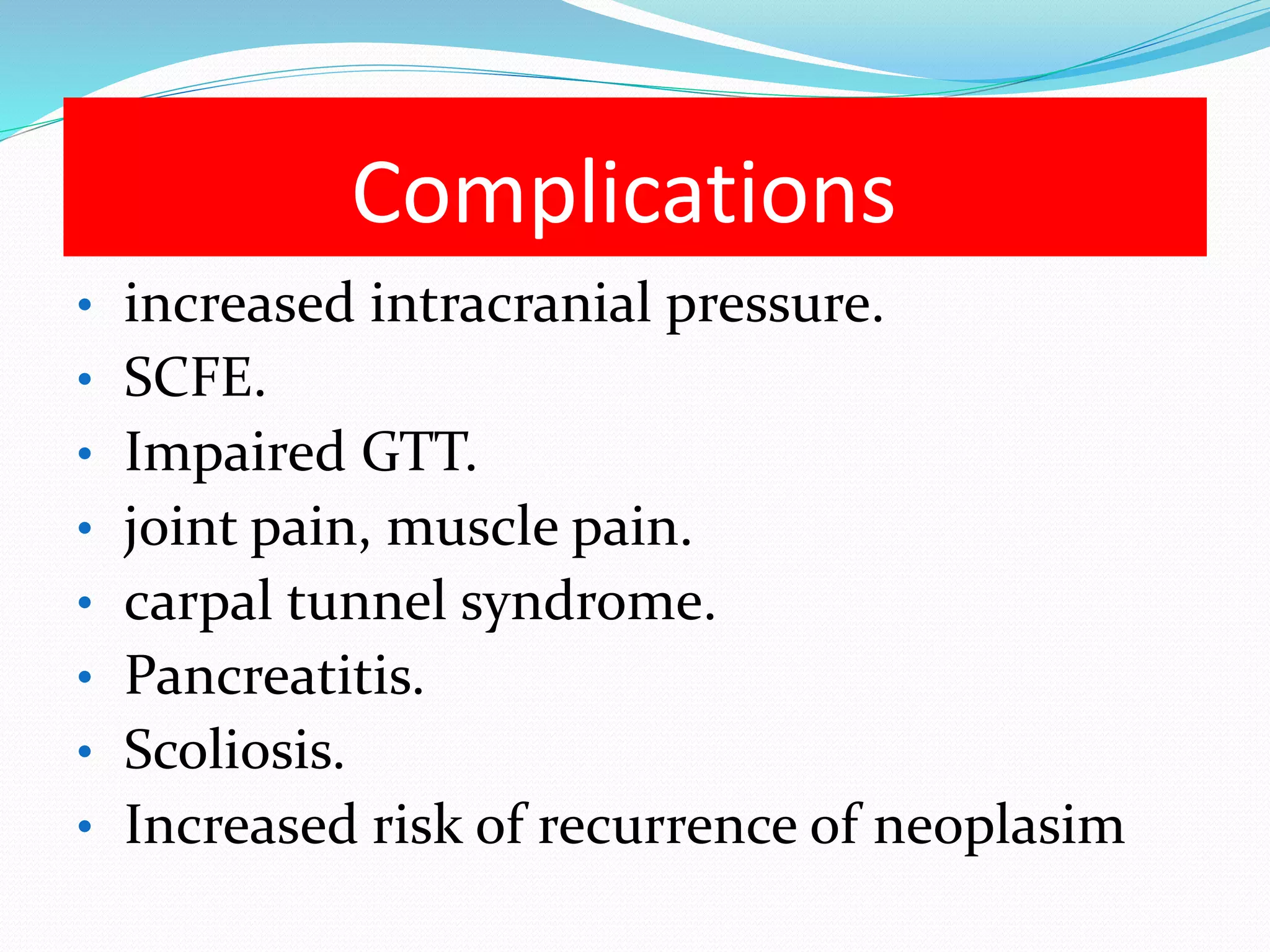
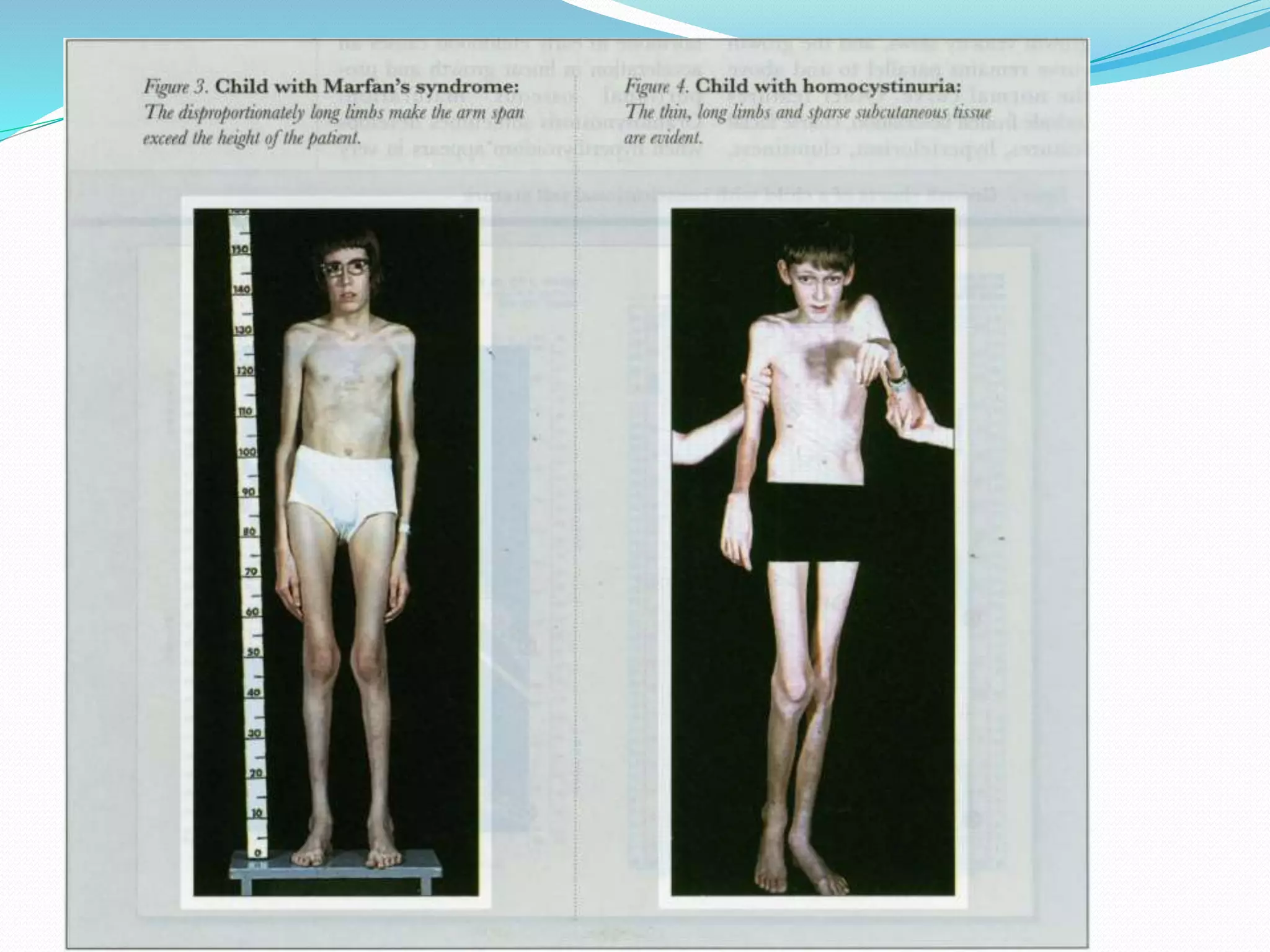
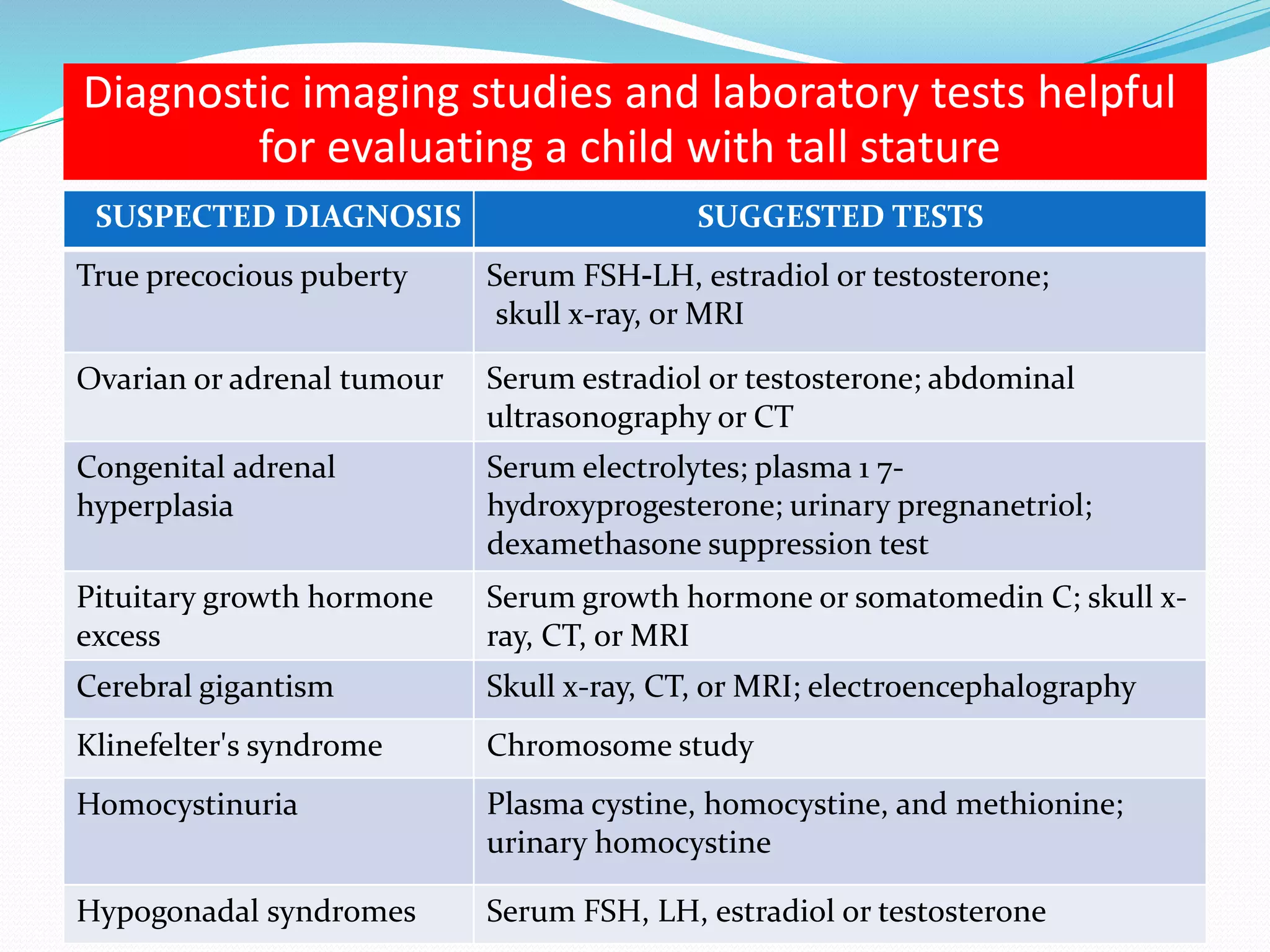
This document provides an overview of growth disorders including short and tall stature. It discusses the evaluation and causes of short stature such as growth hormone deficiency, Turner syndrome, and Prader-Willi syndrome. For growth hormone deficiency, it outlines the diagnostic process including stimulation tests and treatment with growth hormone. For tall stature, it reviews genetic, hormonal, and syndromic causes such as familial tall stature, precocious puberty, and Marfan syndrome.