1. Cell injury refers to changes in a cell's internal and external environment due to stresses like lack of oxygen, toxins, or infections.
2. Causes of cell injury include hypoxia, physical and chemical agents, microbes, immunological reactions, nutritional imbalances, and genetic factors.
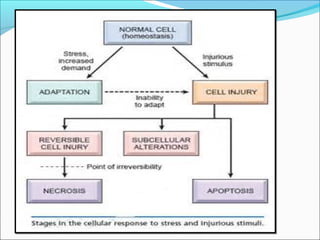
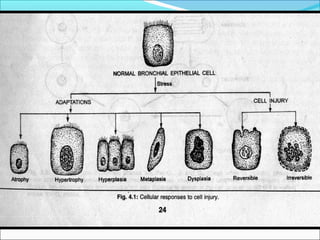
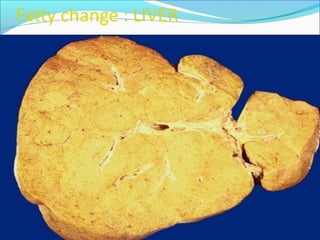
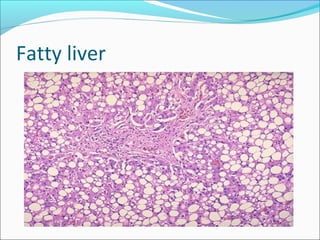
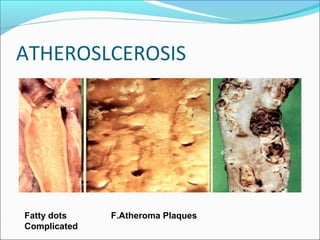
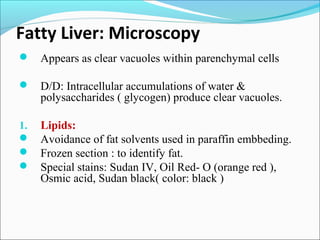
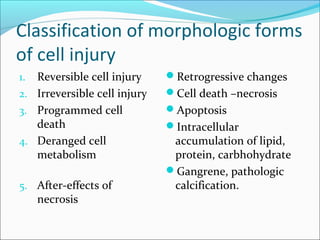
3. Cellular responses to injury include reversible changes like fatty change and swelling, or irreversible cell death through necrosis or apoptosis. Adaptive changes like hypertrophy and hyperplasia can also occur.