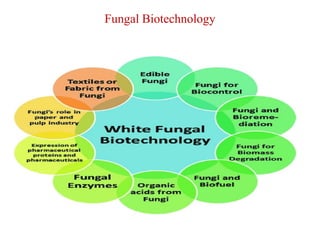
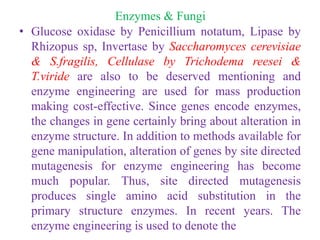
The document discusses the significant role of fungi in biotechnology, highlighting their applications in the food industry, agriculture, and medicine. Fungi are utilized for fermentation, enzyme production, and as bio-fertilizers, and they also contribute to biological control methods in agriculture. The author emphasizes the future potential of fungi in promoting sustainable development and improving agricultural practices through advancements in genetic engineering.