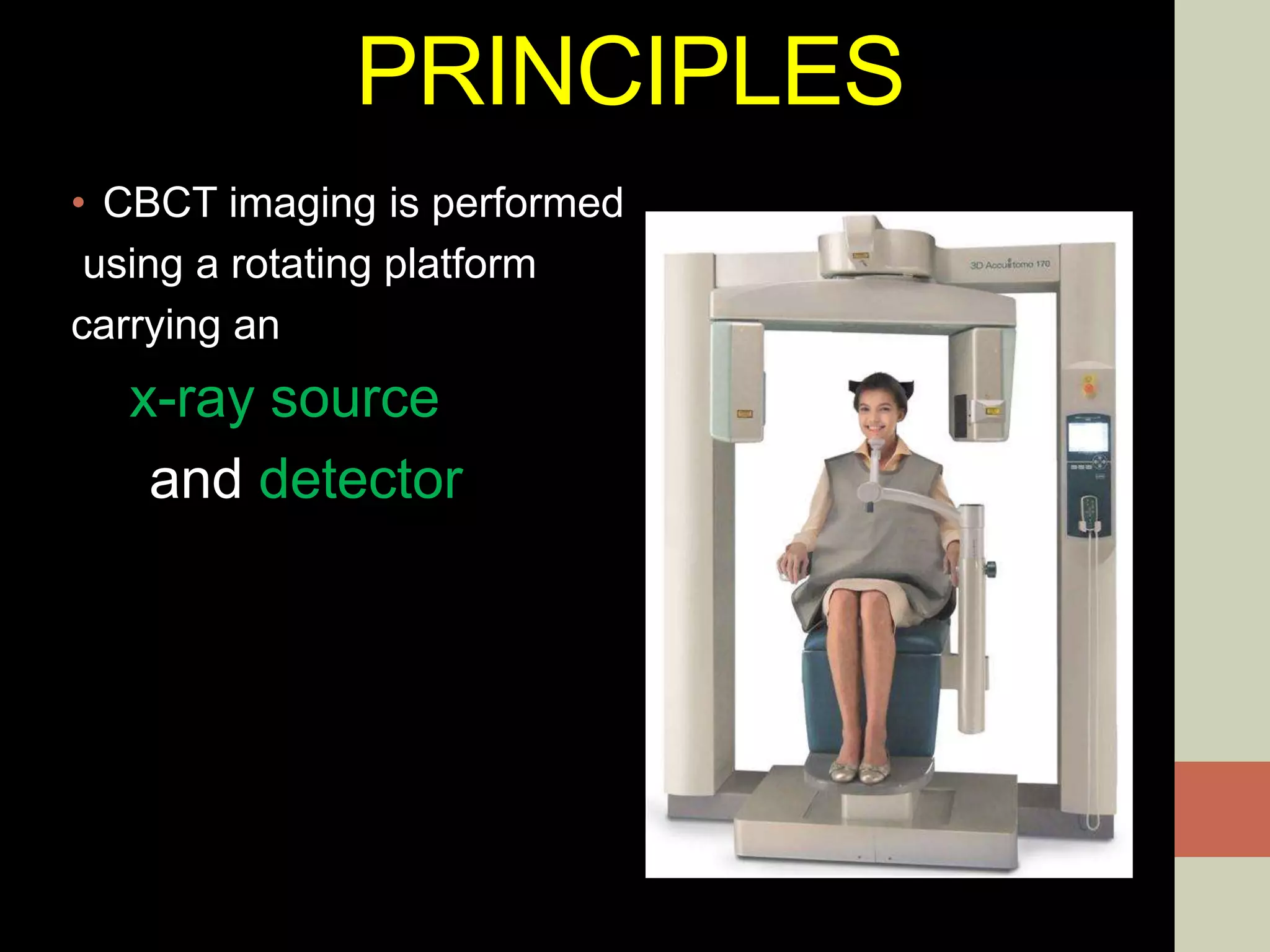
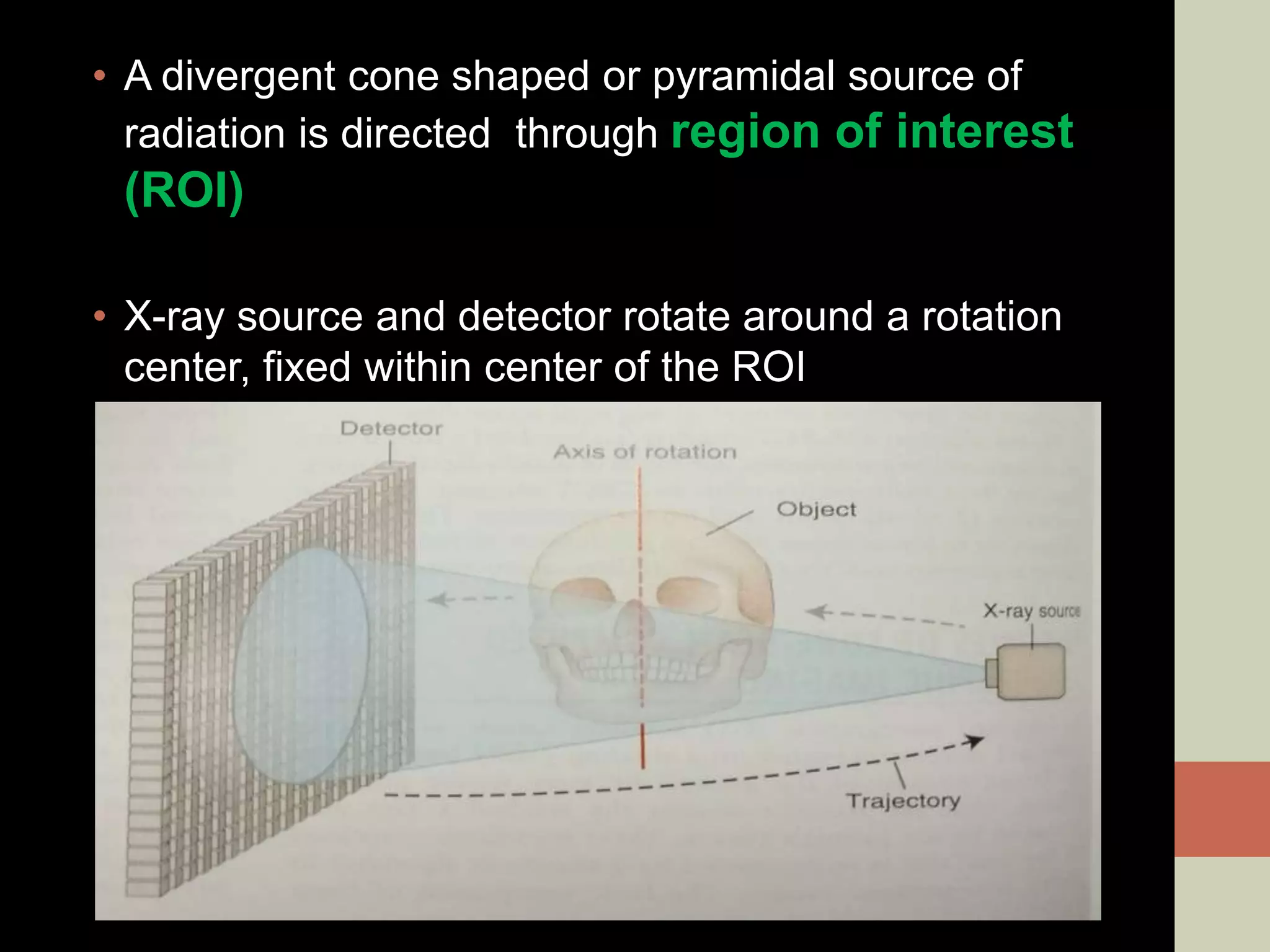
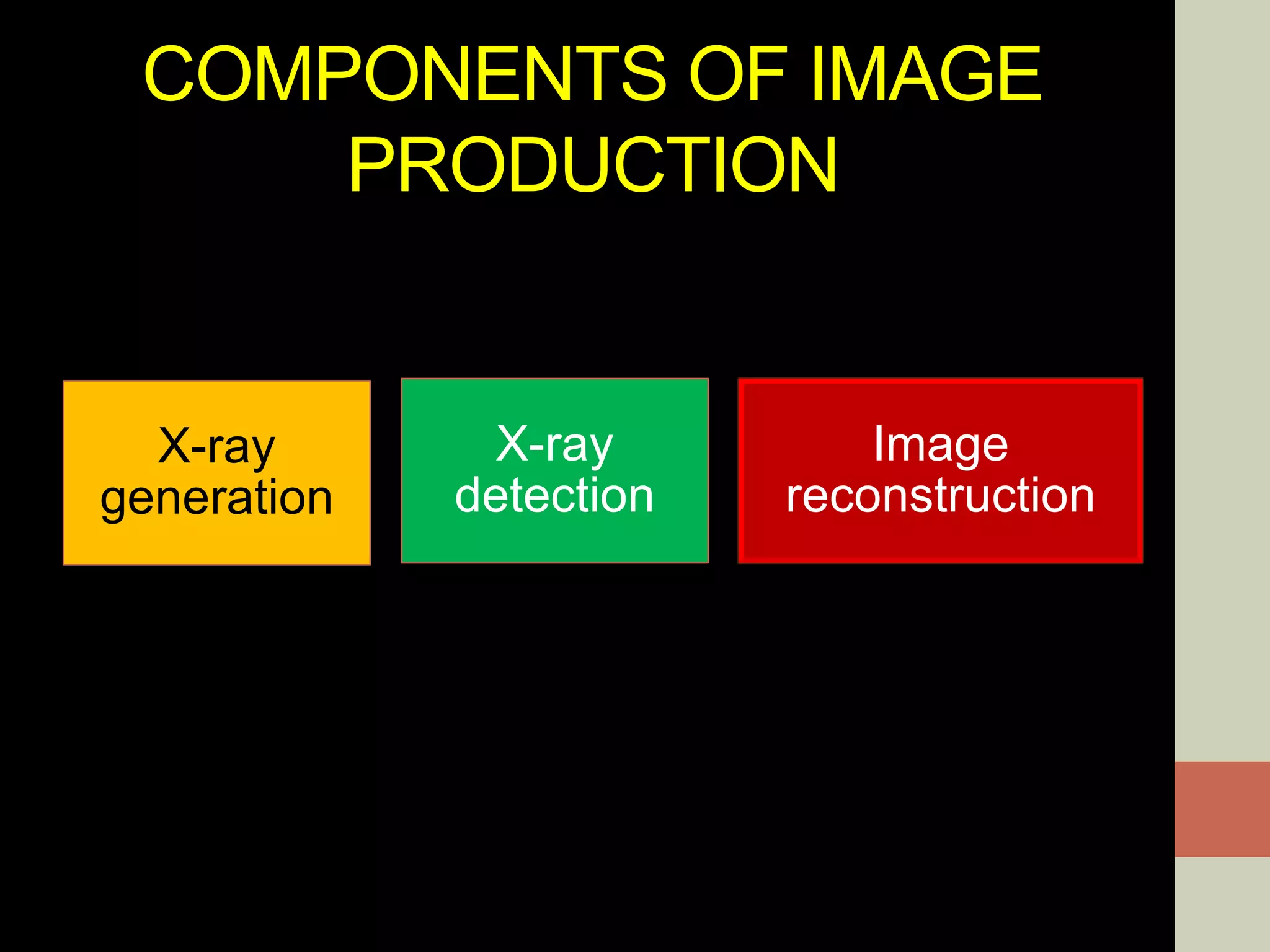
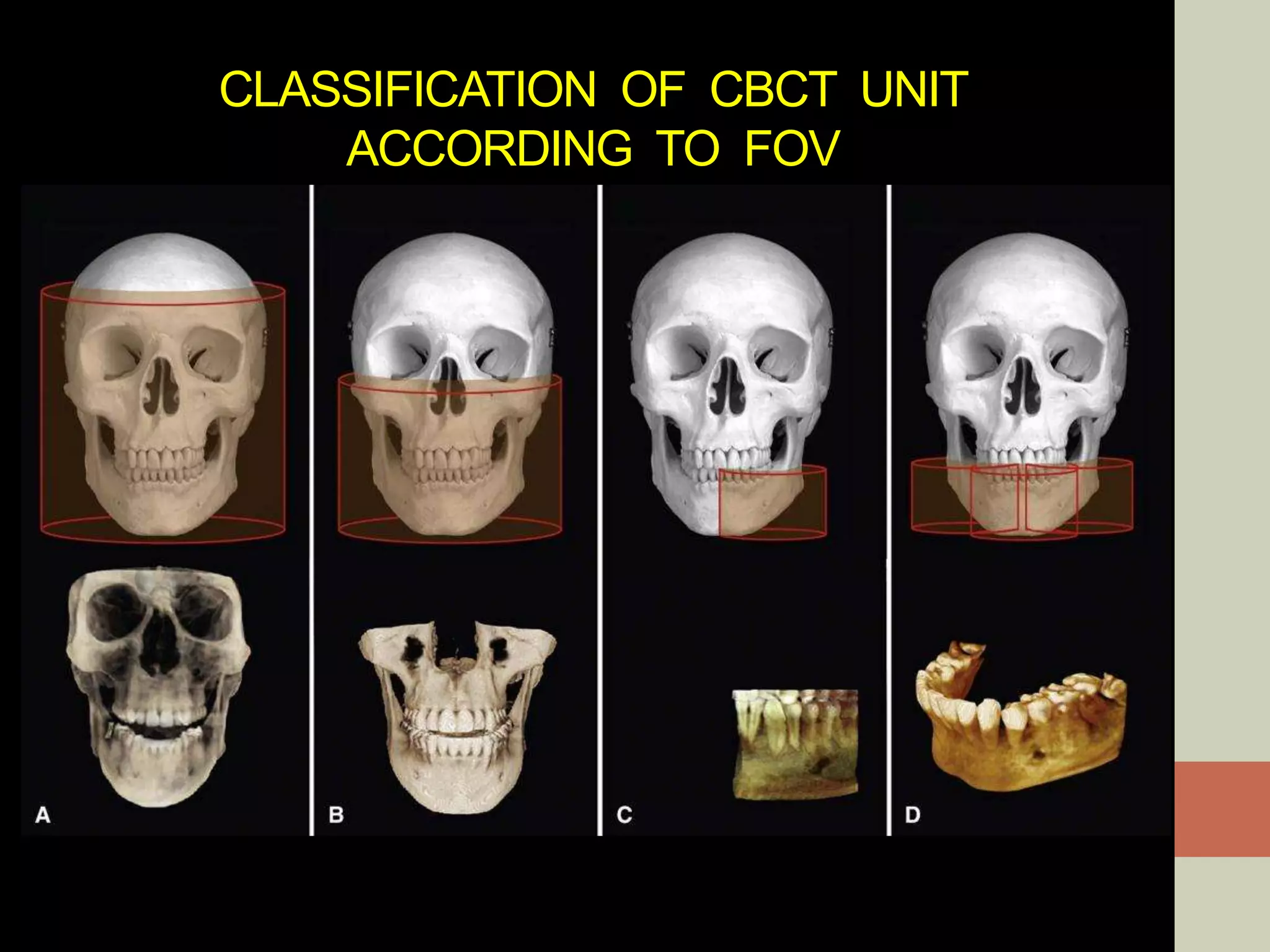
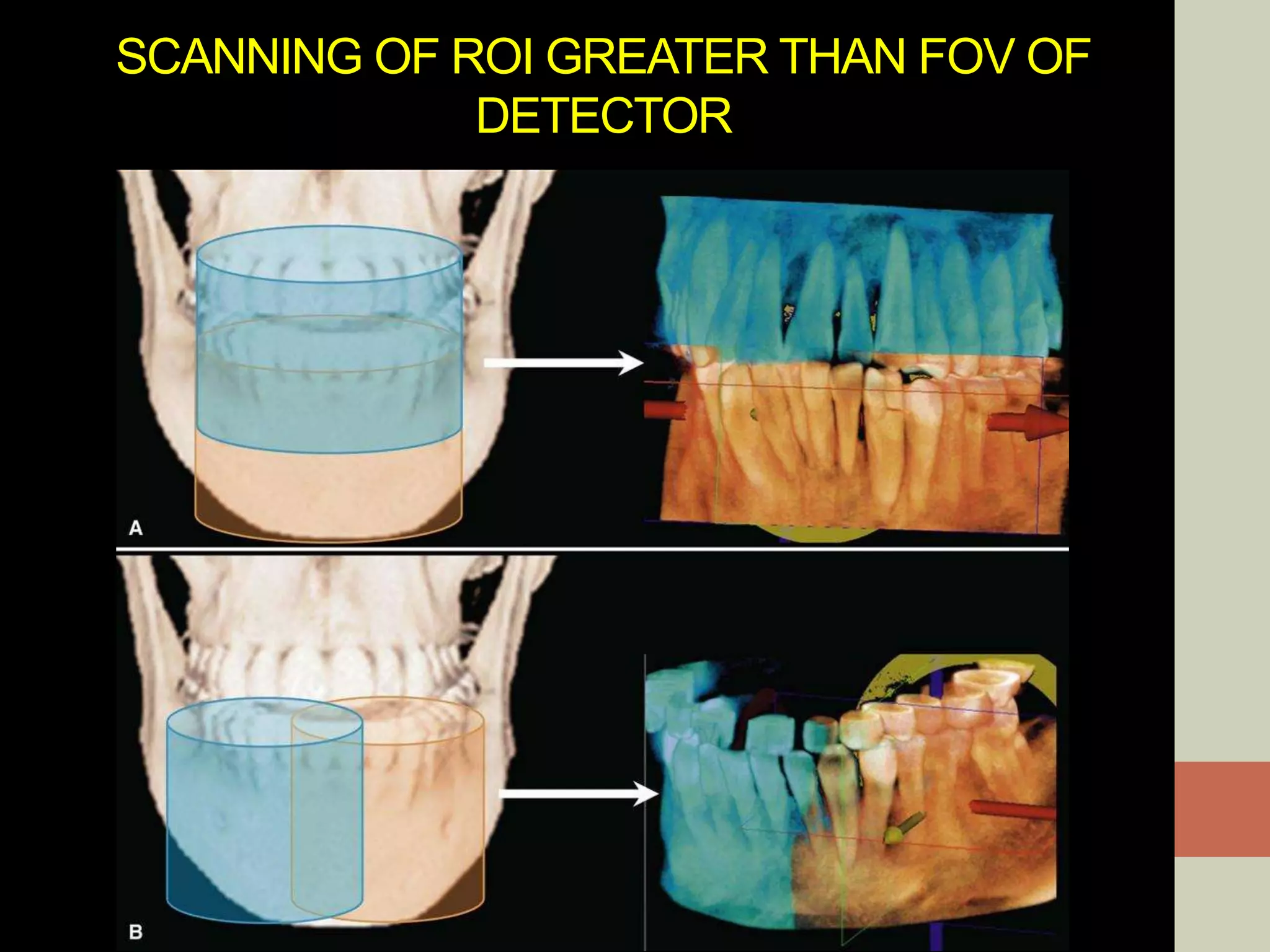
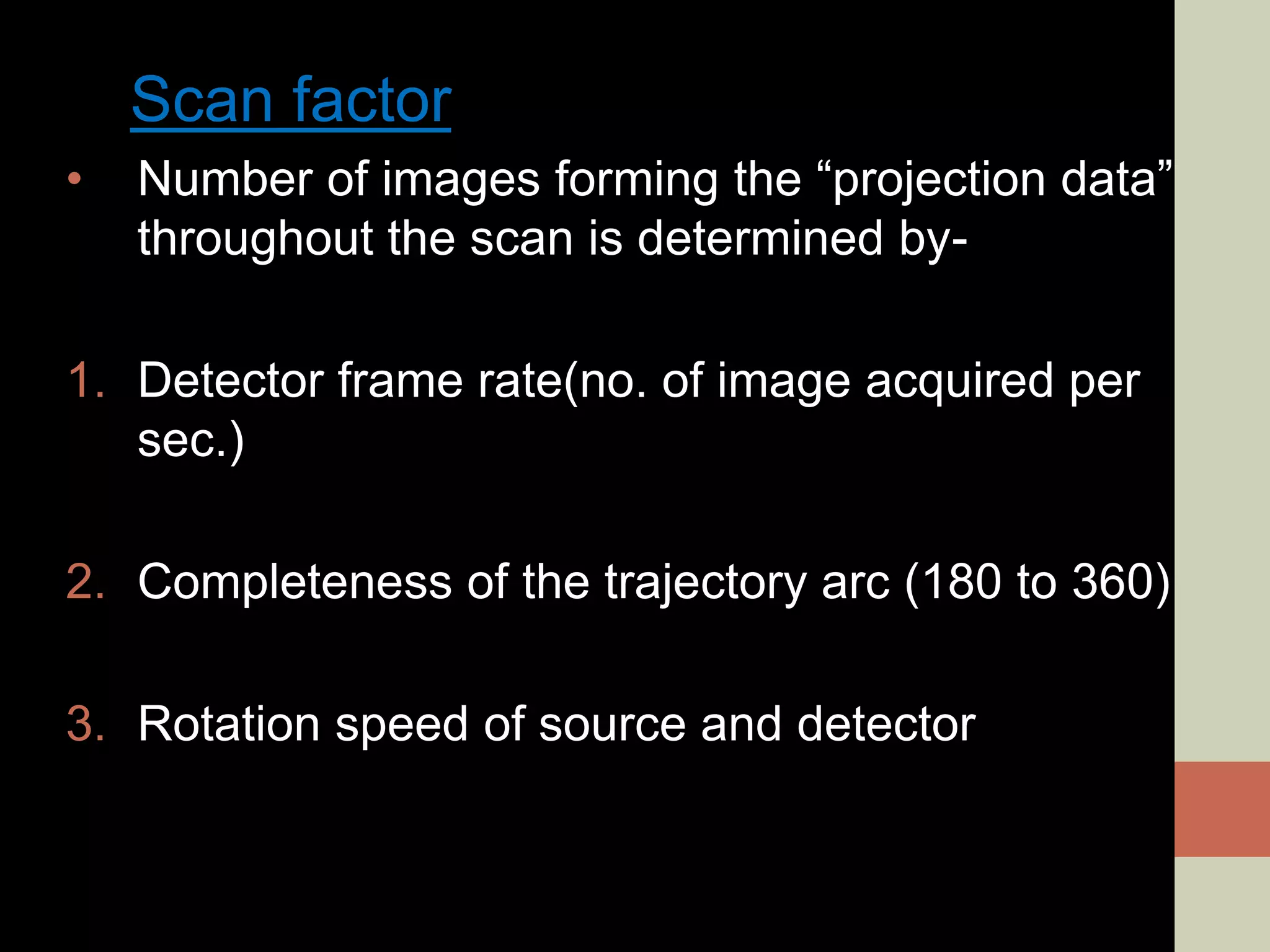
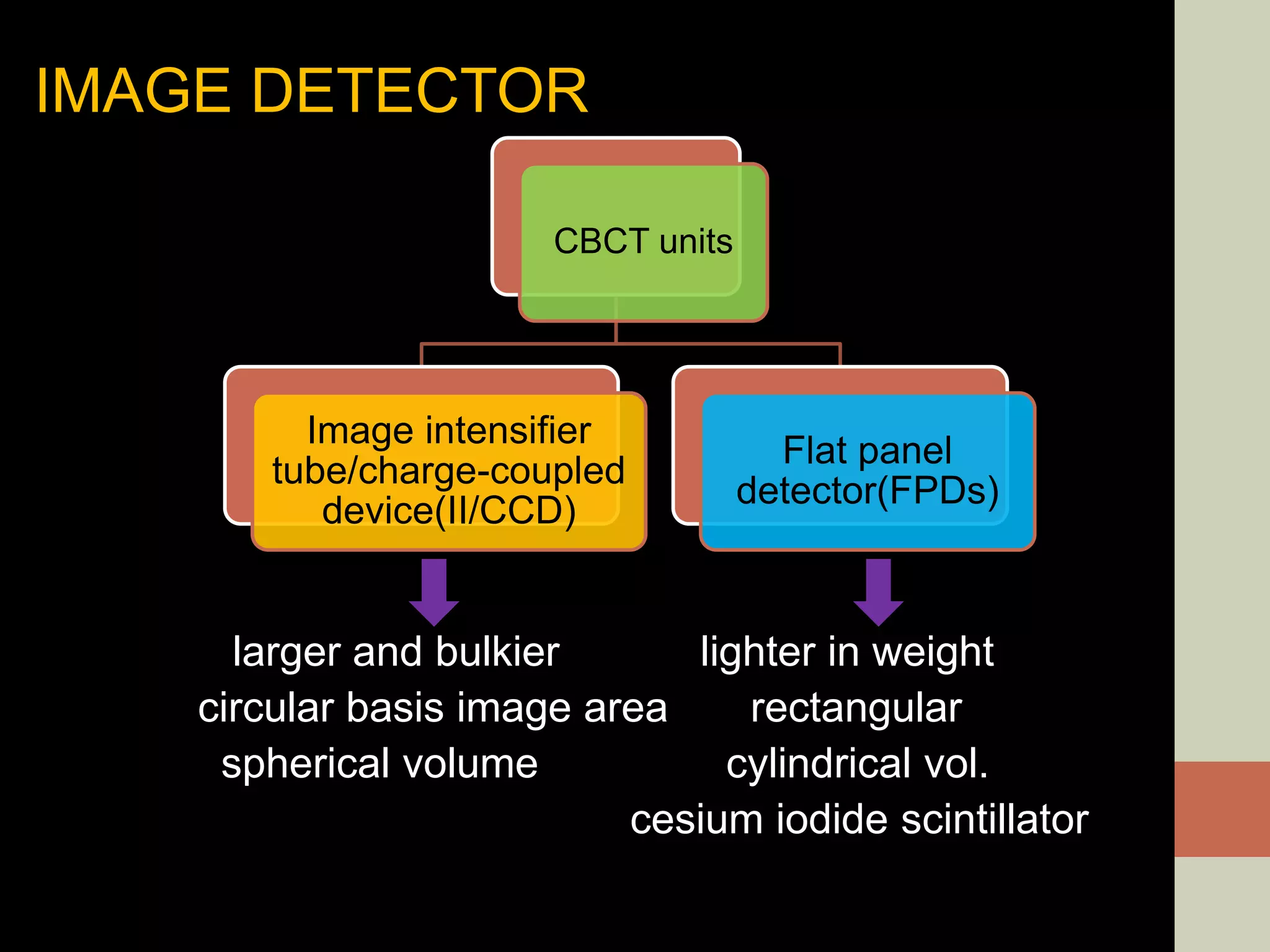
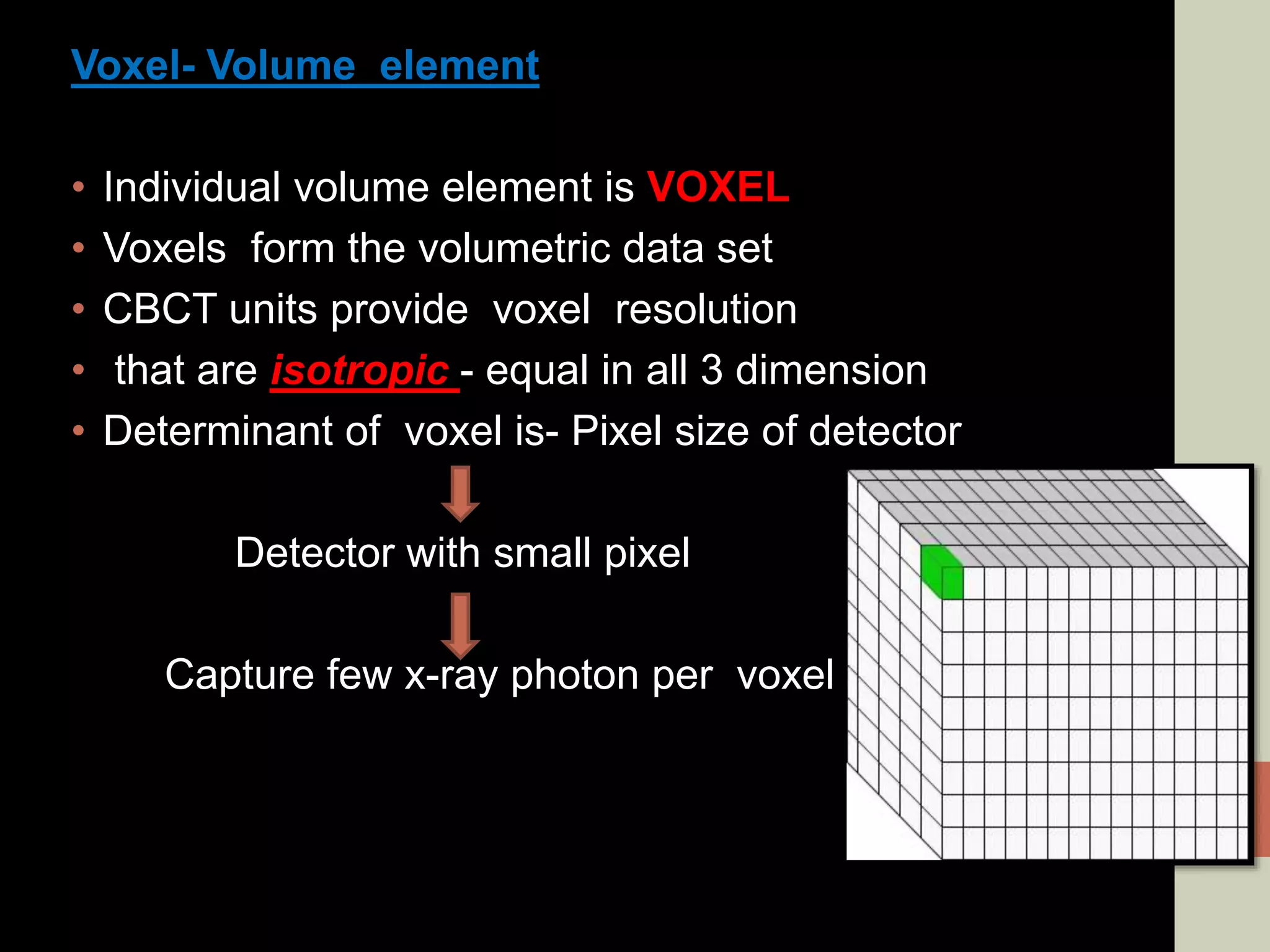
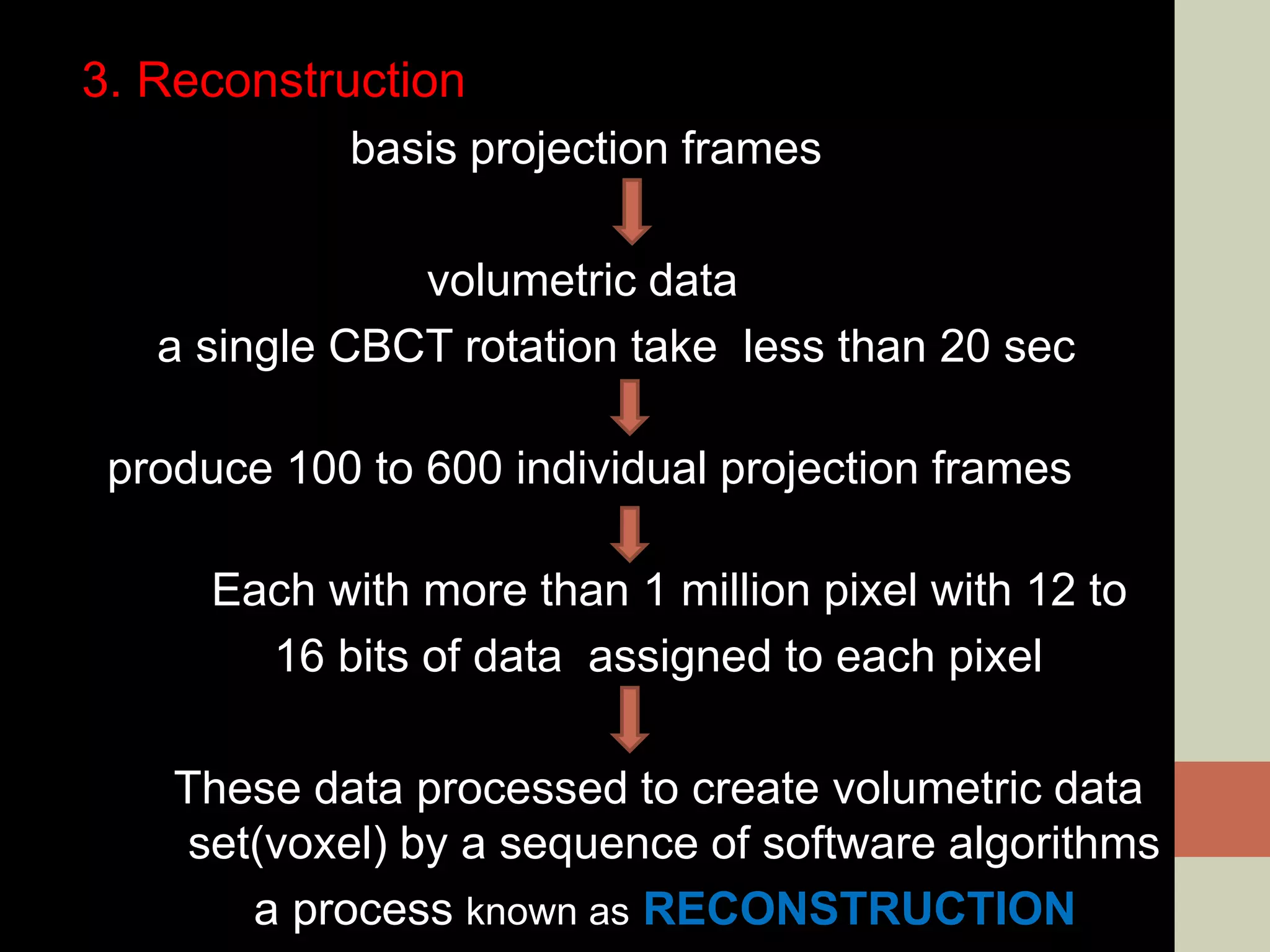
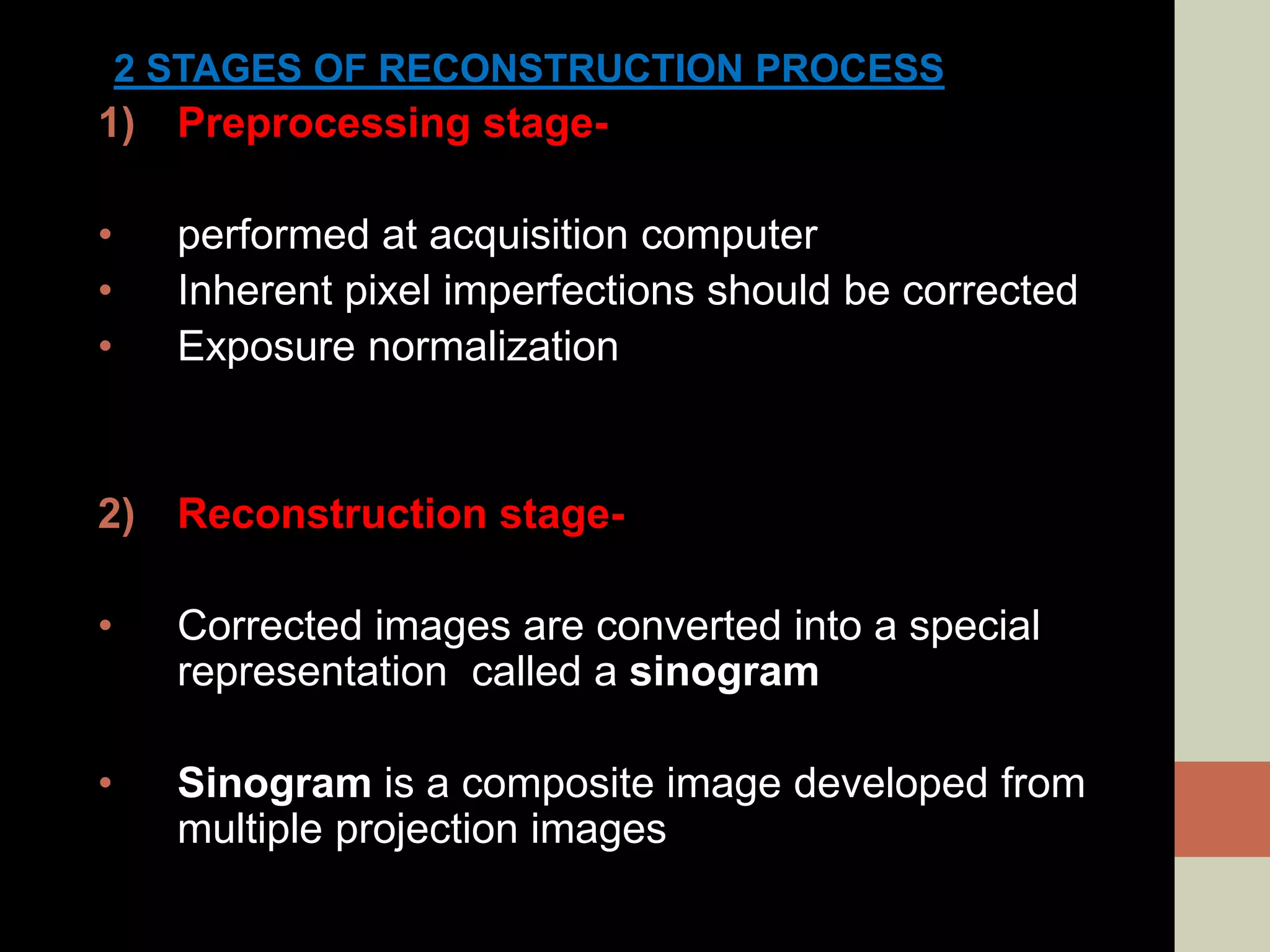
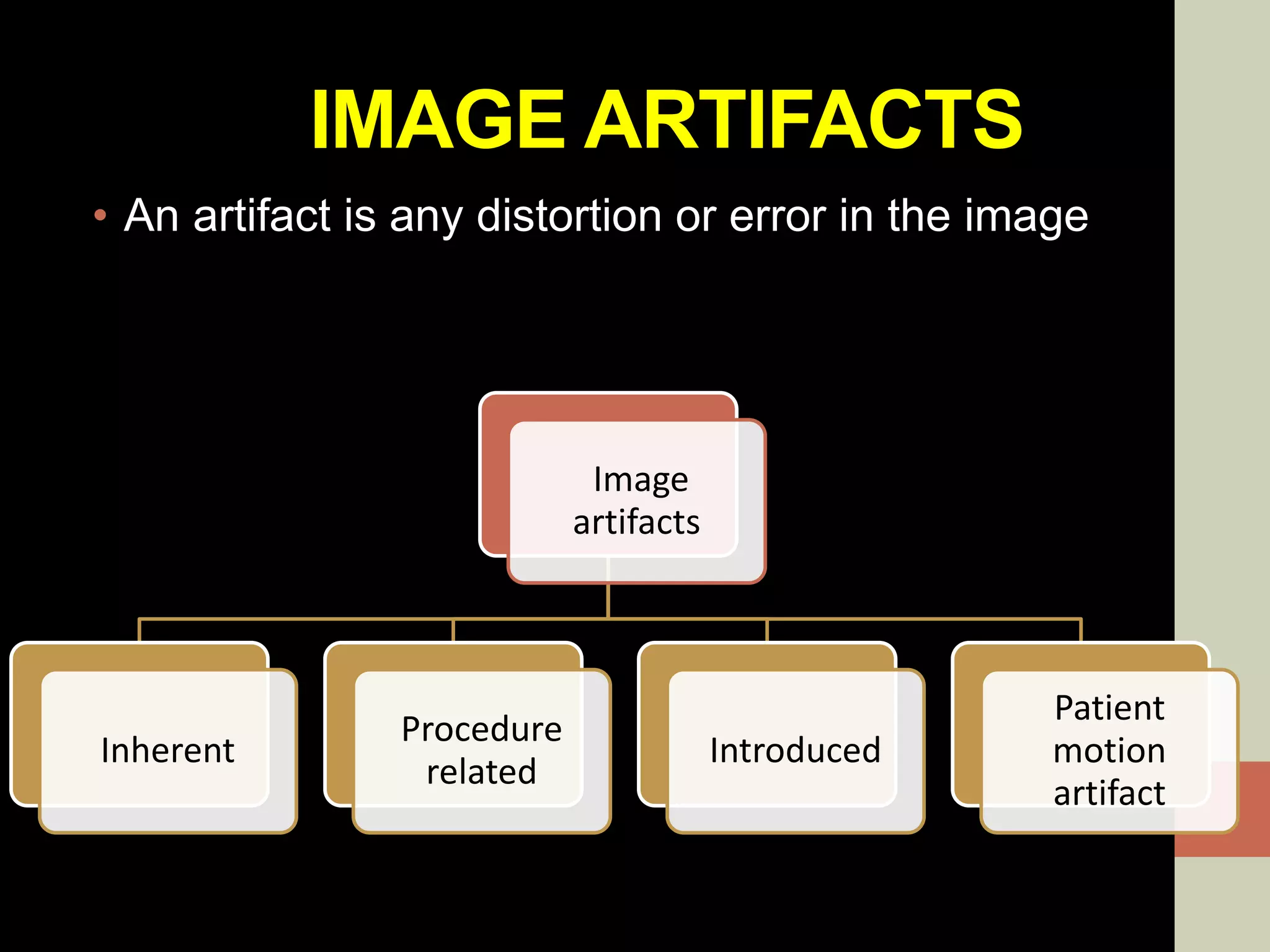
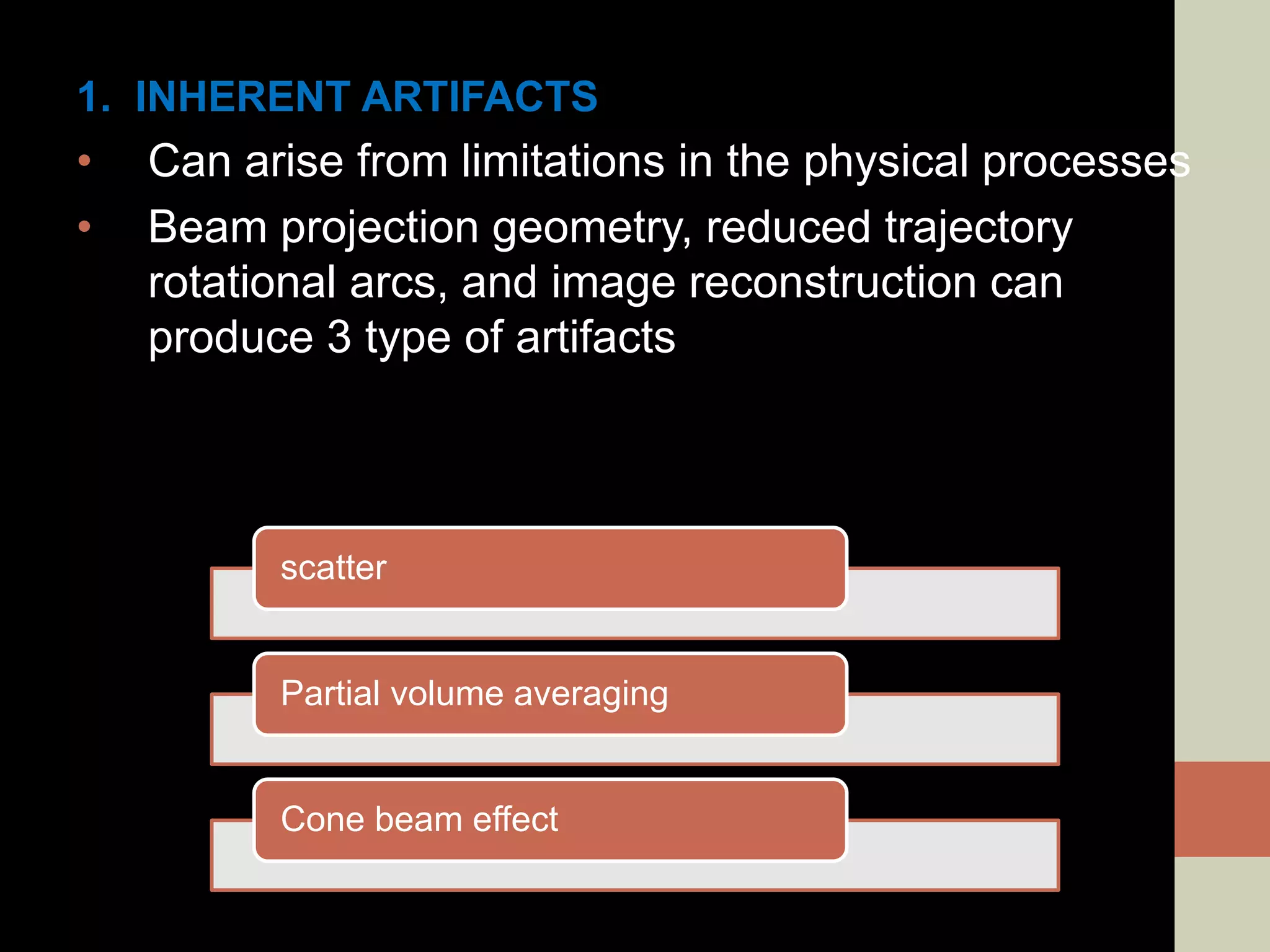
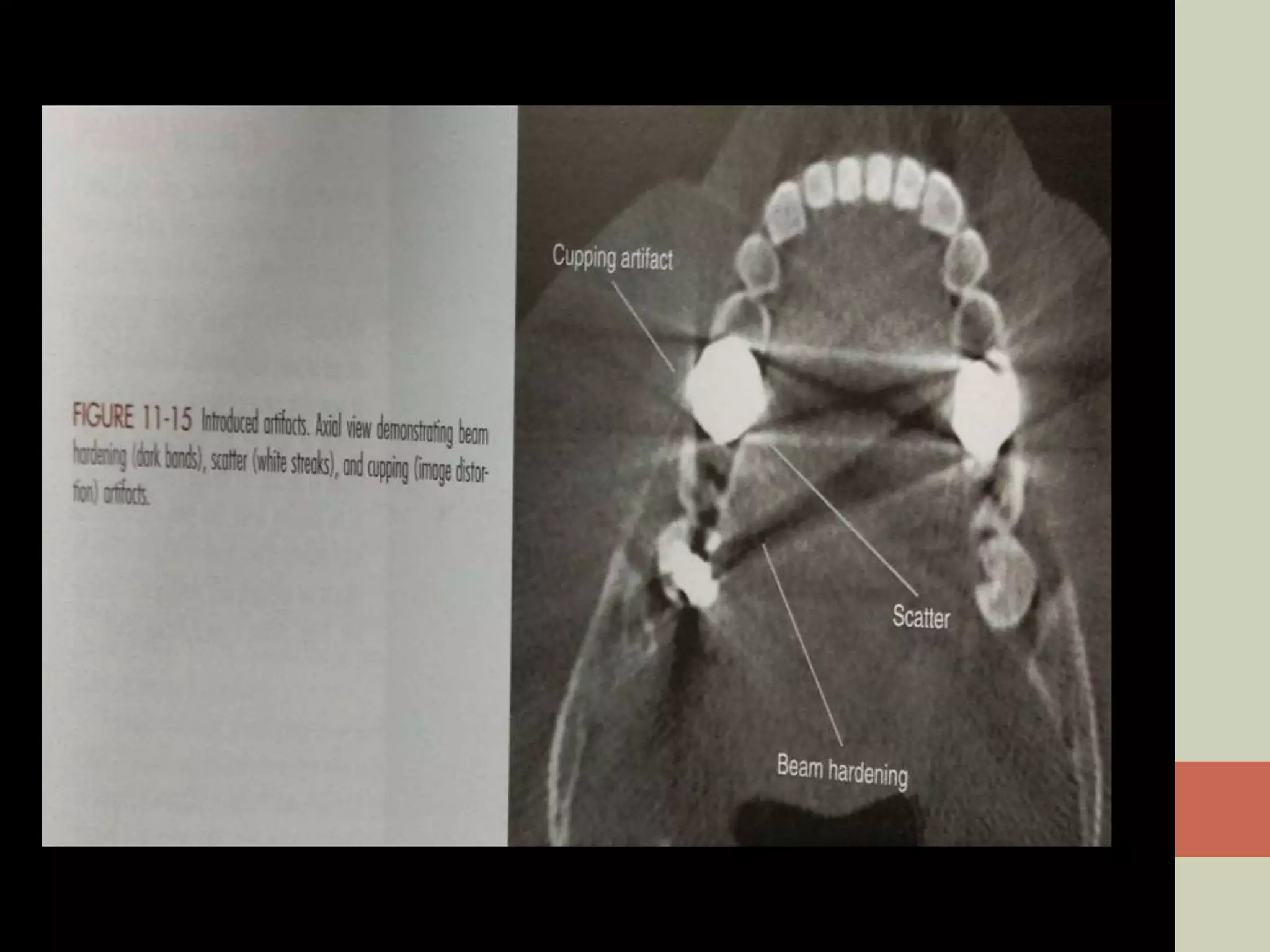
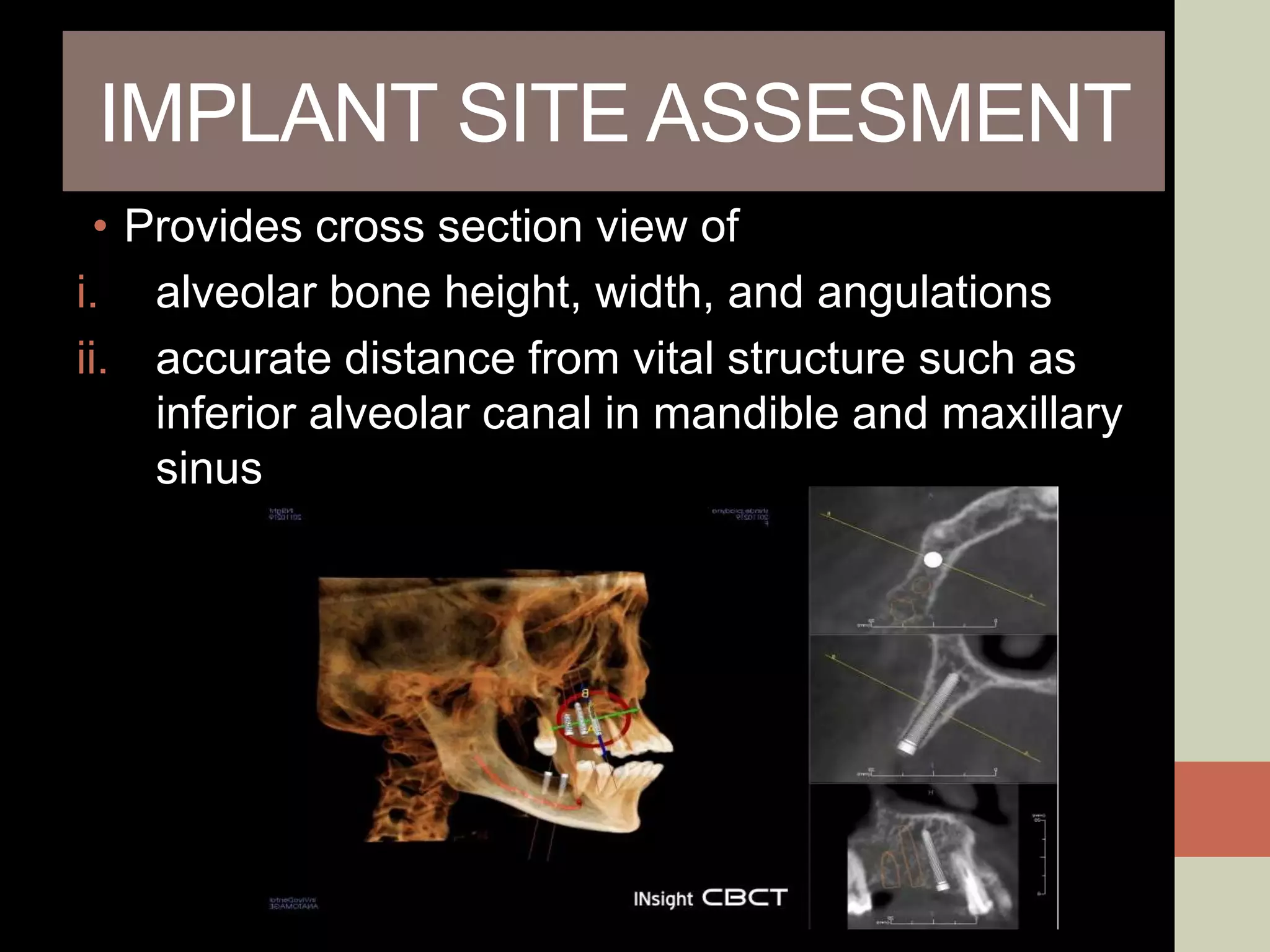
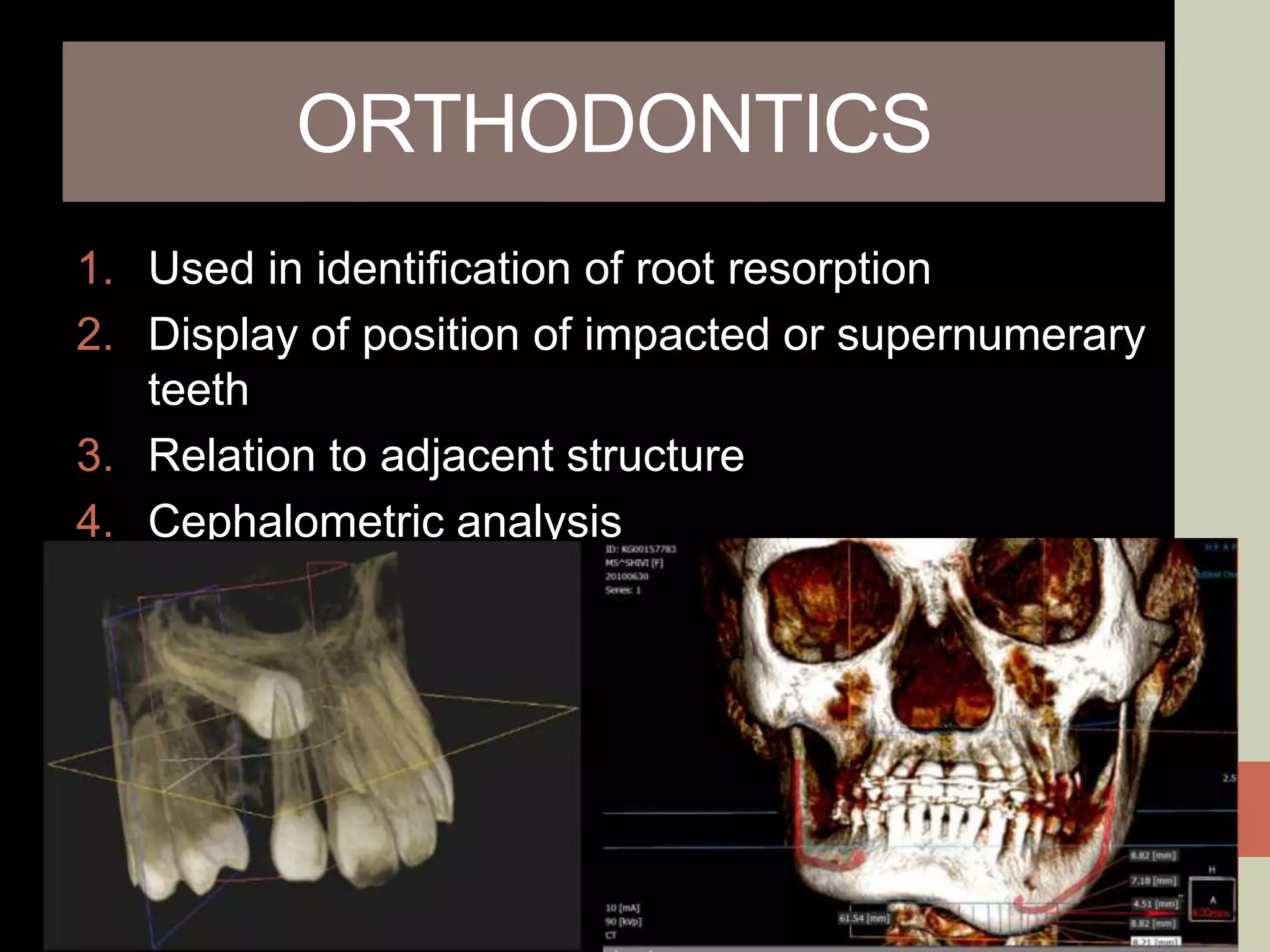
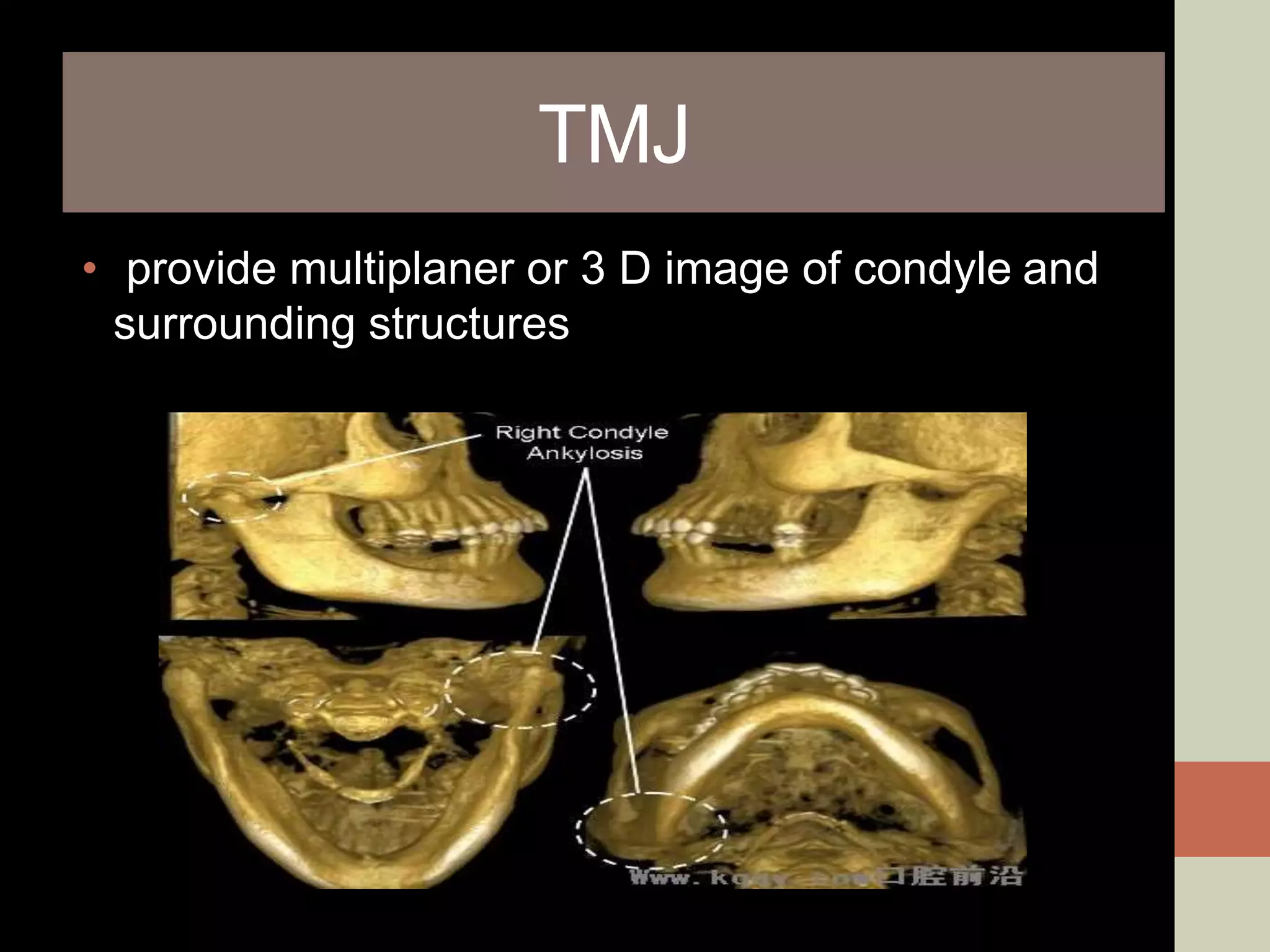
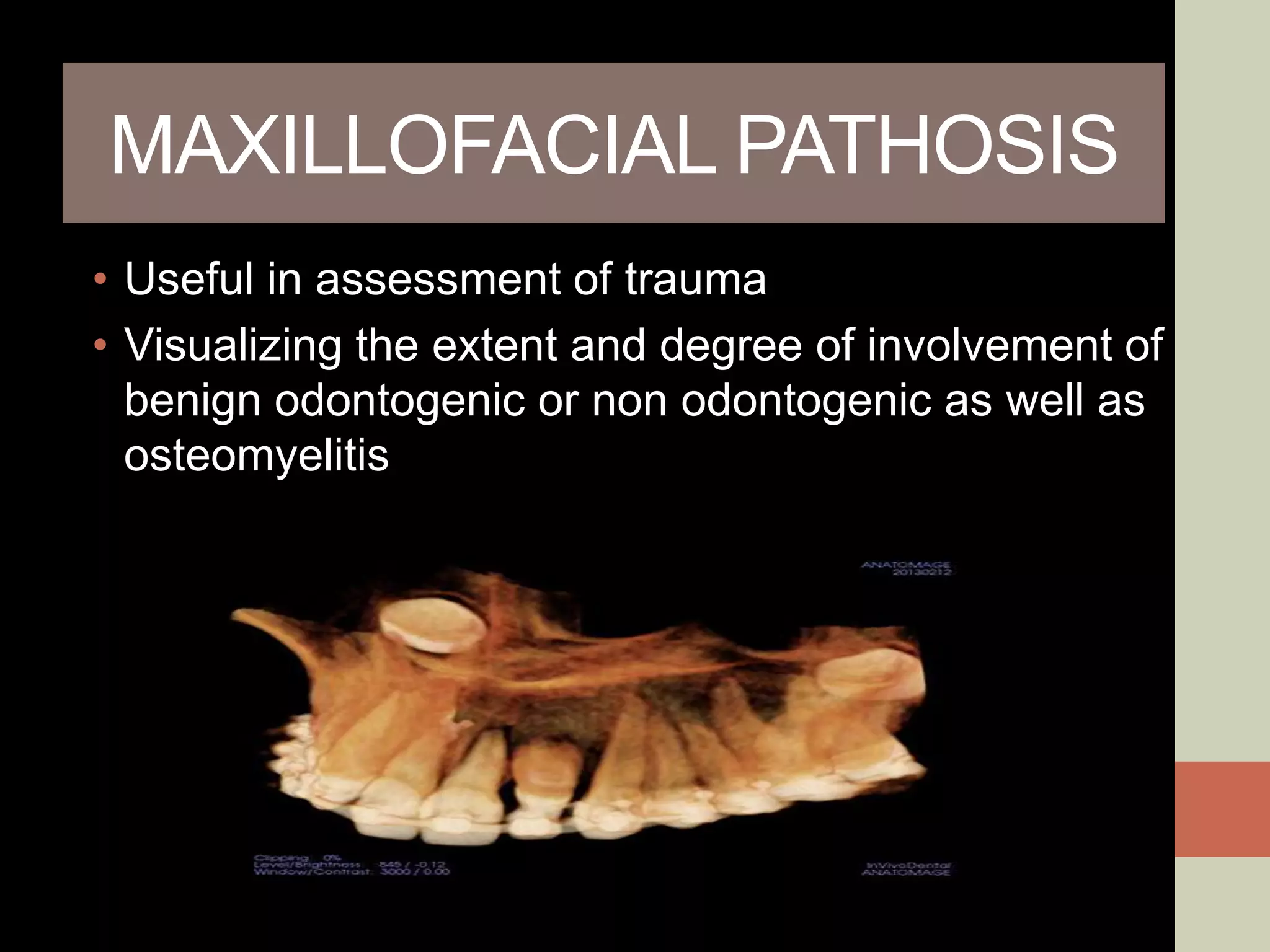
CBCT provides volumetric imaging with less radiation than medical CT. It involves an X-ray source and detector rotating around the patient to obtain multiple 2D projections, which are reconstructed into a 3D volume. This allows visualization of structures like bone and teeth from any angle. CBCT has numerous dental and maxillofacial applications like implant planning, orthodontics, and pathology assessment. While it provides more accuracy than 2D imaging, CBCT images can be affected by artifacts from scatter, motion, and metal objects. Overall, CBCT is a useful tool for evaluating anatomy in 3D.