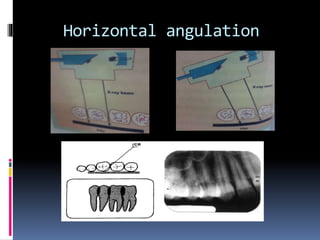
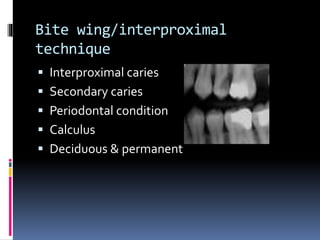
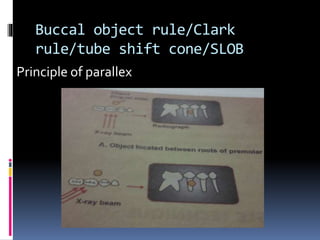
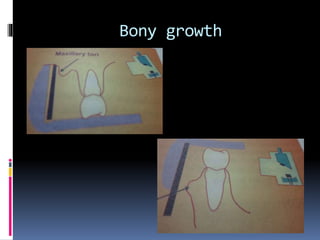
This document discusses various intraoral radiographic techniques used in dentistry. It describes the basic principles and types of intraoral radiography including periapical, bite wing, and occlusal techniques. For each technique, it outlines the indications, basic methodology, important considerations, and examples of anatomical areas that can be imaged. Specialized techniques are also covered such as those used for pediatric patients, endodontics procedures, and localization of foreign objects.