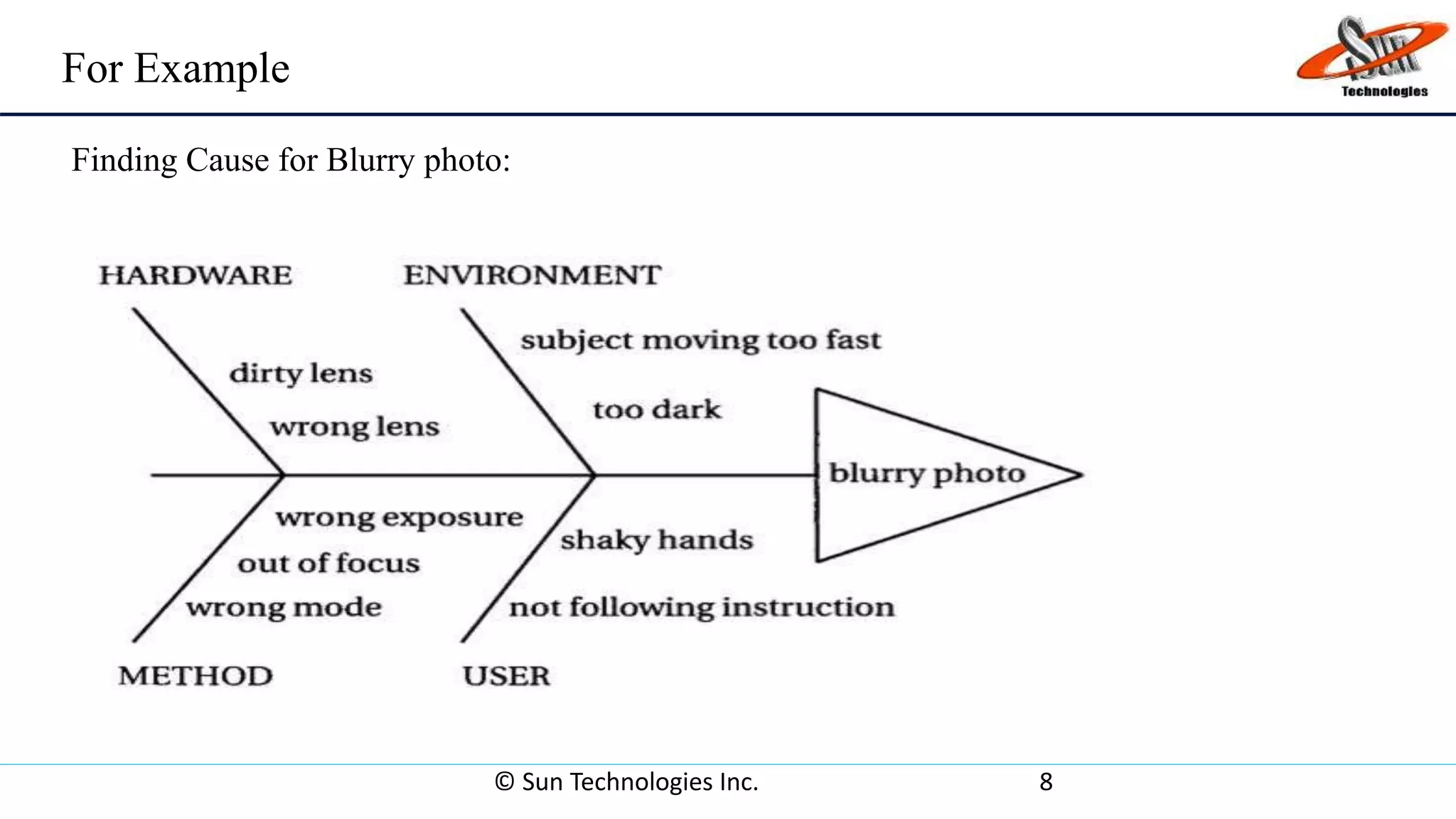
This document provides an overview of cause and effect analysis and cause and effect diagrams. It explains that cause and effect analysis is a technique used to identify all possible causes associated with a problem or effect. A cause and effect diagram visually illustrates the results of this analysis and shows the relationships between potential causes. The document outlines how to construct a cause and effect diagram, including defining the problem, drawing the fishbone structure, and analyzing the diagram to identify the root cause.