Embed presentation
Downloaded 69 times





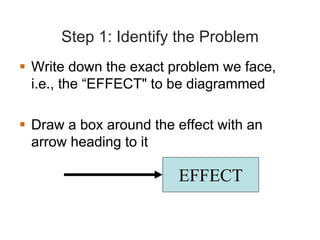


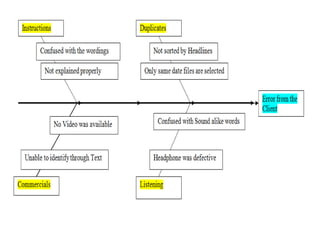


Cause and effect analysis was developed in the 1960s by Kaoru Ishikawa to help identify the root causes of problems. It uses a diagram called an Ishikawa or fishbone diagram to map the potential causes for an effect or problem. The technique helps conduct a thorough analysis by considering all possible causes across major contributing factors. The steps involve identifying the problem or effect, determining key factors, brainstorming potential causes within each factor, and analyzing the diagram to investigate the most likely causes.










