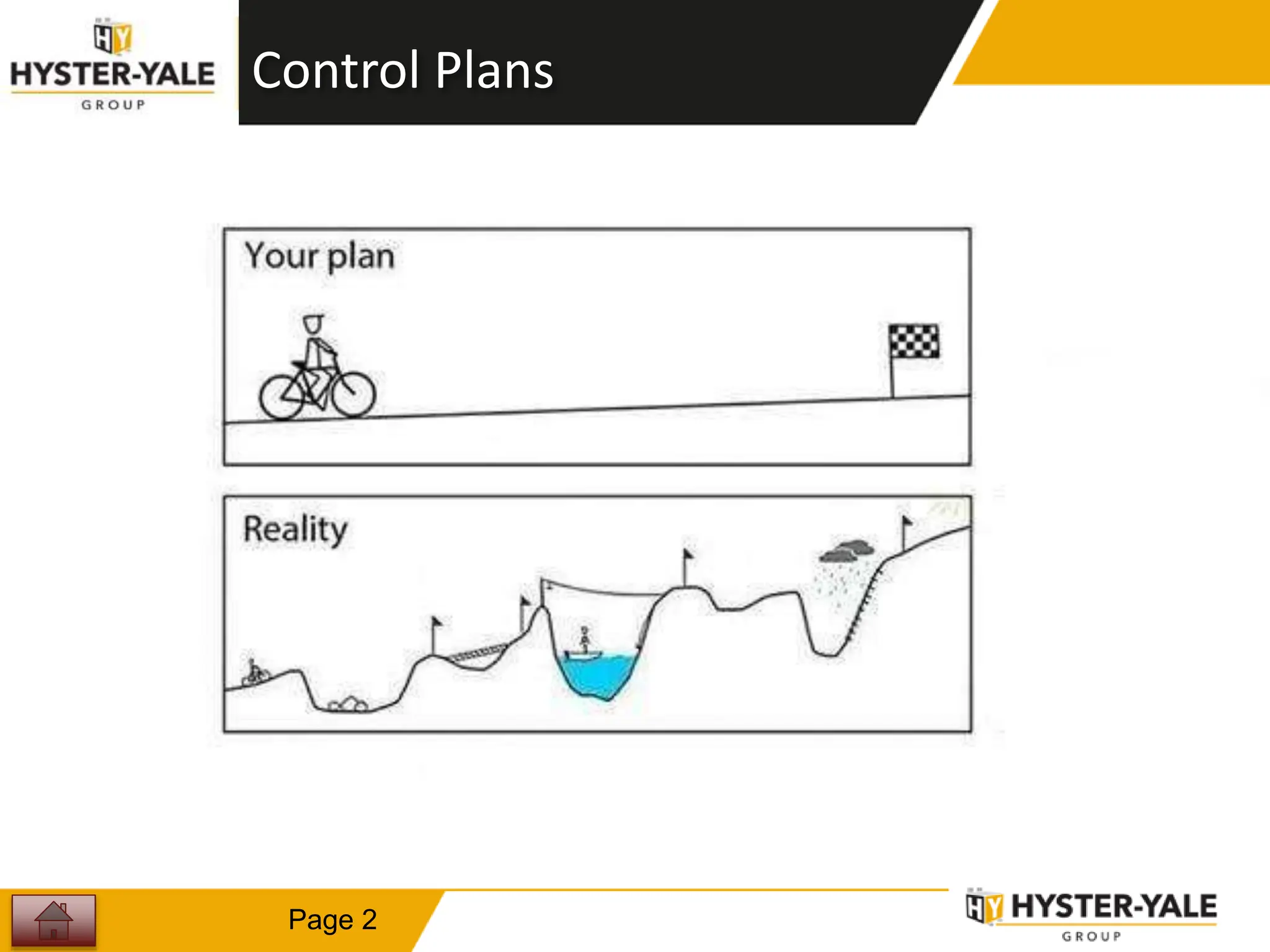
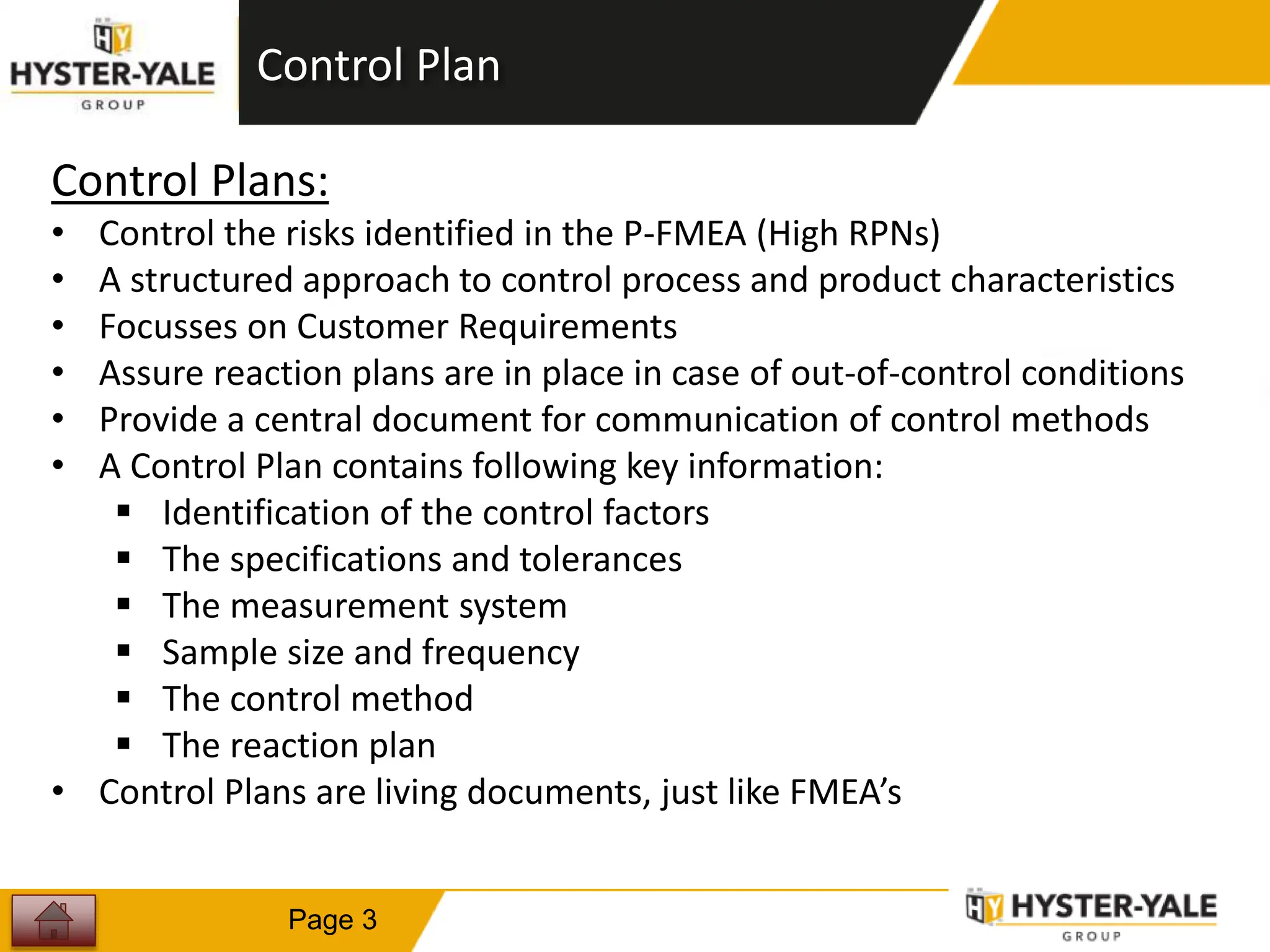
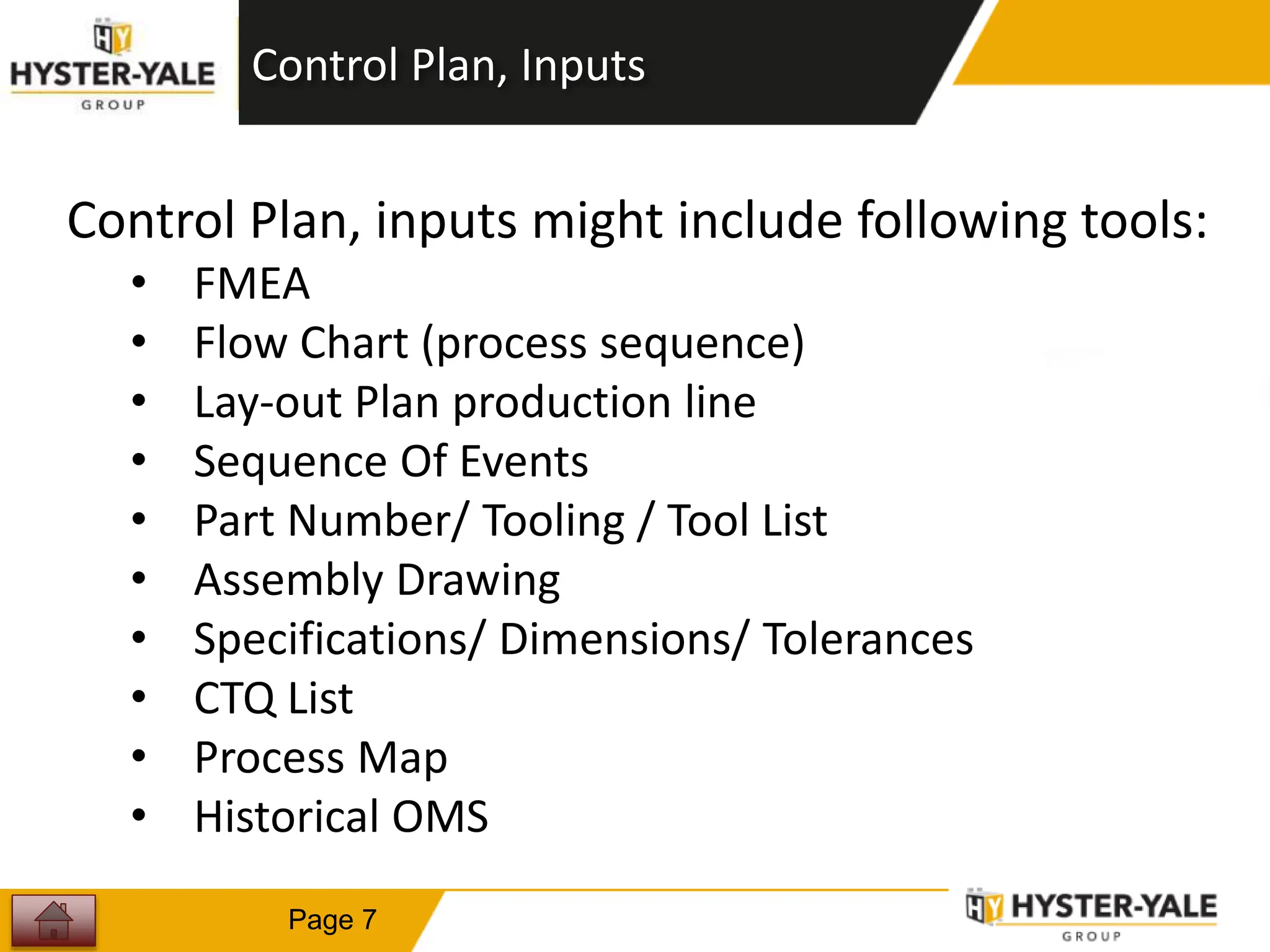
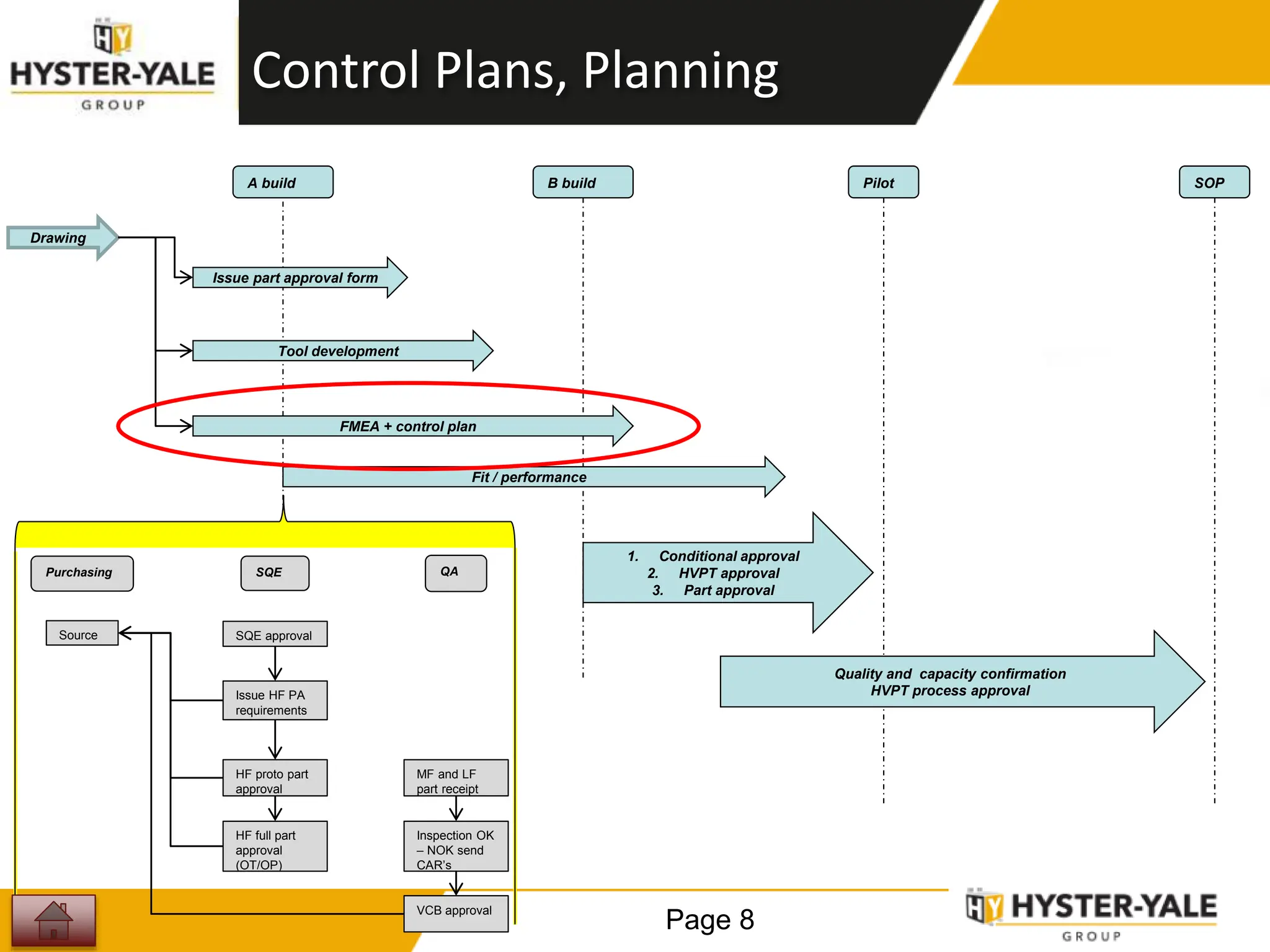
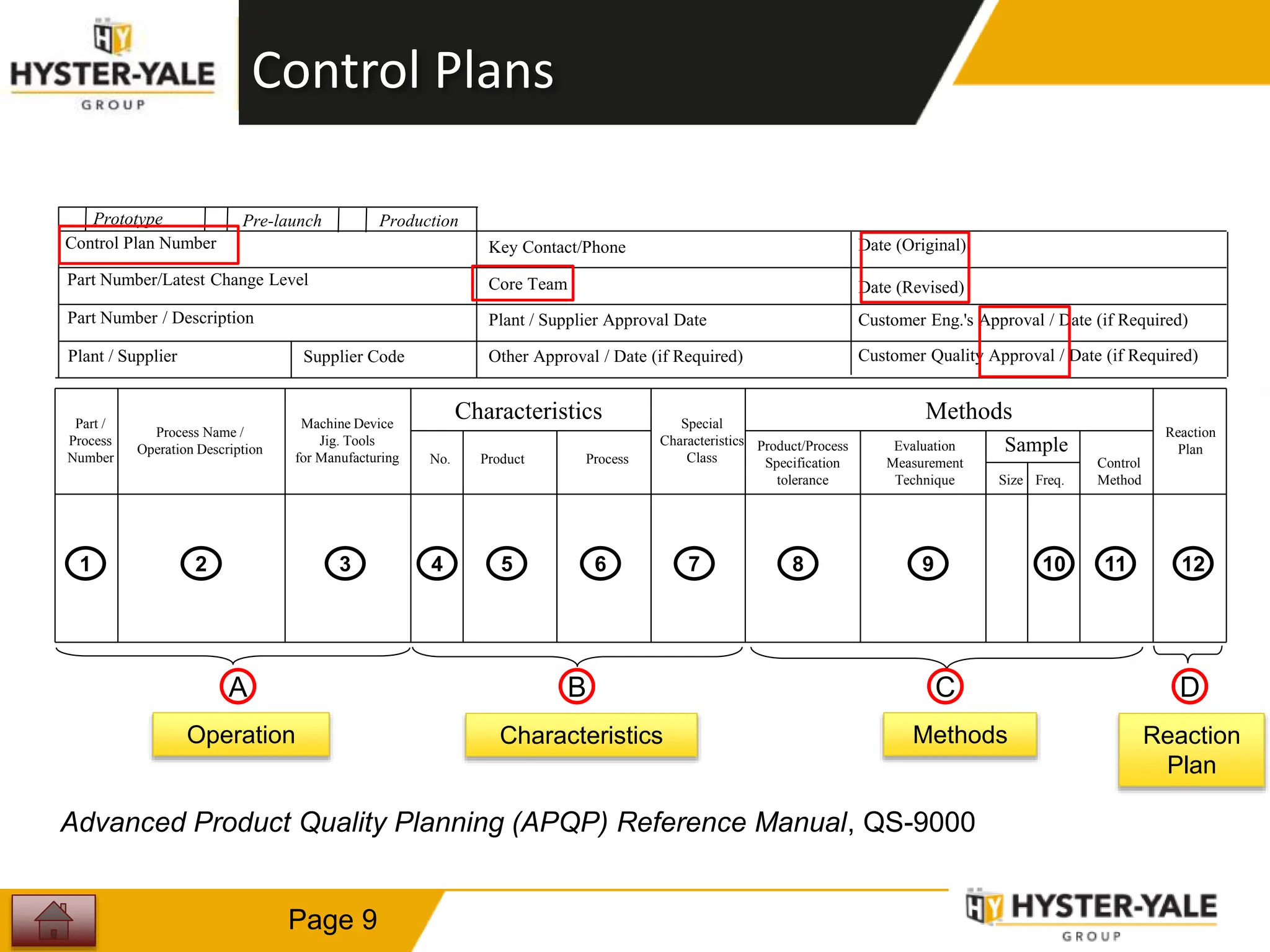
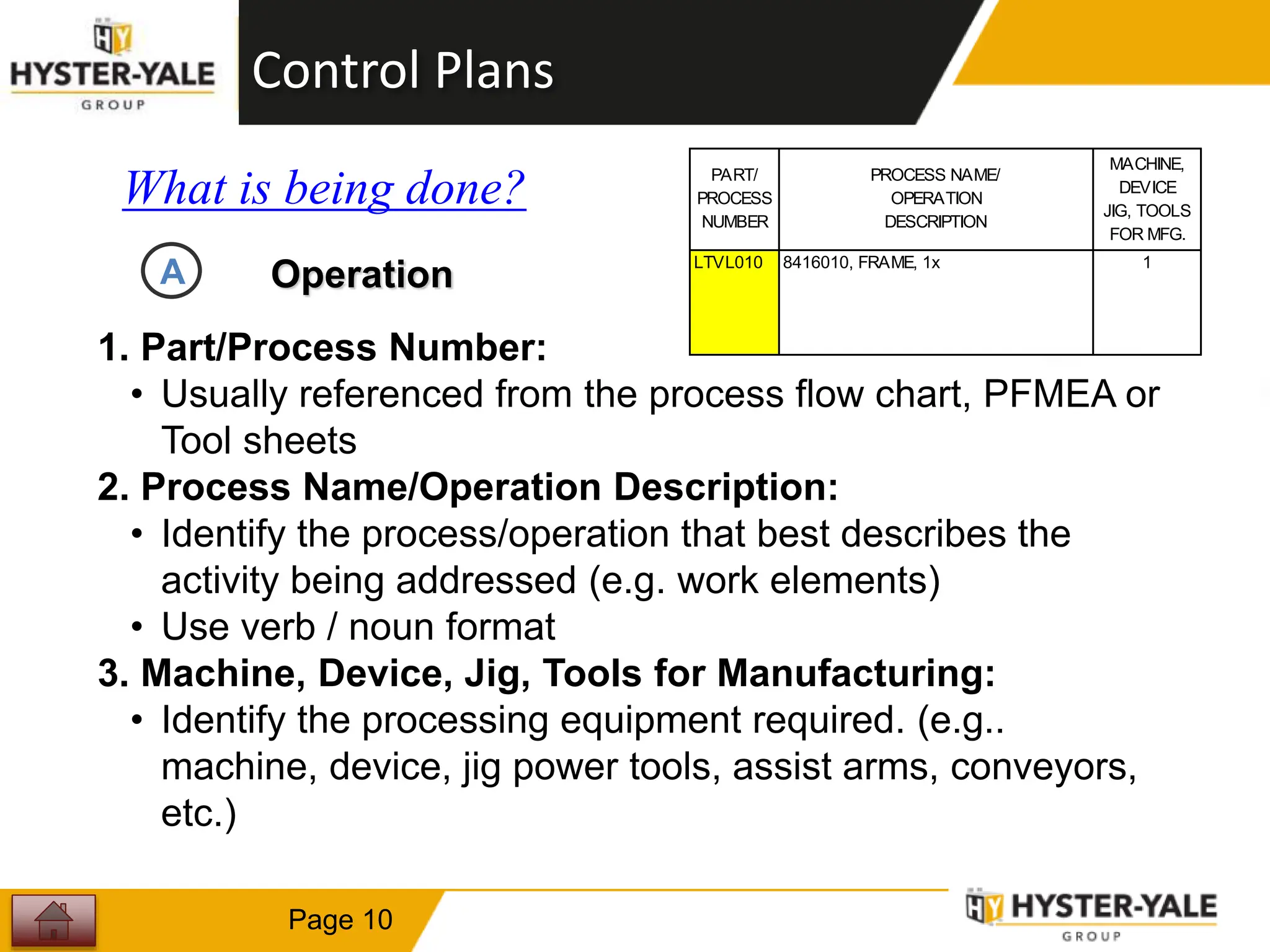
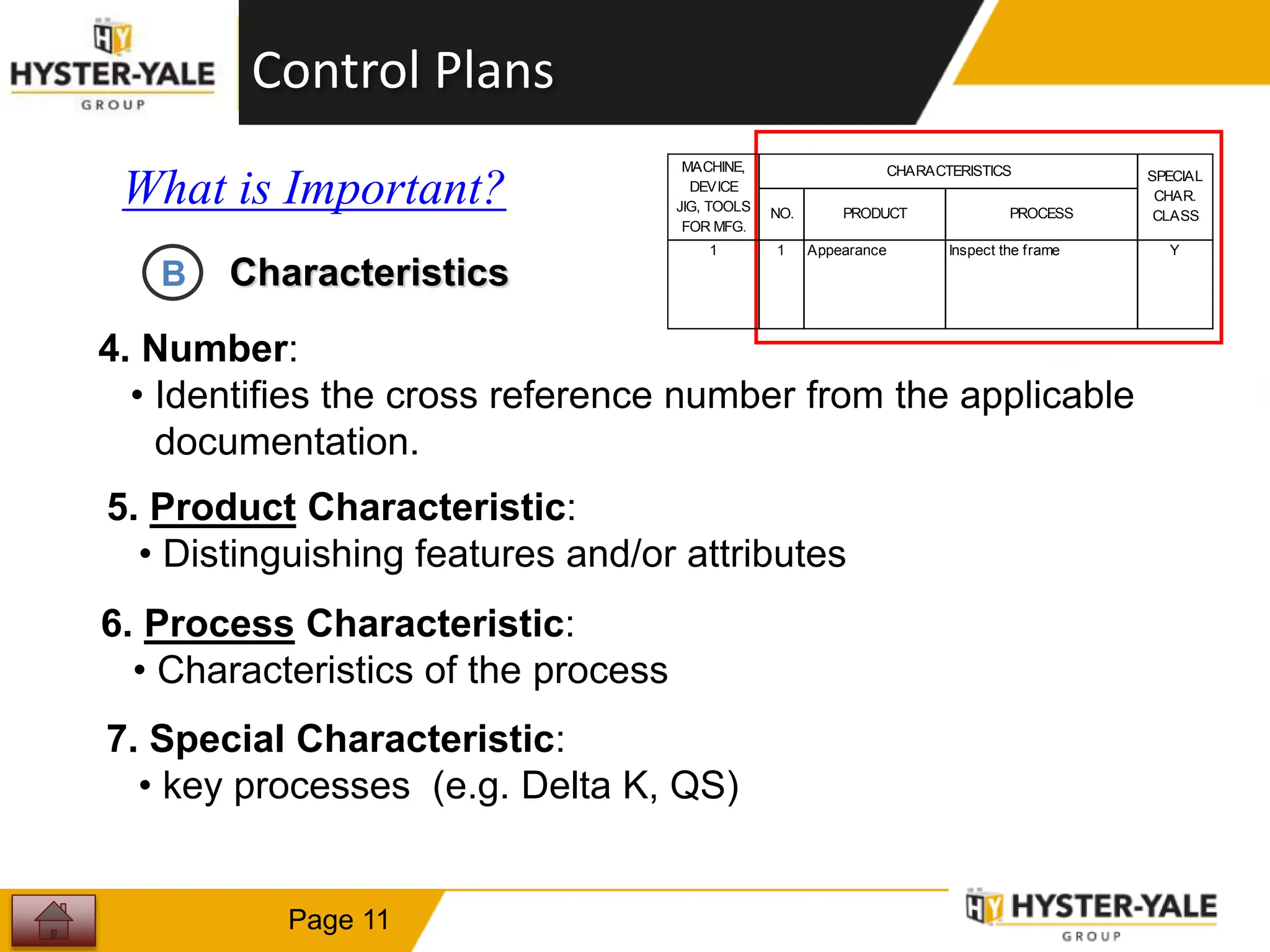
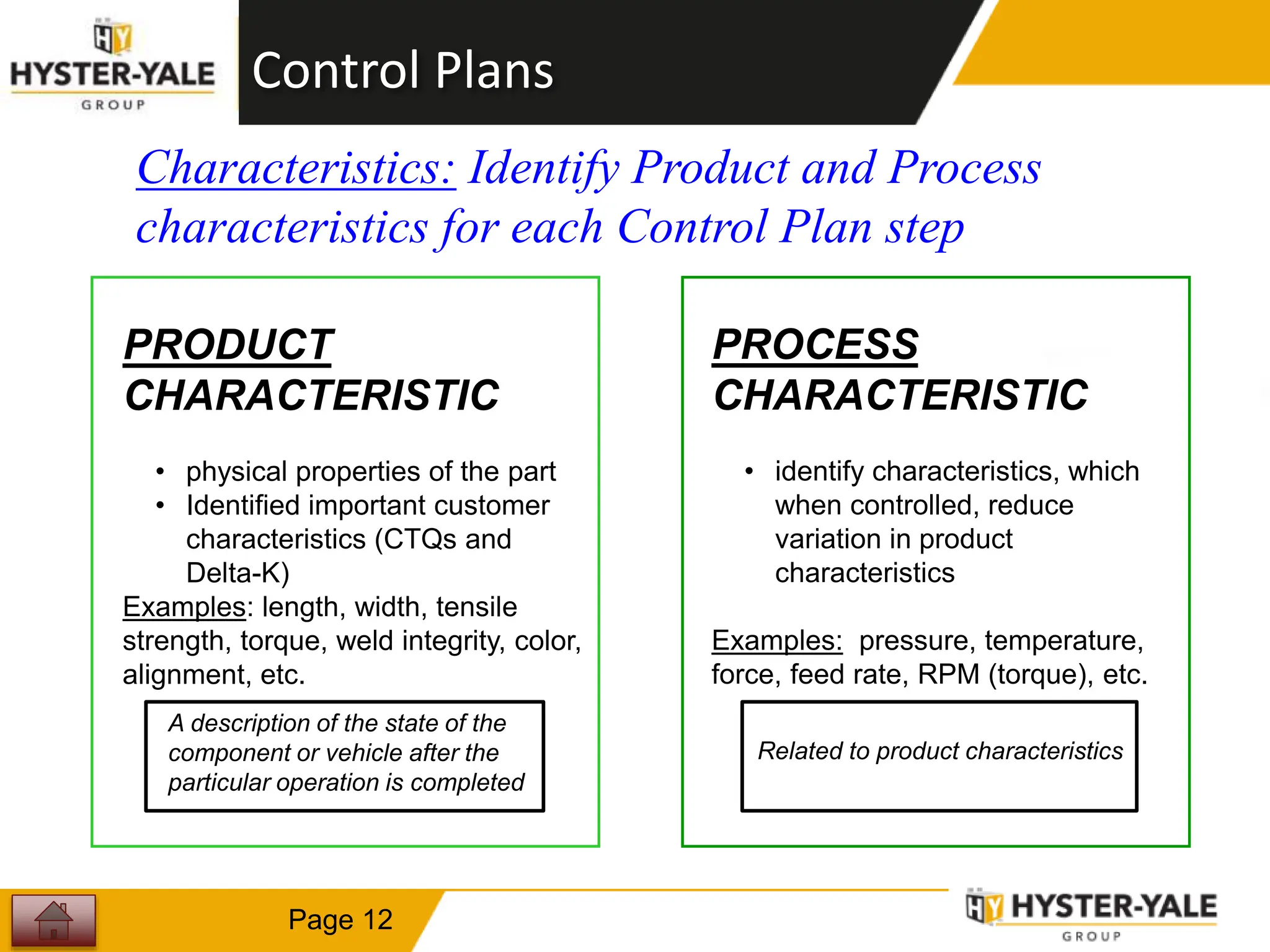
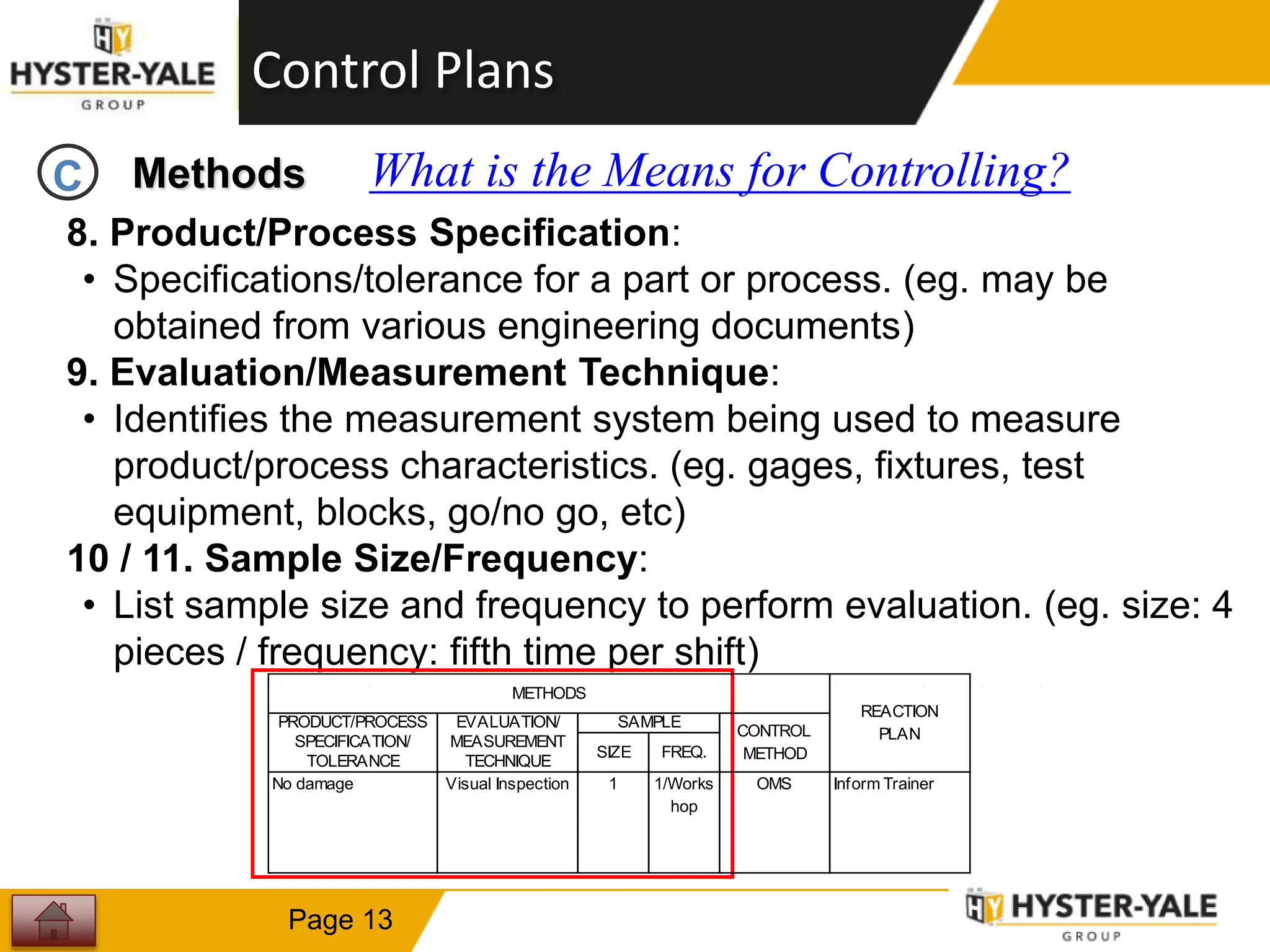
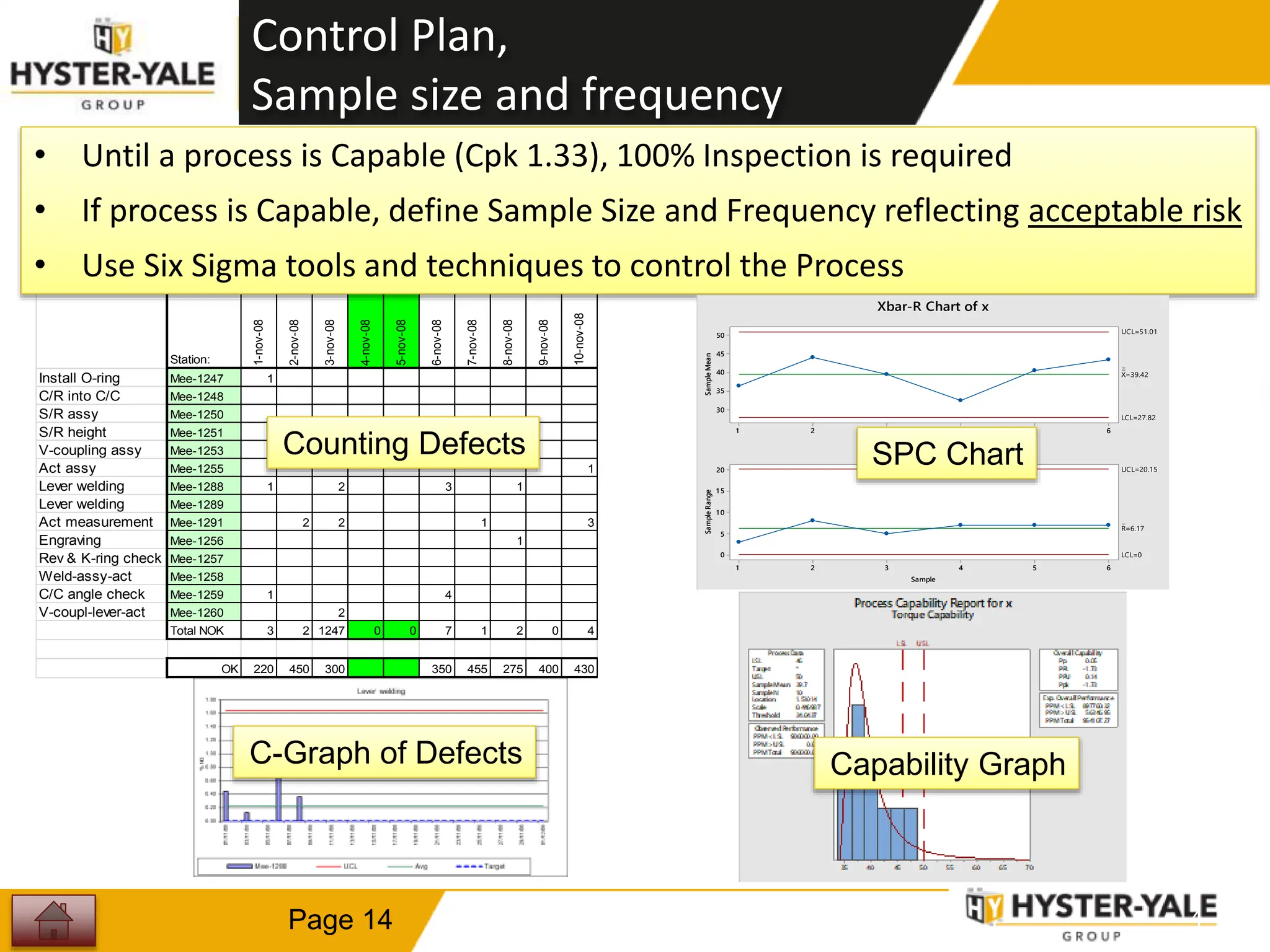
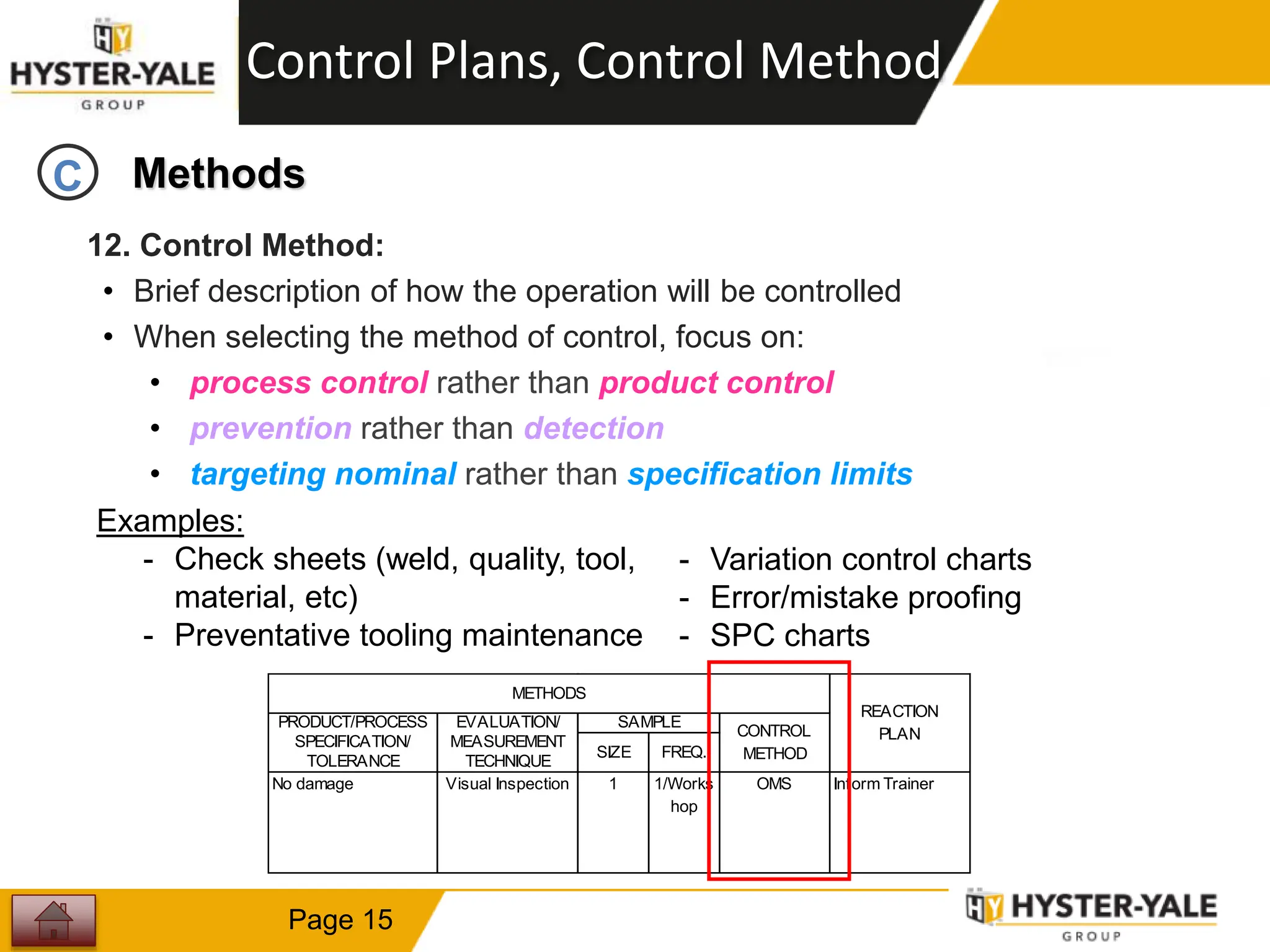
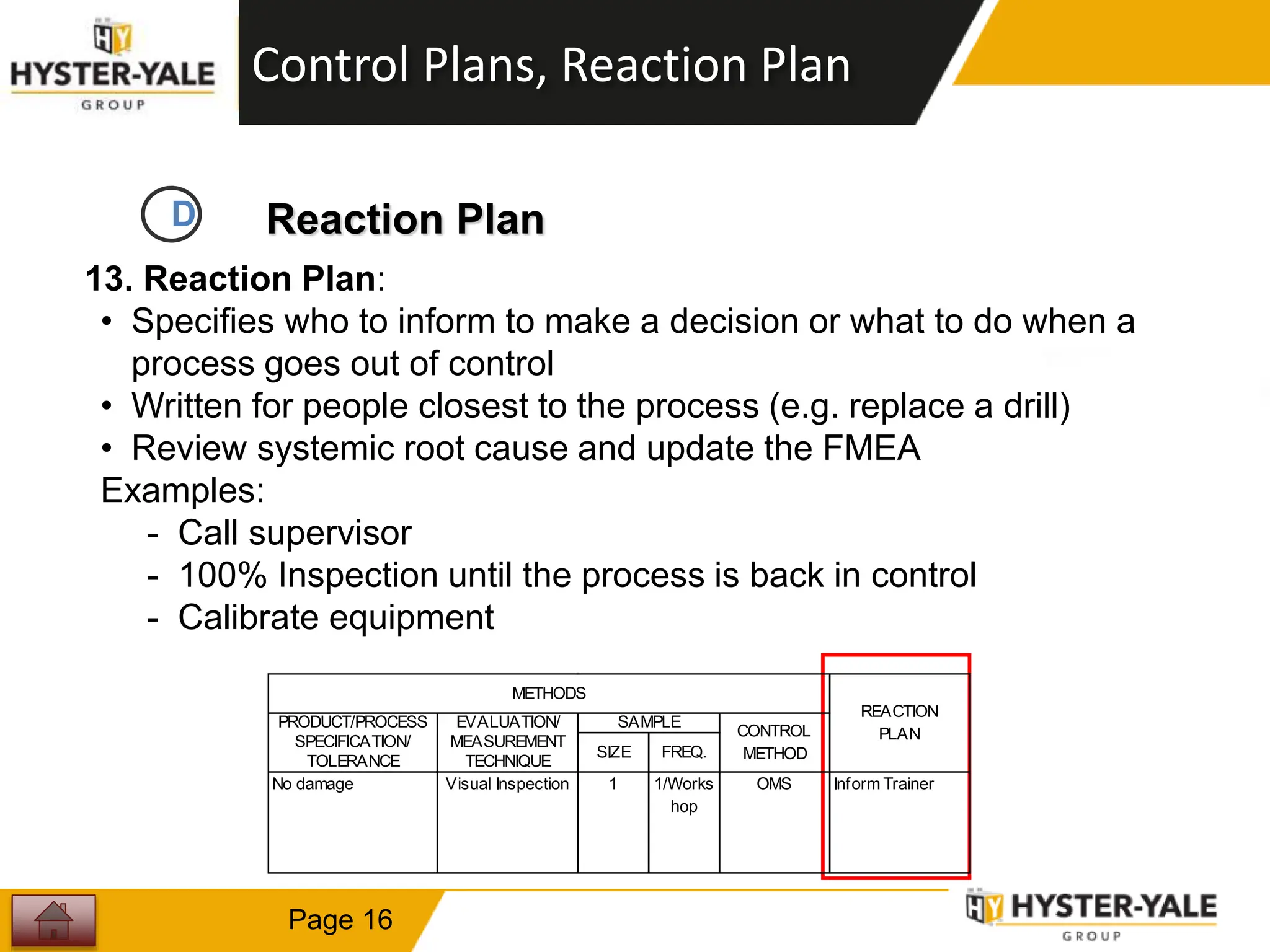
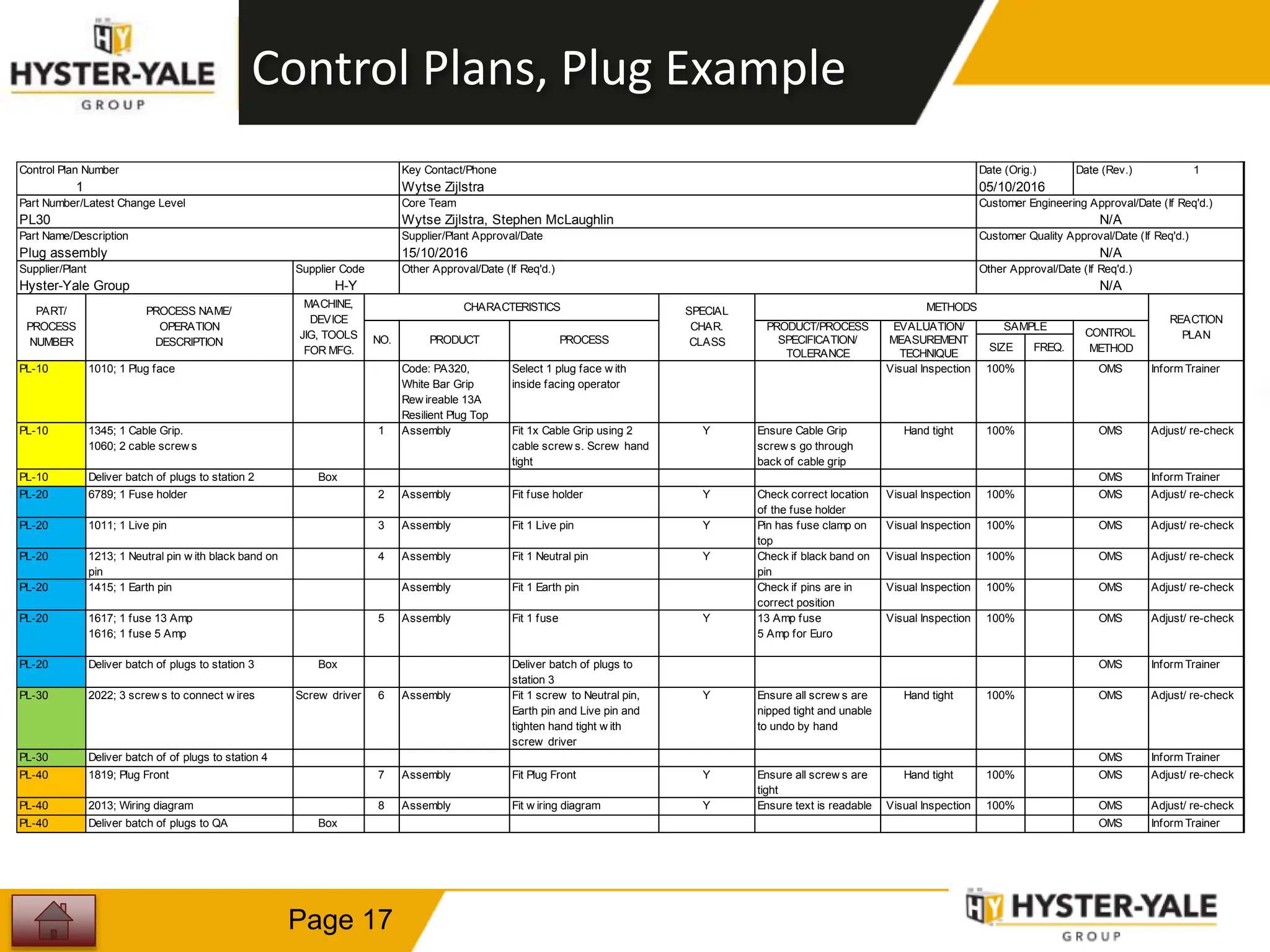
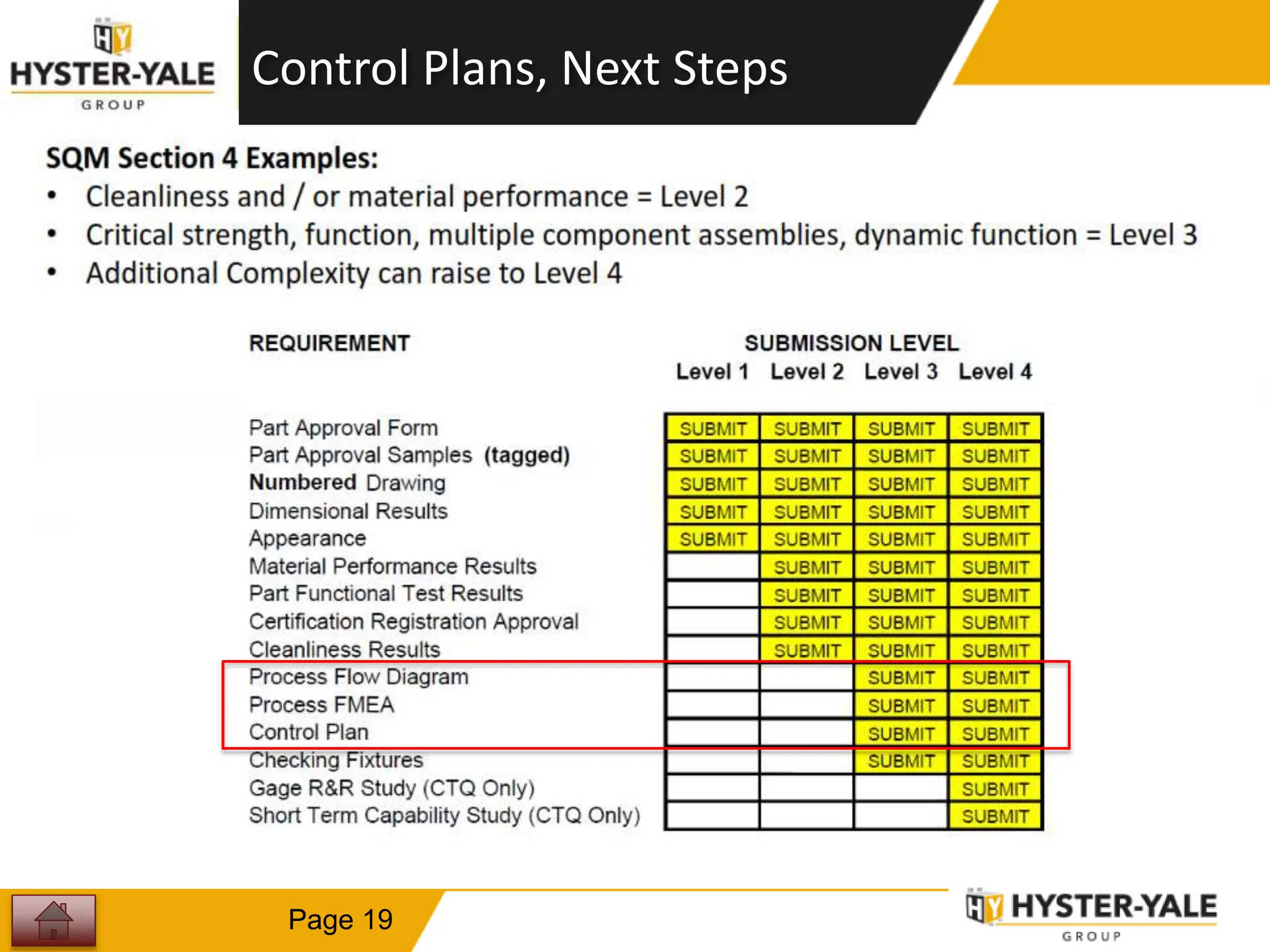
This document provides training on control plans, which are used to systematically control processes. It discusses key aspects of control plans such as identifying product and process characteristics, establishing specifications and control methods, and defining reaction plans. The objectives are to understand how to develop a control plan and link each step to the process FMEA. A plug assembly control plan example is also provided to demonstrate how to structure the control plan.