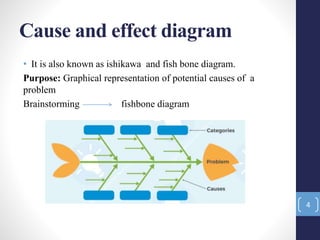
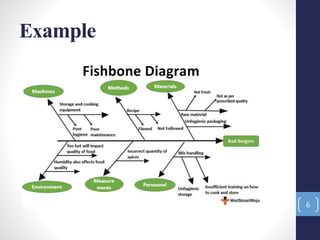
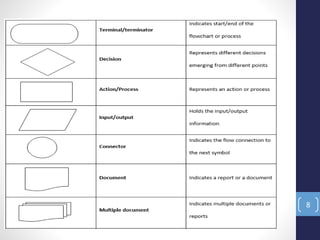
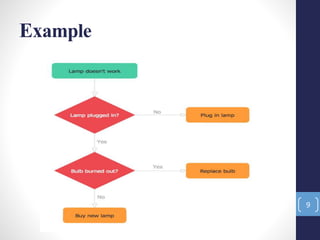
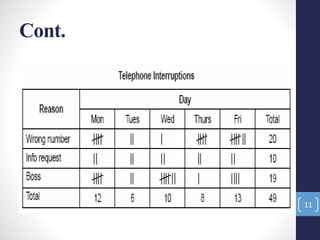
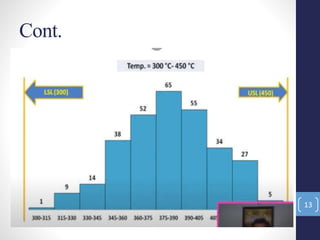
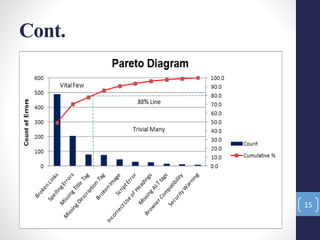
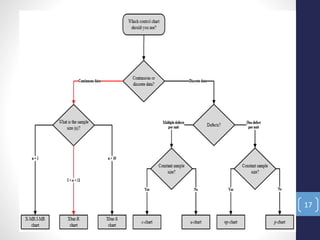
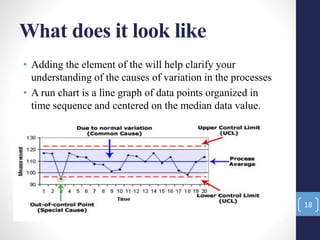
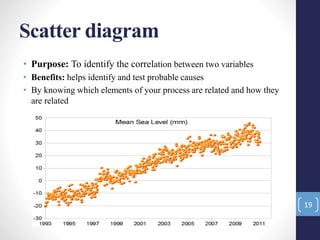
The document introduces the seven quality control tools: cause and effect diagram, Pareto analysis, flow chart, scatter diagram, check sheet, histogram, and control chart. These tools are used to collect and analyze data, identify root causes of problems, and measure results with the goals of process improvement and statistical process control. Each tool is defined along with its purpose and benefits. Examples are also provided for some of the tools.