A randomized controlled trial tested a virtual assistance-based lifestyle intervention to reduce cardiometabolic risk factors in young IT employees in India. Employees with ≥3 risk factors were randomized to a control or intervention group. The intervention group received lifestyle advice plus mobile/email messages for 1 year, while the control received only initial advice. The primary outcome was change in overweight-obesity prevalence. After 1 year, overweight-obesity decreased in the intervention group but increased in controls, with an 11.2% difference between groups. The intervention was effective, cost-effective, and acceptable for reducing risk factors in young IT employees.







![7
Analysis was carried out with the statistical package for social sciences for windows (SPSS, Chicago III),
version 16. The trial was registered with the Clinical Trial Registry of India (ctri.nic.in), number
CTRI/2015/01/005376.
Role of the funding source The funder of the study had no role in study design, data collection, data
analysis, data interpretation, or writing of the report. The corresponding author had full access to all the
data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Results
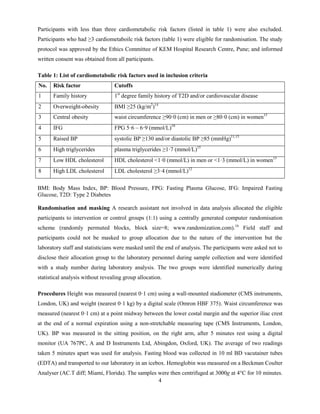
Figure 1 shows the trial profile; 437 participants (mean age 36·2±9·3 years; 74·8% men) were screened.
Seventy-four (16·9%) participants with diabetes, hypertension, triglycerides ≥5·7 mmol/L or on lipid
lowering drugs, and 98 (22·4%) with less than three risk factors were excluded. Thus 265 (60·6%)
participants (mean age 36·2±8·0 years; 72·5% men) with ≥3 risk factors were eligible and randomly
assigned to intervention (n = 133) or control (n = 132) groups. Of them, 205 (77·4%) had overweight-
obesity, 233 (87·9%) had central obesity, 189 (71·3%) had low HDL cholesterol, 71 (26·8%) had high
LDL cholesterol, 70 (26·4%) had high triglycerides, 67 (25·3%) had raised BP, and only three (1·1%)
participants had impaired fasting glucose (cutoffs are given in table 1). Seventy one (26·8%) participants
had metabolic syndrome.13
There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between the
two groups (table 2).
A total of 203 (76·6%) participants [intervention group: 105 (78.9%), control group: 98 (74·2%);
p=0·366] completed the trial (figure 1). Job changes, travel, and busy work schedules were the most
common reasons for missing follow-up assessments. Those who were lost to follow-up were no different
than who continued in the trial in terms of age, gender, years of education, weight, BMI, waist
circumference, BP, FPG, triglycerides, total, HDL and LDL cholesterol levels at baseline. The final
(intention to treat) analysis includes all 265 randomised participants.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thelancet-s-15-05929-170128114444/85/Case-Study-Lifestyle-Modification-Program-for-IT-Industry-9-320.jpg)

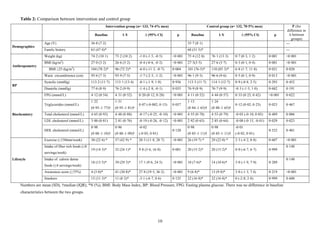
![9
Figure 2: Change in prevalence of overweight-obesity (BMI ≥25 kg/m2
) at different timepoints
At one year, 15 (14·4%) overweight-obese participants in the intervention group lost ≥5% of their
baseline weight while 21 (13·5%) lost between 2·5 to 5% of baseline weight. None of the overweight-
obese participants in the control group could achieve ≥5% weight loss; 9 (8·9%) lost 2·5 to 5% of their
baseline weight.
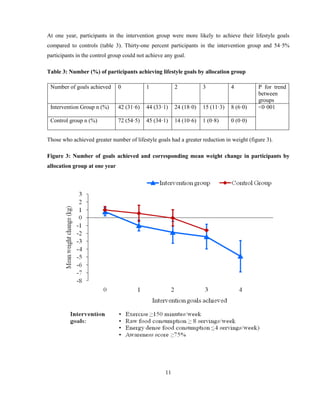
At six months, the intervention group had significantly greater reductions in weight [-1·1 (2·4) vs +0·5
(2·1) kg, p<0·001], waist circumference [-1·5 (2·6) vs +0·5 (1·5) cm, p<0·001], systolic BP [-1·9 (7·6) vs
+0·7 (9·3) mmHg, p=0·012], and diastolic BP [-1·3 (5·7) vs +0·4 (6·7) mmHg, p=0·033] compared to
controls. Improvements were sustained at one year with exception of systolic and diastolic blood pressure
(table 2). Proportion of participants with metabolic syndrome remained the same in both groups.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thelancet-s-15-05929-170128114444/85/Case-Study-Lifestyle-Modification-Program-for-IT-Industry-11-320.jpg)




![16
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, India
[DST/INSPIRE Fellowship/2010/(92)] and Diabetes Unit, KEM Hospital Research Centre, Pune. We
thank Deepa Raut, Manisha Deokar, Pooja Jadhav and Shweta Kate for help with data collection.
Virendra Suryawanshi designed the website for the program. We thank the team at Diabetes Unit, KEM
Hospital Research Centre, Pune and Just for Hearts Healthcare Pvt. Ltd., Pune for practical assistance
during the trial. We are grateful to the participants and the management of the IT industries for their
help.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thelancet-s-15-05929-170128114444/85/Case-Study-Lifestyle-Modification-Program-for-IT-Industry-18-320.jpg)





