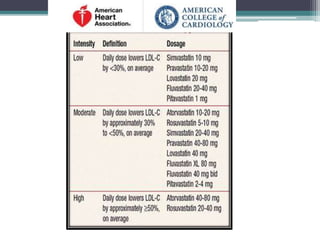
This document summarizes a study that examined the risk of new diabetes with higher potency statins compared to lower potency statins. It discusses two previous meta-analyses that found a small increased risk of diabetes with statin use. The study analyzed administrative databases covering millions of patients and found a 15% higher rate of new diabetes over 2 years in those prescribed higher potency statins for secondary prevention of cardiovascular events compared to lower potency statins. Higher potency statins were associated with one additional case of diabetes for every 342 patients treated over 2 years. The increased risk was highest in the first 4 months of statin use.






















![28th february 2012
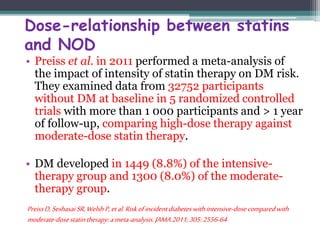
A meta-analysis by Rajpathak et al.,20 which included 6 statin trials with
57,593 FDA’s participants, review of the also results reported from the a small Justification increase for in diabetes the Use of
risk
(Statins relative in risk Primary [RR] 1.13; Prevention: 95% CI 1.03-an Intervention 1.23), with no Trial evidence Evaluating
of
heterogeneity Rosuvastatin across (JUPITER) trials. reported A recent a study 27% increase by Culver in et investigator-reported
al.,26 using data
from the Women’s diabetes mellitus Health Initiative, in rosuvastatin-reported treated that statin patients
use conveys an
increased risk of new-onset diabetes in postmenopausal women, and
noted that the effect appears to be a medication class effect, unrelated to
potency or to individual statin.
Based on clinical trial meta-analyses and epidemiological data from the
published literature, information concerning an effect of statins on
incident diabetes and increases in HbA1c and/or fasting plasma glucose
was added to statin labels.
compared to placebo-treated patients. High-dose atorvastatin had
also been associated with worsening glycemic control in the
Pravastatin or Atorvastatin Evaluation and Infection Therapy –
Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction 22 (PROVE-IT TIMI 22)
substudy. FDA also reviewed the published medical literature. A
meta-analysis by Sattar et al.,19 which included 13 statin trials with
91,140 participants, reported that statin therapy was associated with
a 9% increased risk for incident diabetes (odds ratio [OR] 1.09; 95%
confidence interval [CI] 1.02-1.17), with little heterogeneity
(I2=11%) between trials.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jc2-141203151012-conversion-gate02/85/Jc2-24-320.jpg)
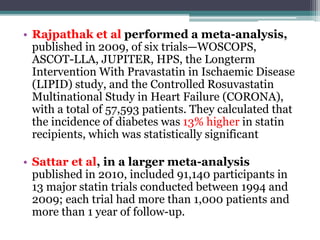
![New diabetes occurred in 2,226 (4.89%) of the
statin recipients and in 2,052 (4.5%) of the
placebo recipients, an absolute difference of
0.39%, or 9% more (odds ratio [OR] 1.09; 95%
confidence interval [CI] 1.02–1.17). The
incidence of diabetes varied substantially among
the 13 trials, with only JUPITER and PROSPER
finding statistically significant increases in rates
(26% and 32%, respectively).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jc2-141203151012-conversion-gate02/85/Jc2-26-320.jpg)




![• A meta-analysis by Sattar et al. did not find a clear
difference between lipophilic statins (OR 1.10 vs
placebo) and hydrophilic statins (OR 1.08). In
analysis by statin type, the combined rosuvastatin
trials were significant in favor of a higher DM risk
(odds ratio[OR]: 1.18; 95%CI; 1.04-1.44).
Insignificant trends were noted for atorvastatin trials
(OR: 1.14) and simvastatin trials (OR: 1.11) and less
so for pravastatin (OR: 1.03); the OR for lovastatin
was 0.98.
• This may suggest that there is a stronger effect with
more potent statins or with greater lowering of LDL-C.
Furthermore, this evidence does not support a
protective or neutral role for statin hydrophilicity in
the pathogenesis of NOD.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jc2-141203151012-conversion-gate02/85/Jc2-32-320.jpg)