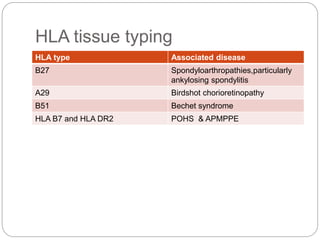
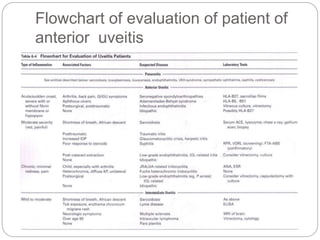
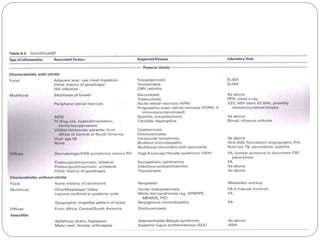
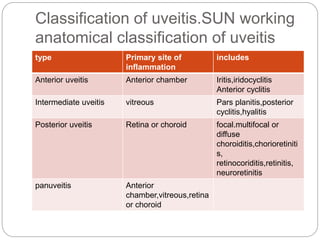
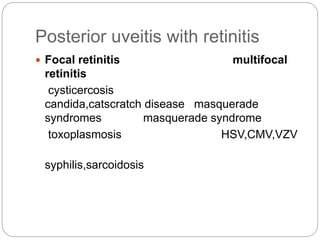
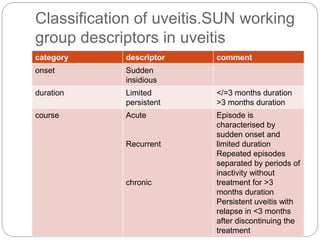
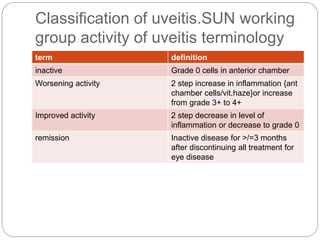
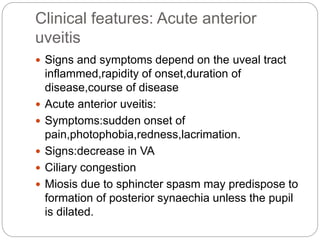
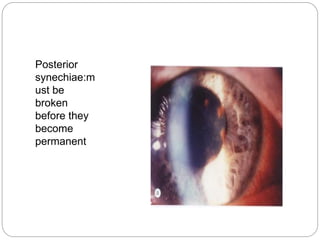
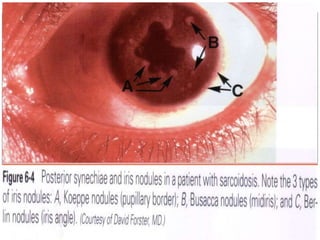
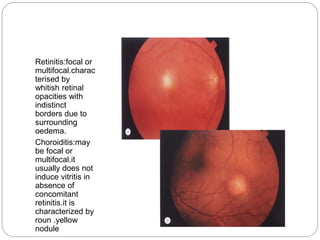
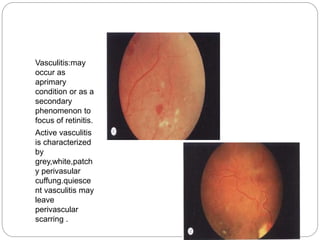
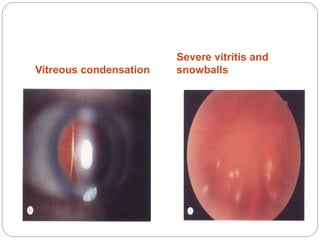
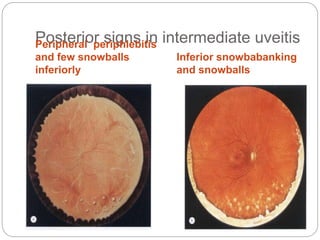
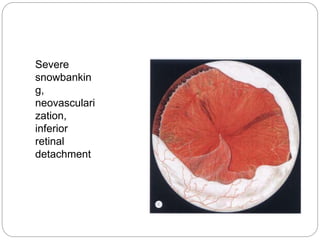
This document discusses the classification and clinical approach to uveitis. It begins by classifying uveitis based on the primary site of inflammation - anterior, intermediate, posterior or panuveitis. It then describes the signs and symptoms of different types of uveitis such as anterior uveitis, chronic anterior uveitis, intermediate uveitis and posterior uveitis. It also discusses historical factors, investigations including serology, imaging and biopsy that are useful in diagnosing the cause of uveitis. It provides a flowchart for evaluation of a patient with anterior uveitis.

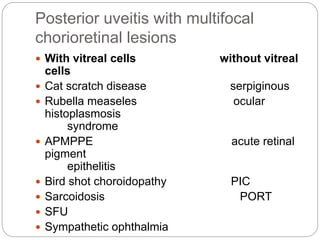
![Posterior uveitis with a focal [solitary]
chorioretinal lesion
With vitreal cells without vitreal
cells
Toxocarisis tumour
Tuberculosis serpenginous
choroidopathy Sarcoidosis
Cat scratch disease](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clinicalapproachtouveitis-200515133047/85/Clinical-approach-to-uveitis-4-320.jpg)


![ 8.past medical history:h/o systemic medications ,oral
ulcers,genital ulcers.
9.hygiene and dietary habits:history of
pica[toxocariasis],undercooked meat,ingestion of
water in rural areas[toxoplasmosis],ingestion of pork
in endemic areas[cystecercosis]
10.history of sexual practices:for diagnosis of HIV and
syphilis
11.recreational drugs:for HIV infection,fungal
endophthalmitis
12.pets:cats are associated with transmission of
toxoplasmosis,cat scratch disease,while puppies are
associated to toxocariasis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clinicalapproachtouveitis-200515133047/85/Clinical-approach-to-uveitis-10-320.jpg)

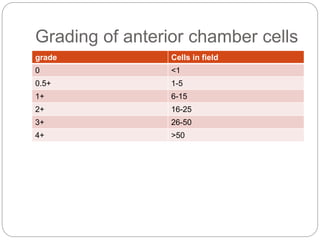

![grade description
0 nil
1+ Faint[just detectable]
2+ Moderate[iris lens details are clear]
3+ Marked[iris,lens details are hazy]
4+ Intense[fibrinous exudates]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clinicalapproachtouveitis-200515133047/85/Clinical-approach-to-uveitis-15-320.jpg)










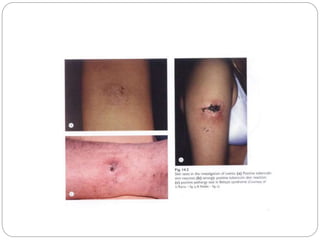
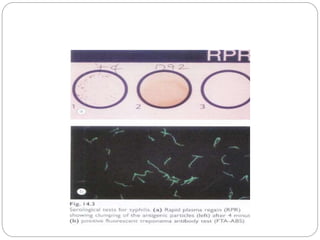
![serology
Syphilis:serology test depend on detection of non
specific antibodies [cardiolipin]or specific treponemal
antibodies .
1.non treponema test:RPR,VDRL are best used to
diagnose primary infection,monitor disease
actvity,response to therapy based on the titre.the
results may be negative in 30% of the patients with
documented syphilitic uveitis.they tend to become –ve
6-18 months after therapy
2.treponema antibody test:higly senitive and specific
to prove past infection,secondary or tertiry form of
infections.fluorescent treponema antibody absorption
test[FTA-ABS],microhaemagglutination treponema
pallidium test[MHA-TP]are commonlu used.it cannot
be titrated.it is either –ve or +ve.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clinicalapproachtouveitis-200515133047/85/Clinical-approach-to-uveitis-38-320.jpg)