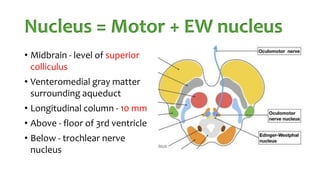
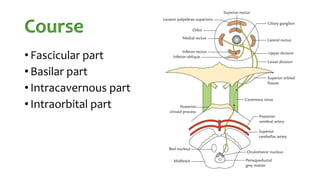
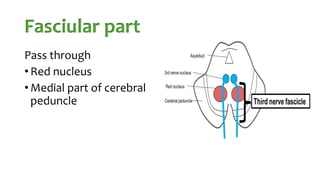
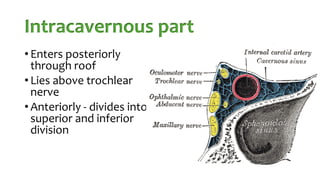
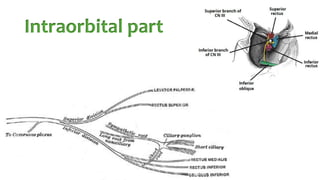
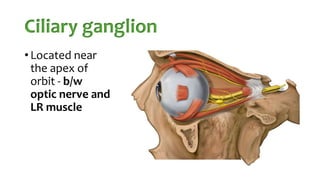
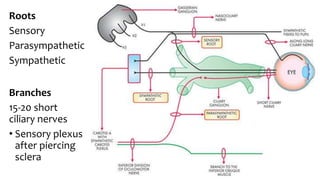
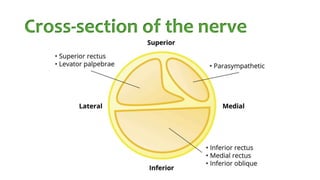
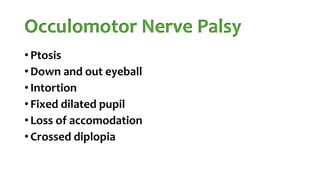
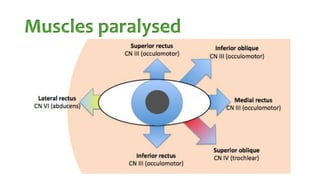
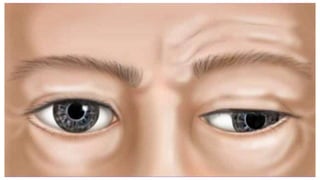
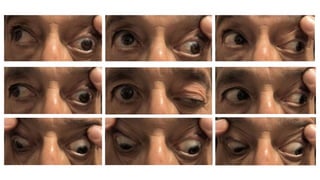
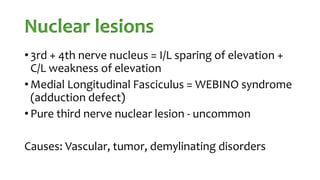
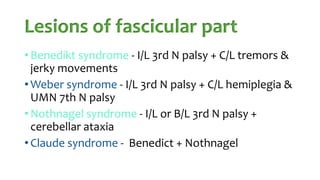
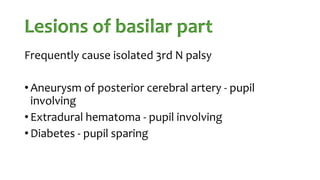
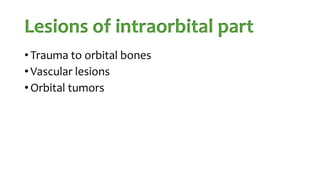
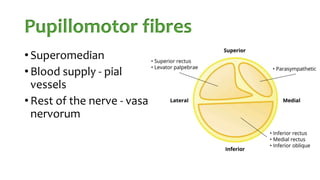
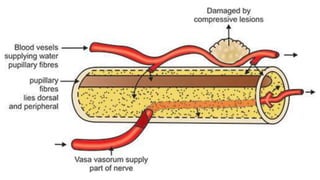
The document summarizes key details about the occulomotor nerve (CN III) including its anatomy, nuclei, course through the brain and orbit, functions of the muscles it innervates, and causes of occulomotor nerve palsy. The occulomotor nerve is a purely motor cranial nerve that controls four extraocular muscles and pupil constriction/accommodation. It can be affected at different levels from supranuclear to intraorbital portions. Lesions are diagnosed based on the specific muscles and eye movements involved.