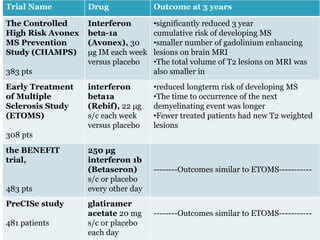
Optic neuritis is an inflammatory condition causing acute visual loss, usually in one eye. It affects women aged 20-40 more commonly and is a presenting symptom in 15-20% of multiple sclerosis (MS) cases. Pathology involves inflammatory demyelination of the optic nerve. Treatment involves steroids like IV methylprednisolone which can accelerate visual recovery and reduce MS risk. Up to 50% of optic neuritis patients may develop MS over 15 years, with MRI white matter lesions and retinal perivenous sheathing increasing MS risk. Immunomodulators after an attack may delay MS but have side effects. Prognosis is generally good for vision recovery but recurrent attacks or NMO antibody positivity carry