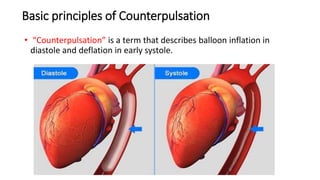
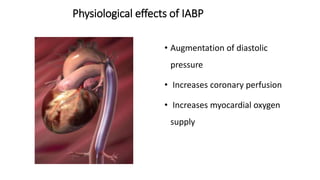
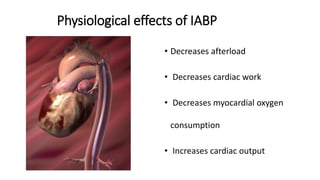
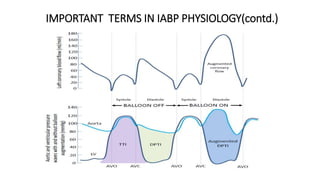
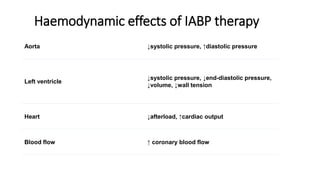
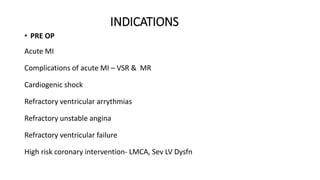
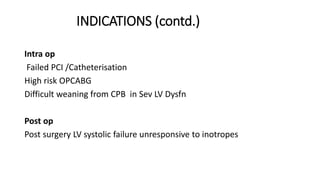
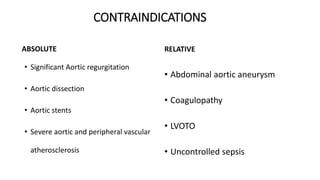
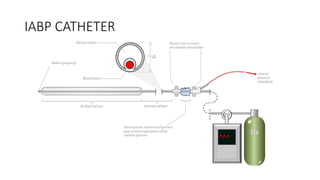
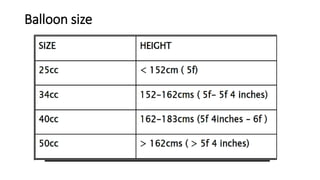
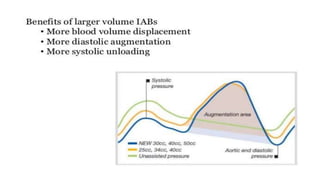
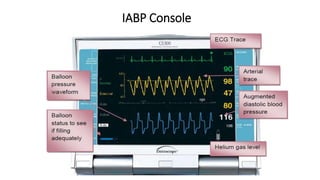
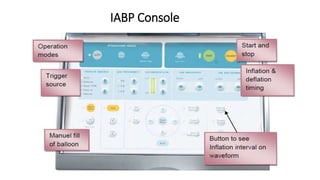
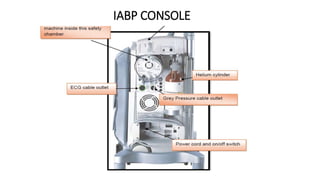
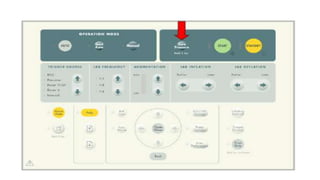
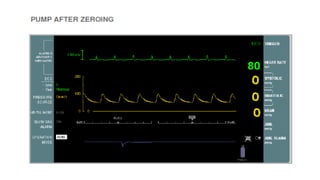
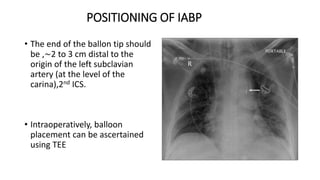
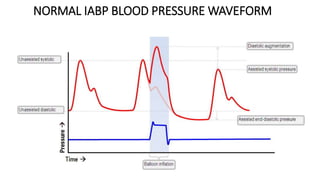
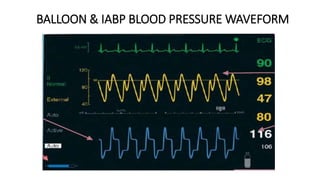
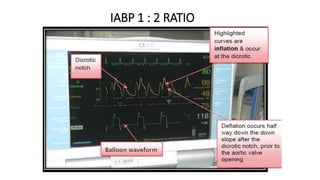
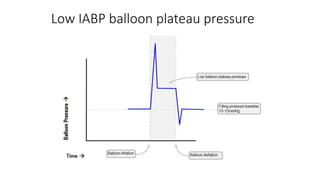
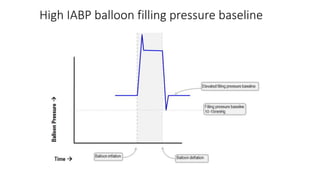
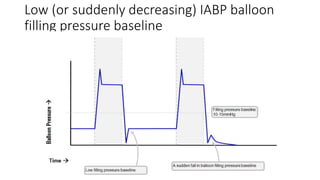
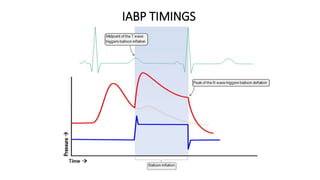
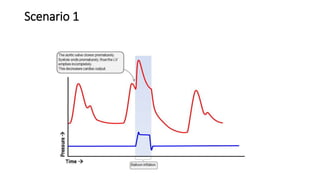
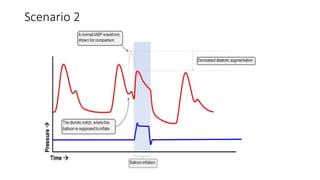
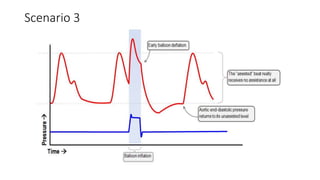
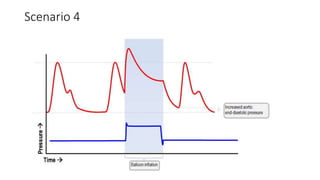
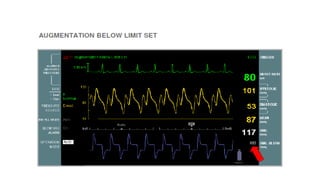
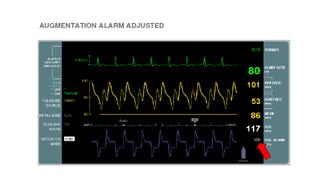
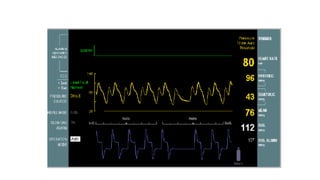
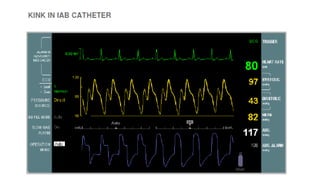
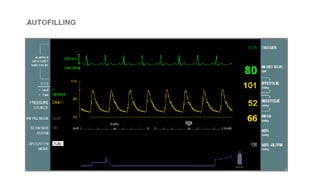
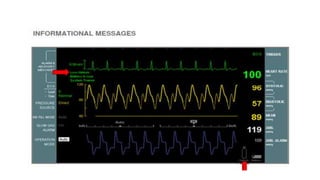
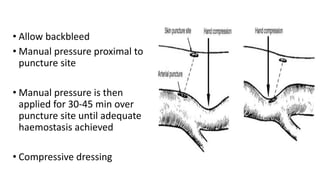
This document provides an overview of intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation (IABP). It discusses the history and physiological effects of IABP, including increasing coronary perfusion and decreasing cardiac work. Indications for IABP include acute myocardial infarction and cardiogenic shock. The document reviews IABP instrumentation, monitoring, waveforms, timing, complications, weaning, and removal. IABP is a temporary circulatory support device that aims to improve heart function through counterpulsation.