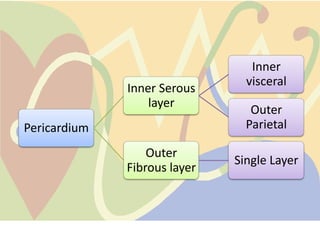
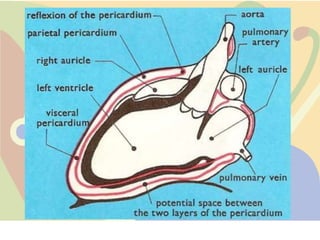
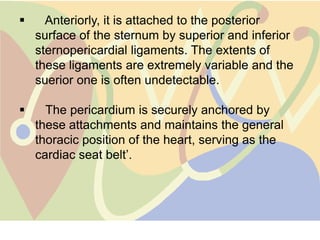
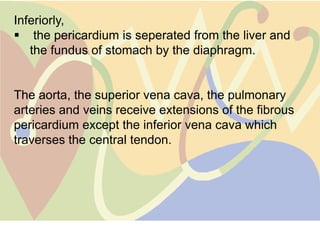
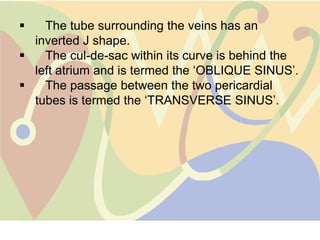
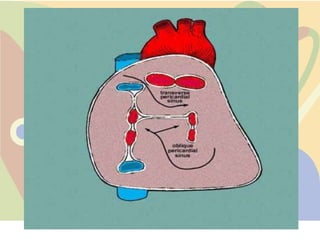
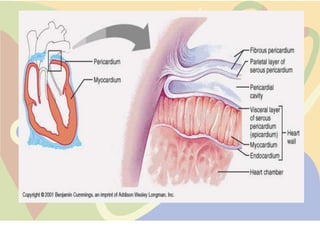
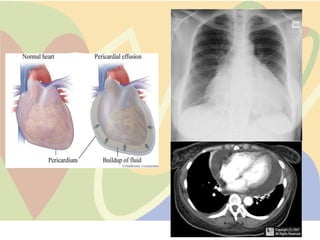
The pericardium is a double-walled sac that surrounds the heart and prevents overexpansion. It has an outer fibrous layer and inner serous layer. The pericardium supports the heart, limits its movement, and acts as a shock absorber. Pericardial effusion or inflammation can occur from infection, cancer, or other causes. Effusion is treated by draining fluid while inflammation is treated with anti-inflammatory drugs or identifying the underlying cause. Complications like tamponade require draining fluid from the pericardial sac.