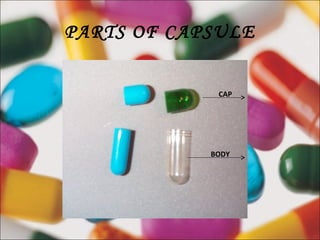
This document provides information on capsules, including definitions, advantages, disadvantages, types (hard gelatin and soft gelatin capsules), and manufacturing processes. It defines capsules as solid preparations with shells containing a single dose of active ingredients. Hard gelatin capsules are made of gelatin and can contain powders, granules, or pellets, while soft gelatin capsules contain liquids, suspensions, or semisolids. The manufacturing of both types involves processes like dipping, drying, trimming, and filling. Specifications for gelatin and requirements for capsules in compendia are also outlined.